-
SCAM WARNING! See how this scam works in Classifieds.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
I just saw the moon
- Thread starter TheMadDabber
- Start date
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
The tail of a comet streams across this three degree wide telescopic field of view captured under dark Namibian skies on December 21. In outburst only a few days ago and just reaching naked eye visibility Comet Leonard (C/2021 A1) is this year's brightest comet. Binoculars will make the diffuse comet easier to spot though, close to the western horizon after sunset. Details revealed in the sharp image show the comet's coma with a greenish tinge, and follow the interaction of the comet's ion tail with magnetic fields in the solar wind. After passing closest to Earth on December 12 and Venus on December 18, Comet Leonard is heading toward perihelion, its closest approach to the Sun on January 3rd. Appearing in late December's beautiful evening skies Comet Leonard has also become known as 2021's Christmas Comet.

The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on Charles Messier's famous 18th century list of things which are not comets. In fact, the Crab is now known to be a supernova remnant, debris from the death explosion of a massive star, witnessed by astronomers in the year 1054. This sharp, ground-based telescopic view combines broadband color data with narrowband data that tracks emission from ionized sulfur, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms to explore the tangled filaments within the still expanding cloud. One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers, the Crab Pulsar, a neutron star spinning 30 times a second, is visible as a bright spot near the nebula's center. Like a cosmic dynamo, this collapsed remnant of the stellar core powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum. Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is a mere 6,500 light-years away in the constellation Taurus.

Welcome to December's solstice, first day of winter in the north and summer for the southern hemisphere. Astronomical markers of the seasons, solstice and equinox dates are based on the Sun's place in its annual journey along the ecliptic, through planet Earth's sky. At this solstice, the Sun reaches its maximum southern declination of -23.5 degrees today at 15:59 UTC, while its right ascension coordinate on the celestial sphere is 18 hours. That puts the Sun in the constellation Sagittarius in a direction near the center of our Milky Way galaxy. In fact, if you could see today's Solstice Sun against faint background stars and nebulae (that's really hard to do, especially in the daytime ...) your view might look something like this composited panorama. To make it, images of our fair galaxy were taken under dark Namibian night skies, then stitched together in a panoramic view. From a snapshot made on 2015 December 21, the Sun was digitally overlayed as a brilliant star at today's northern winter solstice position, close to the center of the Milky Way.

The first identified compact galaxy group, Stephan's Quintet is featured in this eye-catching image constructed with data drawn from the extensive Hubble Legacy Archive. About 300 million light-years away, only four of these five galaxies are actually locked in a cosmic dance of repeated close encounters. The odd man out is easy to spot, though. The interacting galaxies, NGC 7319, 7318A, 7318B, and 7317 have an overall yellowish cast. They also tend to have distorted loops and tails, grown under the influence of disruptive gravitational tides. But the predominantly bluish galaxy, NGC 7320, is closer, just 40 million light-years distant, and isn't part of the interacting group. Stephan's Quintet lies within the boundaries of the high flying constellation Pegasus. At the estimated distance of the quartet of interacting galaxies, this field of view spans about 500,000 light-years. But moving just beyond this field, up and to the right, astronomers can identify another galaxy, NGC 7320C, that is also 300 million light-years distant. Including it would bring the interacting quartet back up to quintet status.


The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on Charles Messier's famous 18th century list of things which are not comets. In fact, the Crab is now known to be a supernova remnant, debris from the death explosion of a massive star, witnessed by astronomers in the year 1054. This sharp, ground-based telescopic view combines broadband color data with narrowband data that tracks emission from ionized sulfur, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms to explore the tangled filaments within the still expanding cloud. One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers, the Crab Pulsar, a neutron star spinning 30 times a second, is visible as a bright spot near the nebula's center. Like a cosmic dynamo, this collapsed remnant of the stellar core powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum. Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is a mere 6,500 light-years away in the constellation Taurus.

