CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
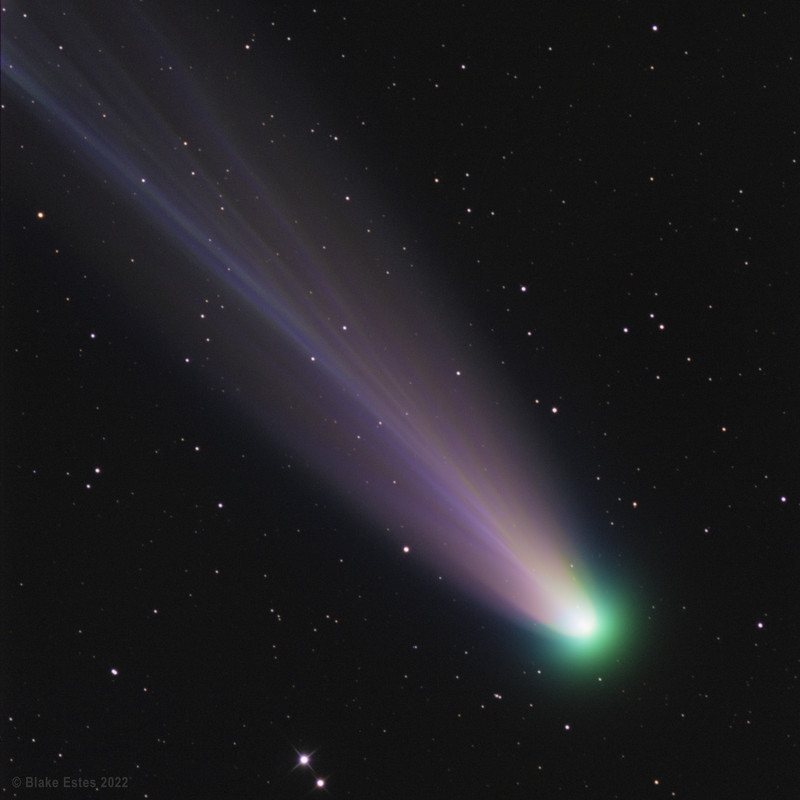
What does Comet Leonard look like up close? Although we can't go there, imaging the comet's coma and inner tails through a small telescope gives us a good idea. As the name implies, the ion tail is made of ionized gas -- gas energized by ultraviolet light from the Sun and pushed outward by the solar wind. The solar wind is quite structured and sculpted by the Sun's complex and ever changing magnetic field. The effect of the variable solar wind combined with different gas jets venting from the comet's nucleus accounts for the tail's complex structure. Following the wind, structure in Comet Leonard's tail can be seen to move outward from the Sun even alter its wavy appearance over time. The blue color of the ion tail is dominated by recombining carbon monoxide molecules, while the green color of the coma surrounding the head of the comet is created mostly by a slight amount of recombining diatomic carbon molecules. Diatomic carbon is destroyed by sunlight in about 50 hours -- which is why its green glow does not make it far into the ion tail. The featured image was taken on January 2 from Siding Spring Observatory in Australia. Comet Leonard, presently best viewed from Earth's Southern Hemisphere, has rounded the Sun and is now headed out of the Solar System.

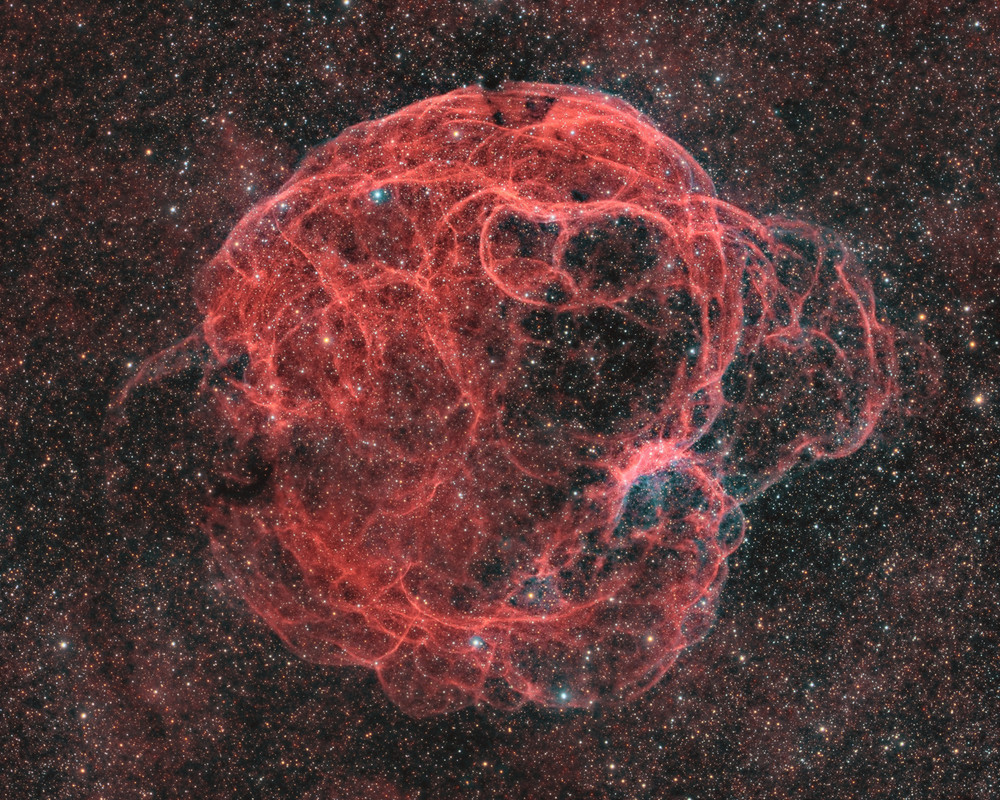