Welcome to December's solstice, first day of winter in the north and summer for the southern hemisphere. Astronomical markers of the seasons, solstice and equinox dates are based on the Sun's place in its annual journey along the ecliptic, through planet Earth's sky. At this solstice, the Sun reaches its maximum southern declination of -23.5 degrees today at 15:59 UTC, while its right ascension coordinate on the celestial sphere is 18 hours. That puts the Sun in the constellation Sagittarius in a direction near the center of our Milky Way galaxy. In fact, if you could see today's Solstice Sun against faint background stars and nebulae (that's really hard to do, especially in the daytime ...) your view might look something like this composited panorama. To make it, images of our fair galaxy were taken under dark Namibian night skies, then stitched together in a panoramic view. From a snapshot made on 2015 December 21, the Sun was digitally overlayed as a brilliant star at today's northern winter solstice position, close to the center of the Milky Way.

The first identified compact galaxy group, Stephan's Quintet is featured in this eye-catching image constructed with data drawn from the extensive Hubble Legacy Archive. About 300 million light-years away, only four of these five galaxies are actually locked in a cosmic dance of repeated close encounters. The odd man out is easy to spot, though. The interacting galaxies, NGC 7319, 7318A, 7318B, and 7317 have an overall yellowish cast. They also tend to have distorted loops and tails, grown under the influence of disruptive gravitational tides. But the predominantly bluish galaxy, NGC 7320, is closer, just 40 million light-years distant, and isn't part of the interacting group. Stephan's Quintet lies within the boundaries of the high flying constellation Pegasus. At the estimated distance of the quartet of interacting galaxies, this field of view spans about 500,000 light-years. But moving just beyond this field, up and to the right, astronomers can identify another galaxy, NGC 7320C, that is also 300 million light-years distant. Including it would bring the interacting quartet back up to quintet status.
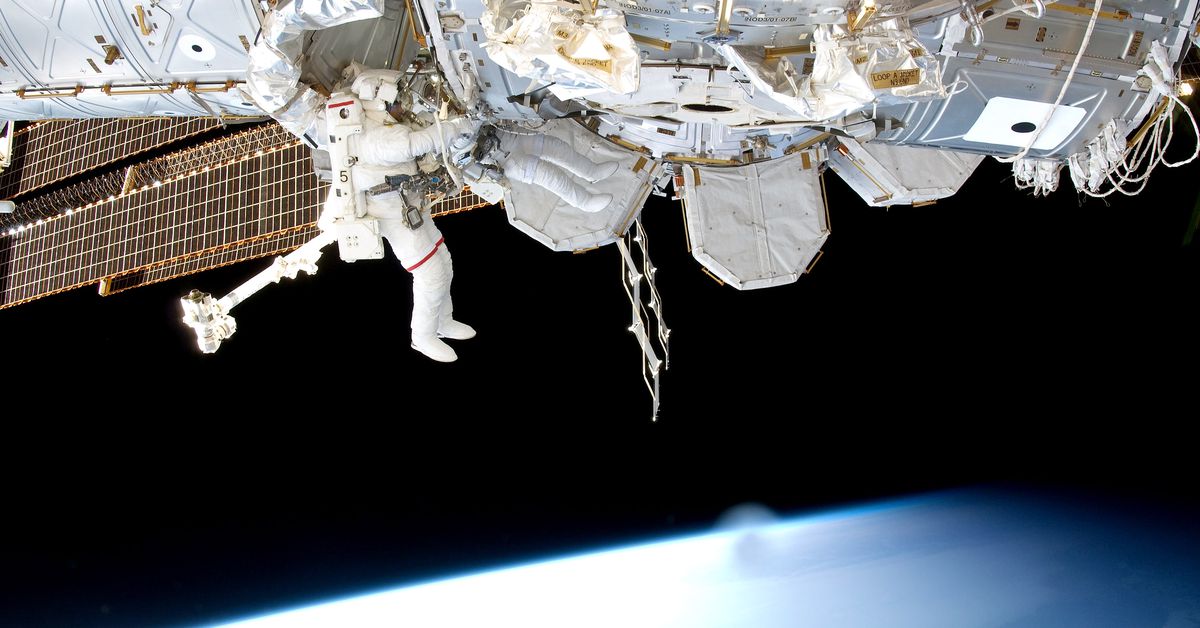


The space station race
The ISS will burn up in Earth’s atmosphere in a few years, paving the way for new businesses in space.