It's easy to get lost following the intricate, looping, twisting filaments in this detailed image of supernova remnant Simeis 147. Also cataloged as Sharpless 2-240 it goes by the popular nickname, the Spaghetti Nebula. Seen toward the boundary of the constellations Taurus and Auriga, it covers nearly 3 degrees or 6 full moons on the sky. That's about 150 light-years at the stellar debris cloud's estimated distance of 3,000 light-years. This composite includes image data taken through narrow-band filters where reddish emission from ionized hydrogen atoms and doubly ionized oxygen atoms in faint blue-green hues trace the shocked, glowing gas. The supernova remnant has an estimated age of about 40,000 years, meaning light from the massive stellar explosion first reached Earth 40,000 years ago. But the expanding remnant is not the only aftermath. The cosmic catastrophe also left behind a spinning neutron star or pulsar, all that remains of the original star's core.

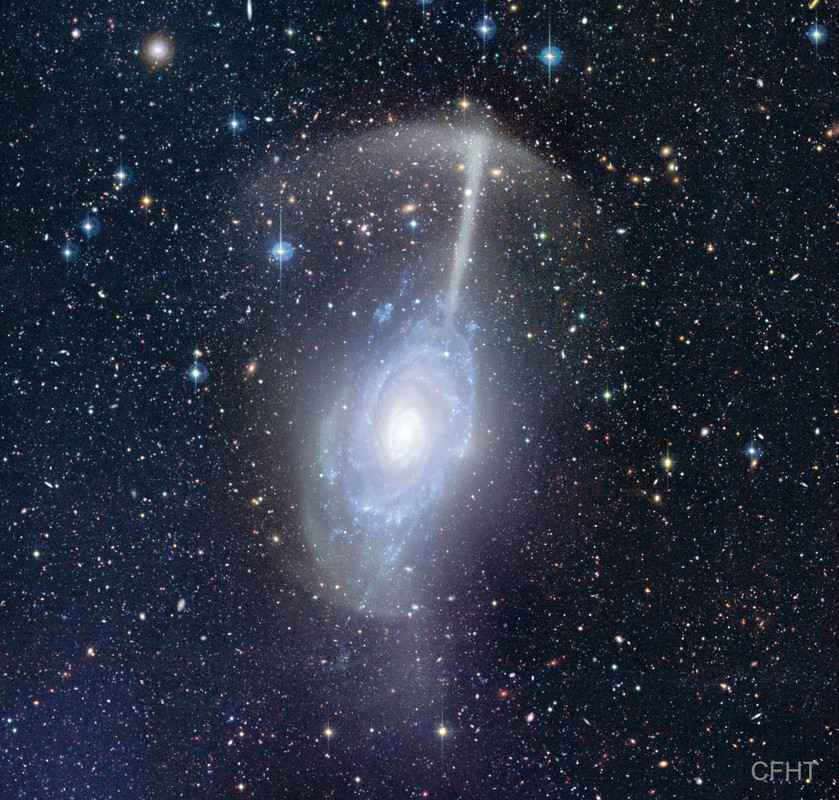
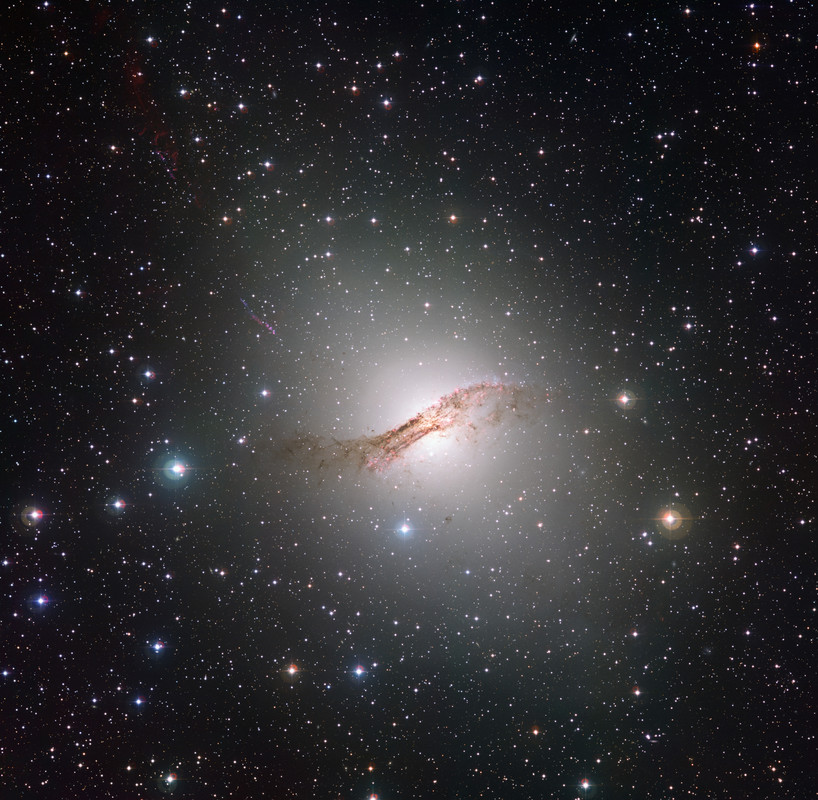
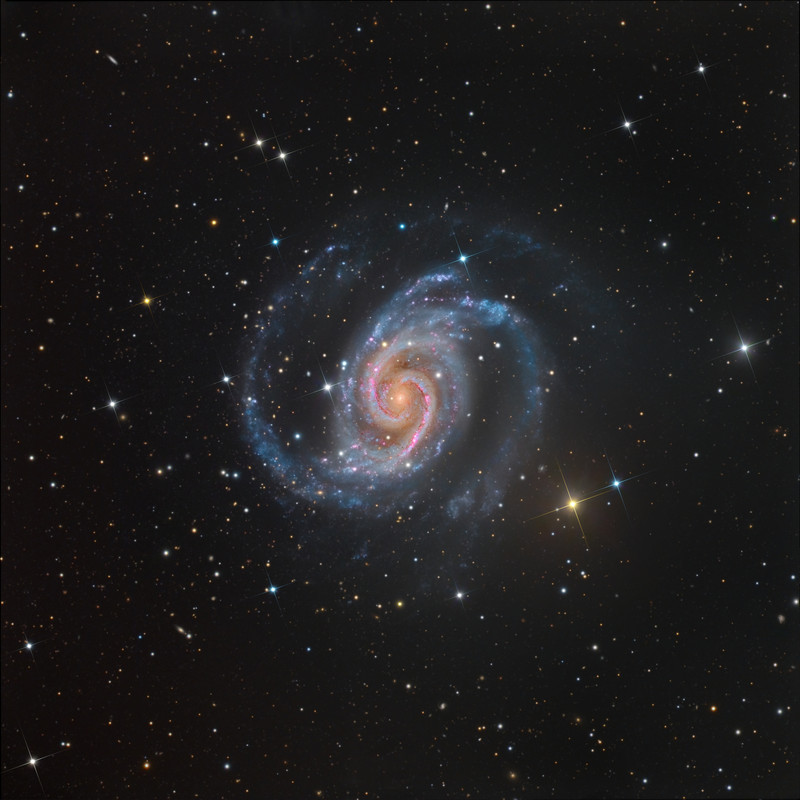
An island universe of billions of stars, NGC 1566 lies about 60 million light-years away in the southern constellation Dorado. Popularly known as the Spanish Dancer galaxy, it's seen face-on from our Milky Way perspective. A gorgeous grand design spiral, this galaxy's two graceful spiral arms span over 100,000 light-years, traced by bright blue star clusters, pinkish starforming regions, and swirling cosmic dust lanes. NGC 1566's flaring center makes the spiral one of the closest and brightest Seyfert galaxies. It likely houses a central supermassive black hole wreaking havoc on surrounding stars, gas, and dust. In this sharp southern galaxy portrait, the spiky stars lie well within the Milky Way.

Sometimes the dark dust of interstellar space has an angular elegance. Such is the case toward the far-south constellation of Chamaeleon. Normally too faint to see, dark dust is best known for blocking visible light from stars and galaxies behind it. In this four-hour exposure, however, the dust is seen mostly in light of its own, with its strong red and near-infrared colors giving creating a brown hue. Contrastingly blue, the bright star Beta Chamaeleontis is visible just to the right of center, with the dust that surrounds it preferentially reflecting blue light from its primarily blue-white color. All of the pictured stars and dust occur in our own Milky Way Galaxy with -- but one notable exception: the white spot just below Beta Chamaeleontis is the galaxy IC 3104 which lies far in the distance. Interstellar dust is mostly created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars and dispersed into space by stellar light, stellar winds, and stellar explosions such as supernovas.