Webb telescope fully deploys sunshield in mission milestone: NASA
The James Webb Space Telescope fully deployed its five-layer sunshield Tuesday, a critical milestone for the success of its mission to study every phase of cosmic history, US space agency NASA said."All five layers of the sunshield are fully tensioned," said an announcer at the telescope's...
 www.rawstory.com
www.rawstory.com
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
That sunshield deployment is huge...over 100 latches needed to work right...without the sunshield, no mission as the instruments would not get cold enough to perform the measurements they are designed for.
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
If I'm correct, they just finished deploying the secondary mirror. The project manager announced we are 600,000 miles from Earth and we have a telescope now. Even if the main mirrors segments that need to unfold don't, it can still work. Great news so far!
Edit: Article about it...

 gizmodo.com
gizmodo.com
Edit: Article about it...

Webb Space Telescope Deploys Secondary Mirror as It Zooms Toward Final Destination
Webb launched just 12 days ago, and the next-gen observatory is quickly taking shape.
Last edited:
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild

James Webb Space Telescope has unfolded 1st wing of massive golden mirror
Unfolding the two side wings of the James Webb Space Telescope's golden primary mirror marks the last major task in assembling the observatory.
cybrguy
Putin is a War Criminal
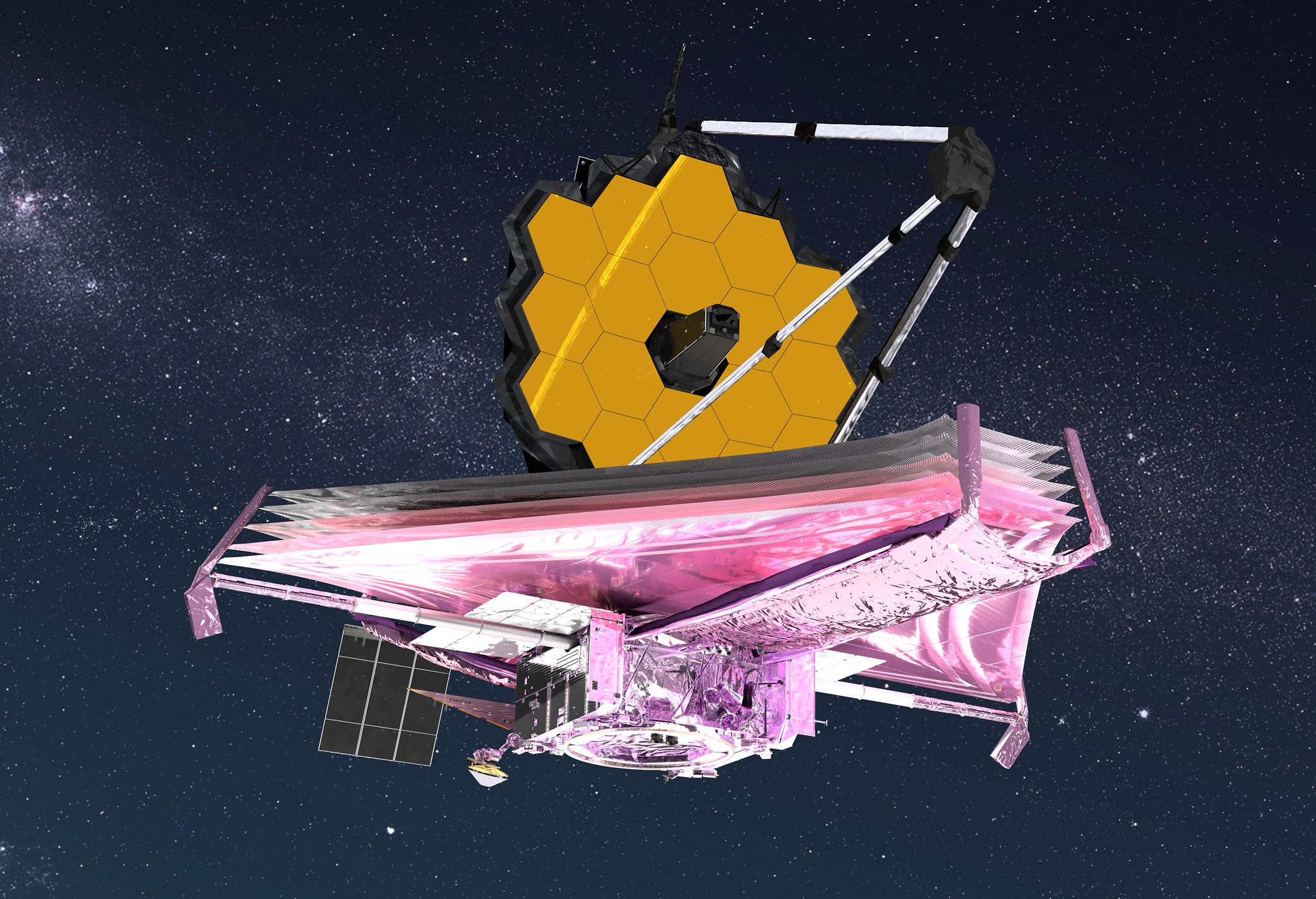