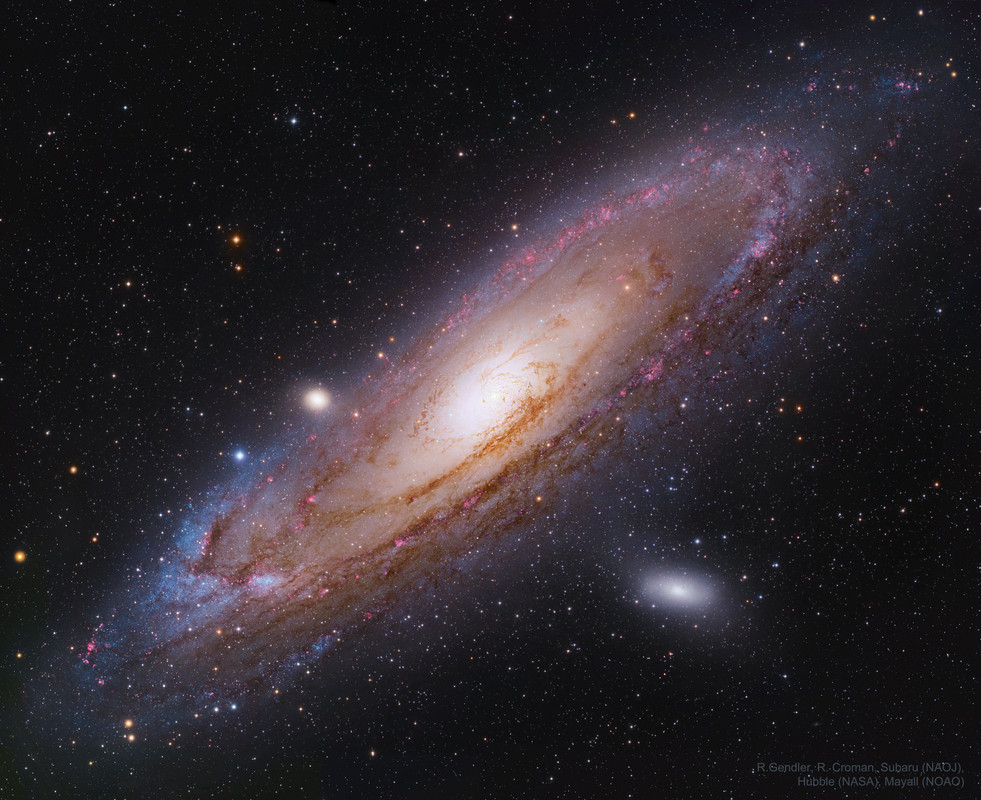
The most distant object easily visible to the unaided eye is M31, the great Andromeda Galaxy. Even at some two and a half million light-years distant, this immense spiral galaxy -- spanning over 200,000 light years -- is visible, although as a faint, nebulous cloud in the constellation Andromeda. In contrast, a bright yellow nucleus, dark winding dust lanes, and expansive spiral arms dotted with blue star clusters and red nebulae, are recorded in this stunning telescopic image which combines data from orbiting Hubble with ground-based images from Subaru and Mayall. In only about 5 billion years, the Andromeda galaxy may be even easier to