James Webb Space Telescope, the biggest ever built, fully unfolds giant mirror to gaze at the cosmos
You can exhale now. The Webb Space Telescope is fully deployed.
Also, wecome back. FC was unavailable for several hours...
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
I got to thinking, imagine how big of a space telescope you could fit into a SpaceX Starship...wouldn't have to have all this unfolding and such. Without seeing the dimensions of either, I bet Webb could have fit into Starship completely deployed, unfolded.
Berzzerkker
Well-Known Member
the shield is the size of a tennis court!!
21.197 m x 14.162 m (69.5 ft x 46.5 ft)
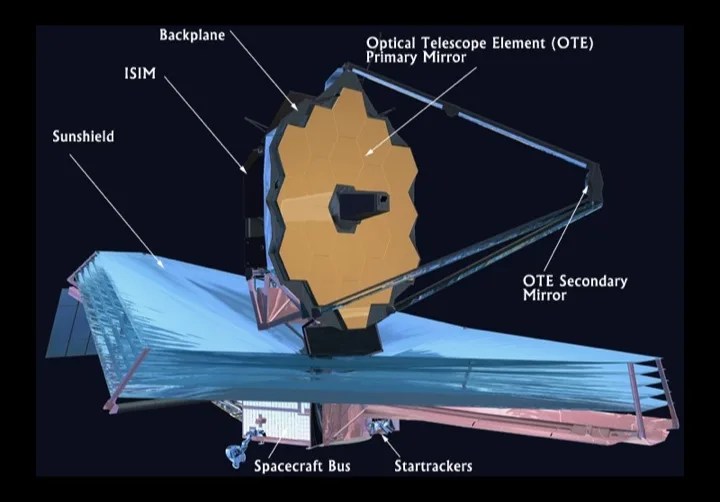
 jwst.nasa.gov
jwst.nasa.gov
21.197 m x 14.162 m (69.5 ft x 46.5 ft)

Fact Sheet - NASA Science
Key Facts Launch Date December 25, 2021 07:20am EST (2021-12-25 12:20 GMT/UTC) Launch Vehicle Ariane 5 ECA Mission Duration 5 - 10 years Total Payload Mass
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
Starship can hold up to 22m in length, but 9m in diameter, so just a small fold in the shield, lol.
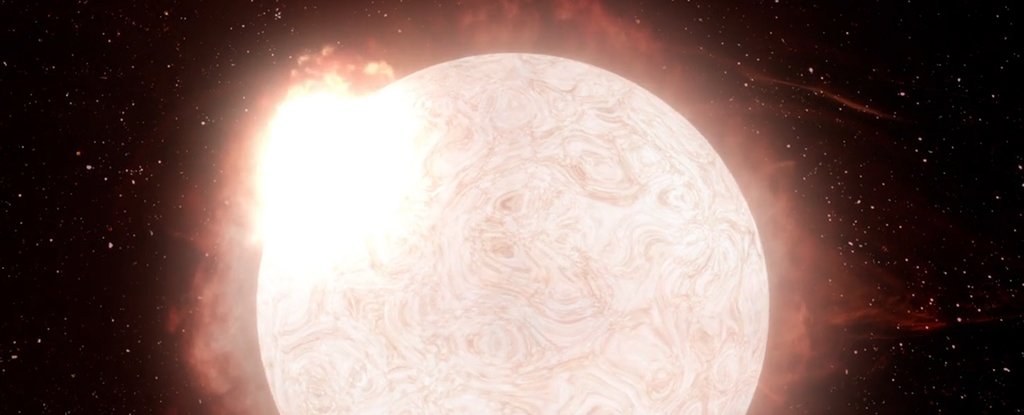