see -- as it will likely span the entire night sky -- just before it merges with our Milky Way Galaxy.

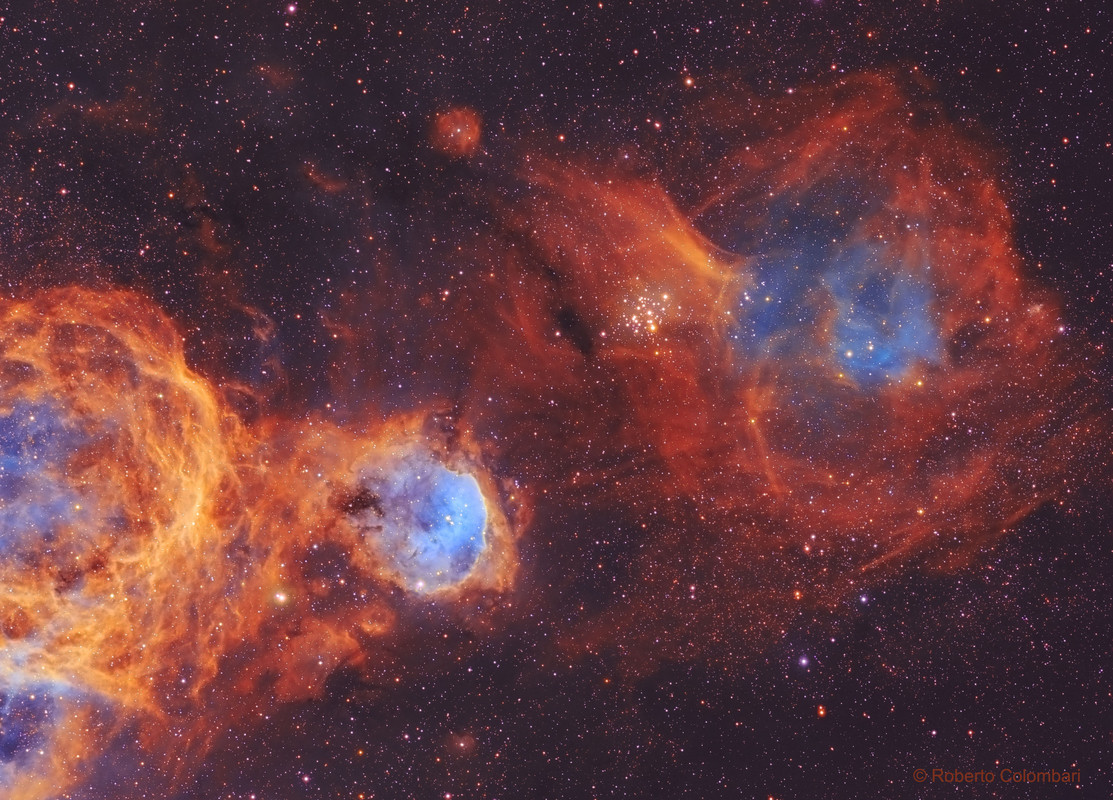
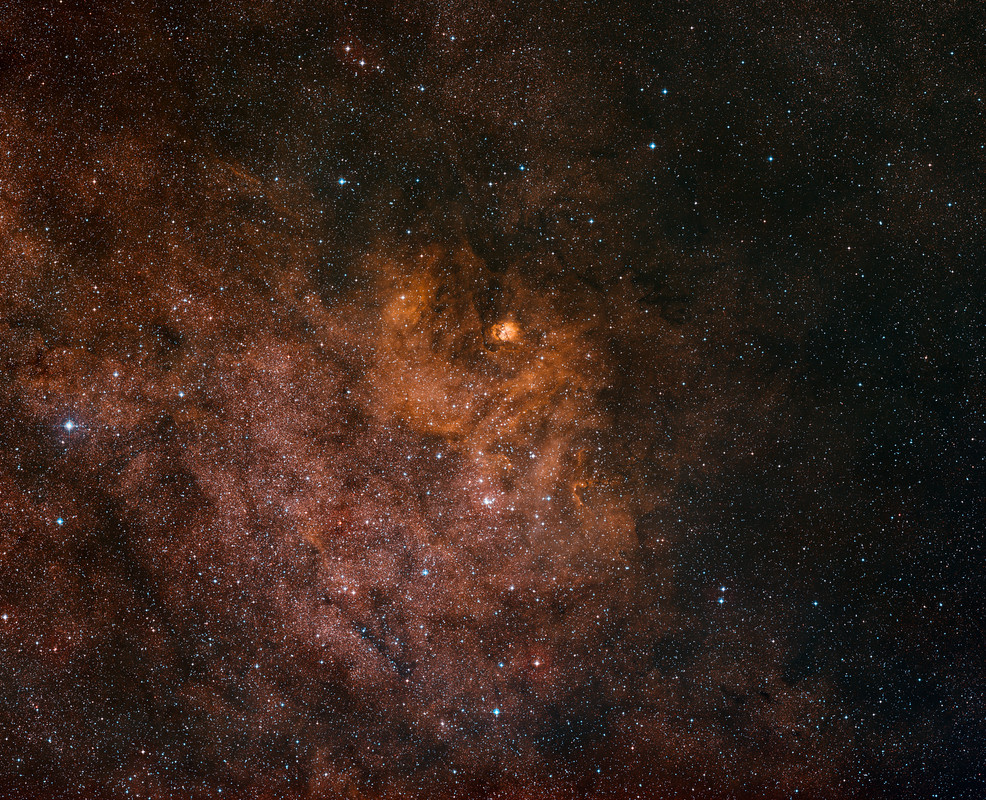
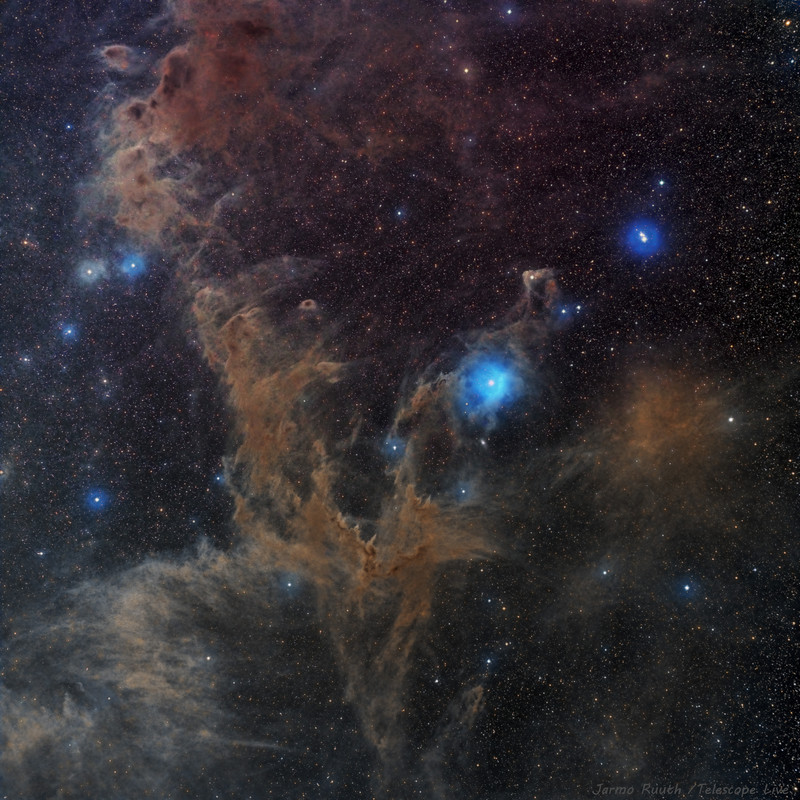
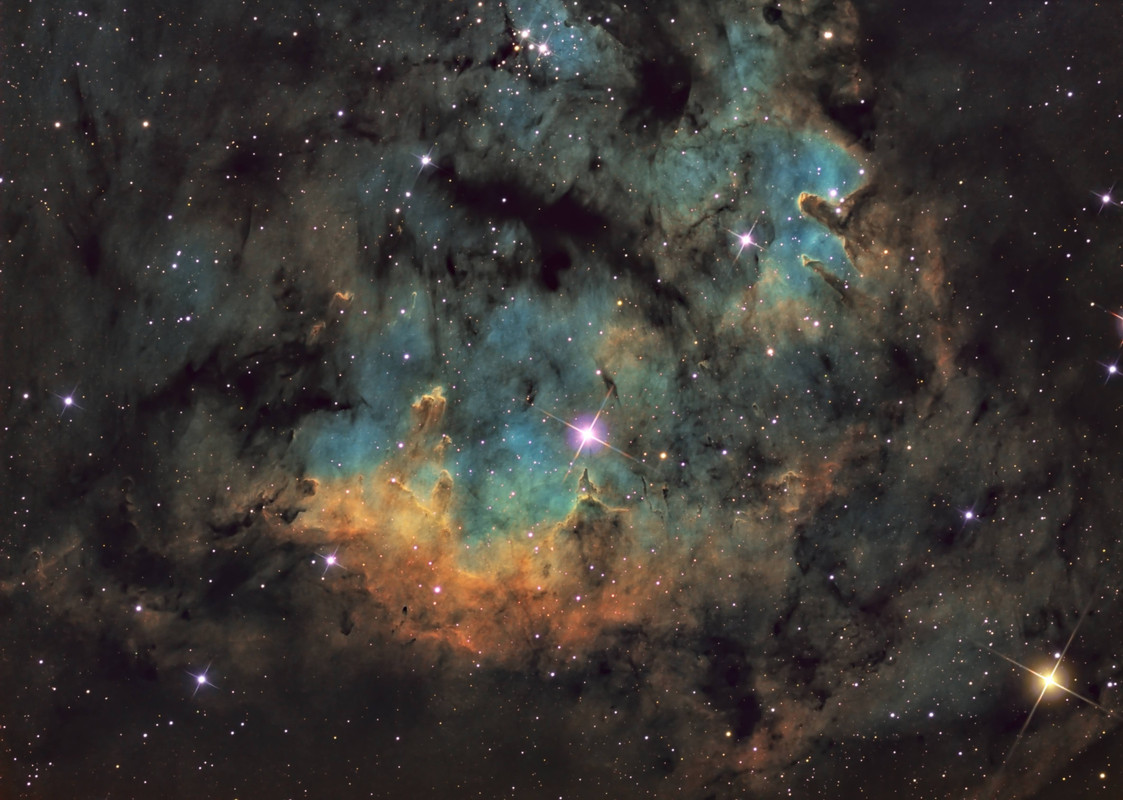
Hot, young stars and cosmic pillars of gas and dust seem to crowd into NGC 7822. At the edge of a giant molecular cloud toward the northern constellation Cepheus, the glowing star forming region lies about 3,000 light-years away. Within the nebula, bright edges and dark shapes stand out in this colorful telescopic skyscape. The image includes data from narrowband filters, mapping emission from atomic oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur into blue, green, and red hues. The emission line and color combination has become well-known as the Hubble palette. The atomic emission is powered by energetic radiation from the central hot stars. Their powerful winds and radiation sculpt and erode the denser pillar shapes and clear out a characteristic cavity light-years across the center of the natal cloud. Stars could still be forming inside the pillars by gravitational collapse but as the pillars are eroded away, any forming stars will ultimately be cutoff from their reservoir of star stuff. This field of view spans about 40 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 7822.