For The First Time, We've Seen a Red Giant Star Transition Into a Supernova
We're seeing many spectacular sights out in space as our telescopes become more powerful, but there's a new contender for the most exciting one yet: According to researchers, we've observed a red supergiant star exploding into a supernova for the fir
Artist's Conception
Last edited:
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
This timelapse gif tracks the James Webb Space Telescope as it streaks across the stars of Orion on its journey to a destination beyond the Moon. Recorded on December 28, 12 consecutive exposures each 10 minutes long were aligned and combined with a subsequent color image of the background stars to create the animation. About 2.5 days after its December 25 launch, JWST cruised past the altitude of the Moon's orbit as it climbed up the gravity ridge from Earth to reach a halo orbit around L2, an Earth-Sun Lagrange point. Lagrange points are convenient locations in space where the combined gravitational attraction of one massive body (Earth) orbiting another massive body (Sun) is in balance with the centripetal force needed to move along with them. So much smaller masses, like spacecraft, will tend to stay there. One of 5 Lagrange points, L2 is about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth directly along the Earth-Sun line. JWST will arrive at L2 on January 23, 29 days after launch. While relaxing in Earth's surface gravity you can follow the James Webb Space Telescope's progress and complicated deployment online.


Berzzerkker
Well-Known Member
JWST Begins Its Months-Long Mirror Alignment

James Webb Space Telescope Archives - NASA Science
ChooChooCharlie
Well-Known Member
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
Have to use a different image host as imgur isn't working here like it used to. If you click the image it will take you to postimage where you can blow it up real big and save if you want.
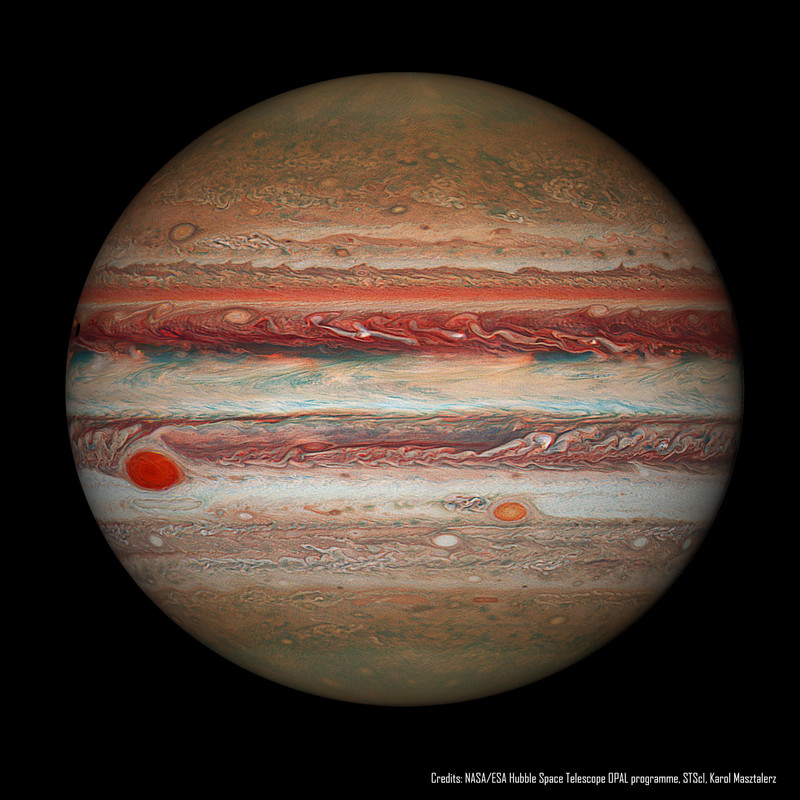