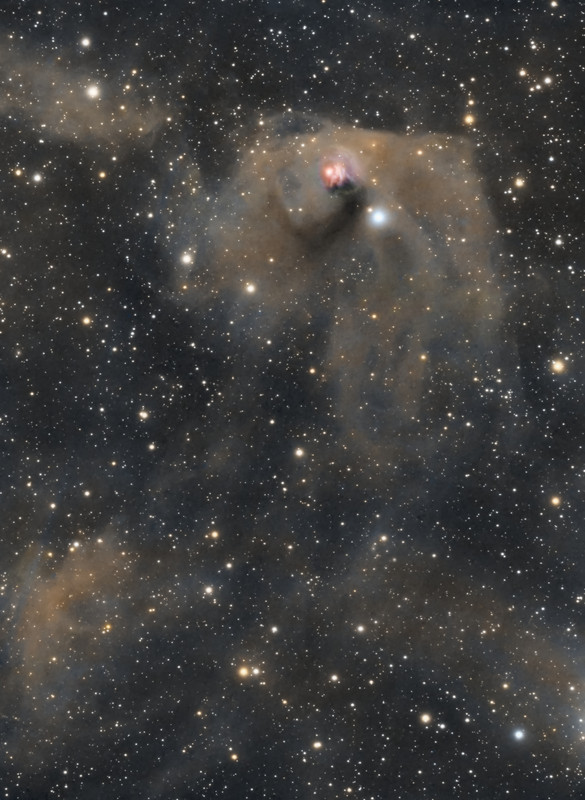
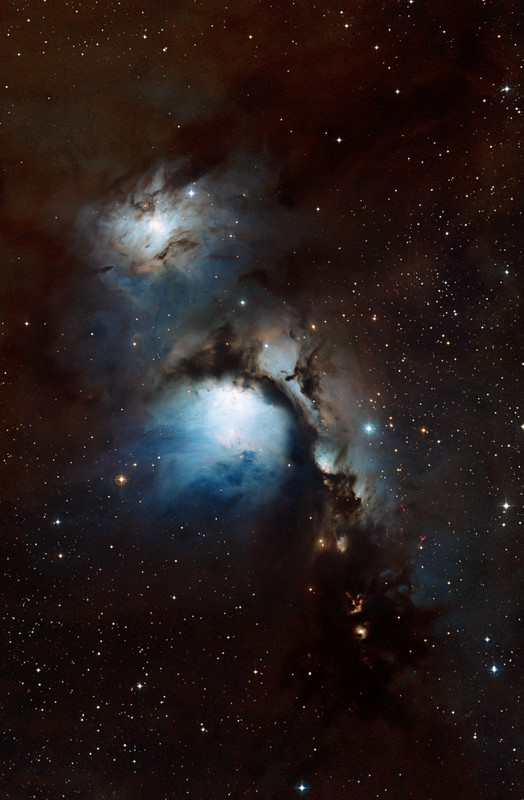
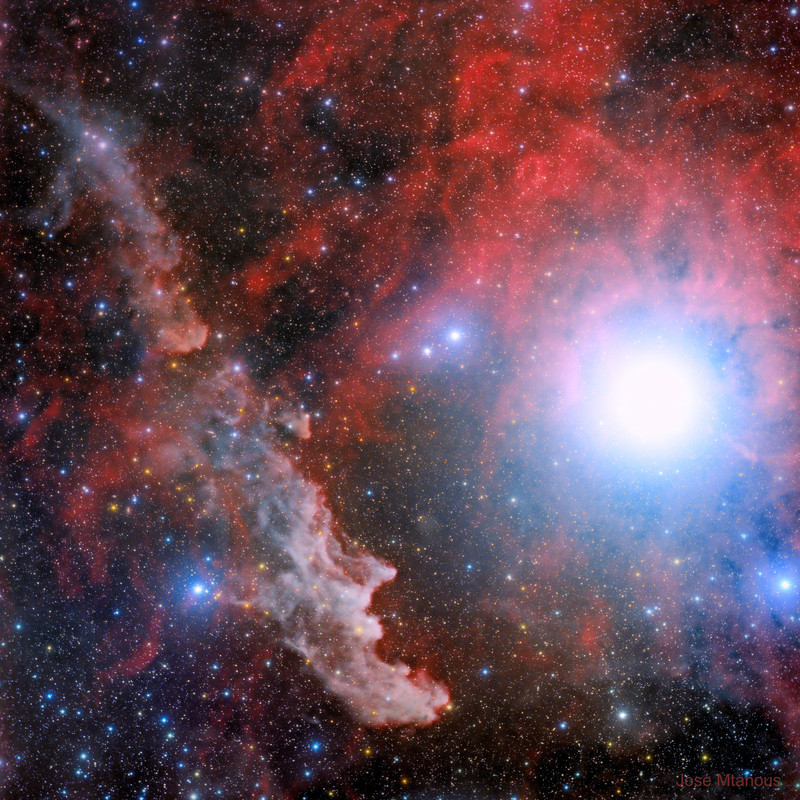
By starlight this eerie visage shines in the dark, a crooked profile evoking its popular name, the Witch Head Nebula. In fact, this entrancing telescopic portrait gives the impression that the witch has fixed her gaze on Orion's bright supergiant star Rigel. More formally known as IC 2118, the Witch Head Nebula spans about 50 light-years and is composed of interstellar dust grains reflecting Rigel's starlight. The blue color of the Witch Head Nebula and of the dust surrounding Rigel is caused not only by Rigel's intense blue starlight but because the dust grains scatter blue light more efficiently than red. The same physical process causes Earth's daytime sky to appear blue, although the scatterers in Earth's atmosphere are molecules of nitrogen and oxygen. Rigel, the Witch Head Nebula, and gas and dust that surrounds them lie about 800 light-years away.


It's easy to get lost following the intricate, looping, twisting filaments in this detailed image of supernova remnant Simeis 147. Also cataloged as Sharpless 2-240 it goes by the popular nickname, the Spaghetti Nebula. Seen toward the boundary of the constellations Taurus and Auriga, it covers nearly 3 degrees or 6 full moons on the sky. That's about 150 light-years at the stellar debris cloud's estimated distance of 3,000 light-years. This composite includes image data taken through narrow-band filters where reddish emission from ionized hydrogen atoms and doubly ionized oxygen atoms in faint blue-green hues trace the shocked, glowing gas. The supernova remnant has an estimated age of about 40,000 years, meaning light from the massive stellar explosion first reached Earth 40,000 years ago. But the expanding remnant is not the only aftermath. The cosmic catastrophe also left behind a spinning neutron star or pulsar, all that remains of the original star's core.

An island universe of billions of stars, NGC 1566 lies about 60 million light-years away in the southern constellation Dorado. Popularly known as the Spanish Dancer galaxy, it's seen face-on from our Milky Way perspective. A gorgeous grand design spiral, this galaxy's two graceful spiral arms span over 100,000 light-years, traced by bright blue star clusters, pinkish starforming regions, and swirling cosmic dust lanes. NGC 1566's flaring center makes the spiral one of the closest and brightest Seyfert galaxies. It likely houses a central supermassive black hole wreaking havoc on surrounding stars, gas, and dust. In this sharp southern galaxy portrait, the spiky stars lie well within the Milky Way.

Sometimes the dark dust of interstellar space has an angular elegance. Such is the case toward the far-south constellation of Chamaeleon. Normally too faint to see, dark dust is best known for blocking visible light from stars and galaxies behind it. In this four-hour exposure, however, the dust is seen mostly in light of its own, with its strong red and near-infrared colors giving creating a brown hue. Contrastingly blue, the bright star Beta Chamaeleontis is visible just to the right of center, with the dust that surrounds it preferentially reflecting blue light from its primarily blue-white color. All of the pictured stars and dust occur in our own Milky Way Galaxy with -- but one notable exception: the white spot just below Beta Chamaeleontis is the galaxy IC 3104 which lies far in the distance. Interstellar dust is mostly created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars and dispersed into space by stellar light, stellar winds, and stellar explosions such as supernovas.

The most distant object easily visible to the unaided eye is M31, the great Andromeda Galaxy. Even at some two and a half million light-years distant, this immense spiral galaxy -- spanning over 200,000 light years -- is visible, although as a faint, nebulous cloud in the constellation Andromeda. In contrast, a bright yellow nucleus, dark winding dust lanes, and expansive spiral arms dotted with blue star clusters and red nebulae, are recorded in this stunning telescopic image which combines data from orbiting Hubble with ground-based images from Subaru and Mayall. In only about 5 billion years, the Andromeda galaxy may be even easier to see -- as it will likely span the entire night sky -- just before it merges with our Milky Way Galaxy.

Hot, young stars and cosmic pillars of gas and dust seem to crowd into NGC 7822. At the edge of a giant molecular cloud toward the northern constellation Cepheus, the glowing star forming region lies about 3,000 light-years away. Within the nebula, bright edges and dark shapes stand out in this colorful telescopic skyscape. The image includes data from narrowband filters, mapping emission from atomic oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur into blue, green, and red hues. The emission line and color combination has become well-known as the Hubble palette. The atomic emission is powered by energetic radiation from the central hot stars. Their powerful winds and radiation sculpt and erode the denser pillar shapes and clear out a characteristic cavity light-years across the center of the natal cloud. Stars could still be forming inside the pillars by gravitational collapse but as the pillars are eroded away, any forming stars will ultimately be cutoff from their reservoir of star stuff. This field of view spans about 40 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 7822.

By starlight this eerie visage shines in the dark, a crooked profile evoking its popular name, the Witch Head Nebula. In fact, this entrancing telescopic portrait gives the impression that the witch has fixed her gaze on Orion's bright supergiant star Rigel. More formally known as IC 2118, the Witch Head Nebula spans about 50 light-years and is composed of interstellar dust grains reflecting Rigel's starlight. The blue color of the Witch Head Nebula and of the dust surrounding Rigel is caused not only by Rigel's intense blue starlight but because the dust grains scatter blue light more efficiently than red. The same physical process causes Earth's daytime sky to appear blue, although the scatterers in Earth's atmosphere are molecules of nitrogen and oxygen. Rigel, the Witch Head Nebula, and gas and dust that surrounds them lie about 800 light-years away.