What will become of Jupiter's Great Red Spot? Gas giant Jupiter is the solar system's largest world with about 320 times the mass of planet Earth. Jupiter is home to one of the largest and longest lasting storm systems known, the Great Red Spot (GRS), visible to the left. The GRS is so large it could swallow Earth, although it has been shrinking. Comparison with historical notes indicate that the storm spans only about one third of the exposed surface area it had 150 years ago. NASA's Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program has been monitoring the storm more recently using the Hubble Space Telescope. The featured Hubble OPAL image shows Jupiter as it appeared in 2016, processed in a way that makes red hues appear quite vibrant. Modern GRS data indicate that the storm continues to constrict its surface area, but is also becoming slightly taller, vertically. No one knows the future of the GRS, including the possibility that if the shrinking trend continues, the GRS might one day even do what smaller spots on Jupiter have done -- disappear completely.
You may have seen Orion's belt before -- but not like this. The three bright stars across this image are, from left to right, Mintaka, Alnilam, and Alnitak: the iconic belt stars of Orion. The rest of the stars in the frame have been digitally removed to highlight the surrounding clouds of glowing gas and dark dust. Some of these clouds have intriguing shapes, including the Horsehead and Flame Nebulas, both near Alnitak on the lower right. This deep image, taken last month from the Marathon Skypark and Observatory in Marathon, Texas, USA, spans about 5 degrees, required about 20 hours of exposure, and was processed to reveal the gas and dust that we would really see if we were much closer. The famous Orion Nebula is off to the upper right of this colorful field. The entire region lies only about 1,500 light-years distant and so is one of the closest and best studied star formation nurseries known
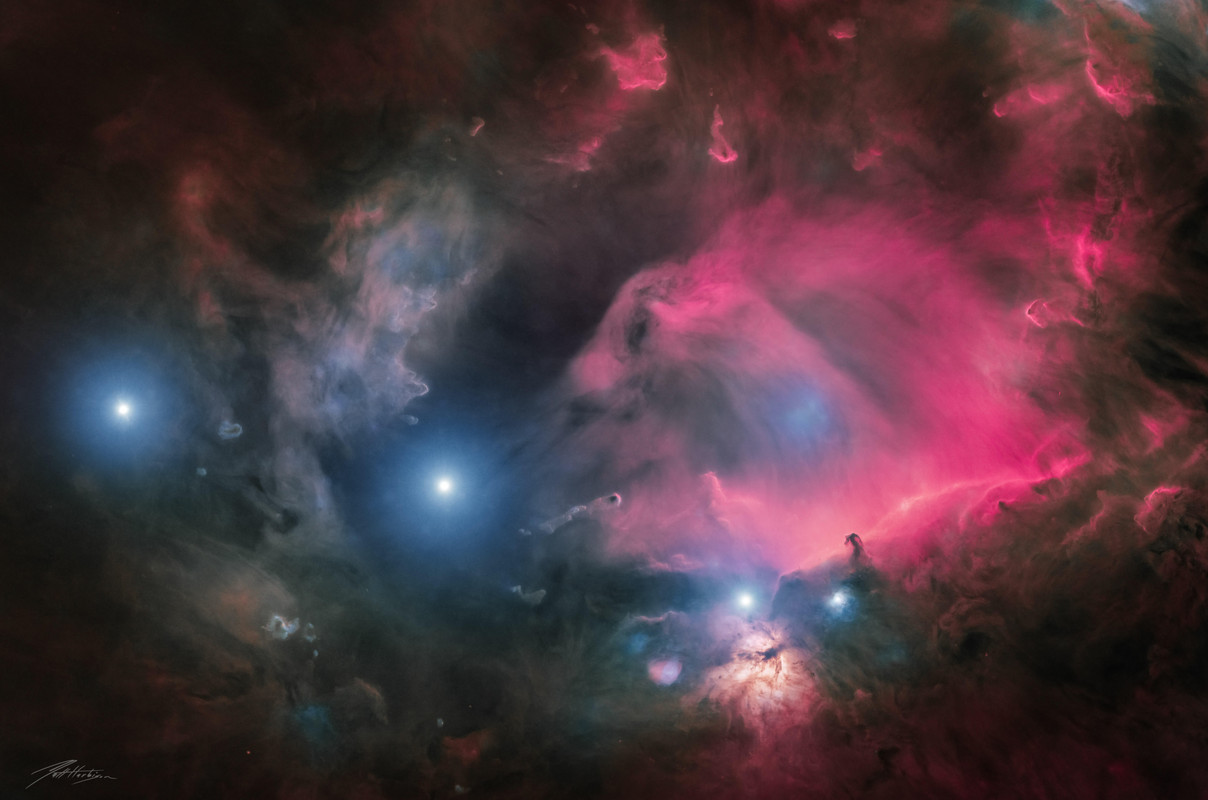

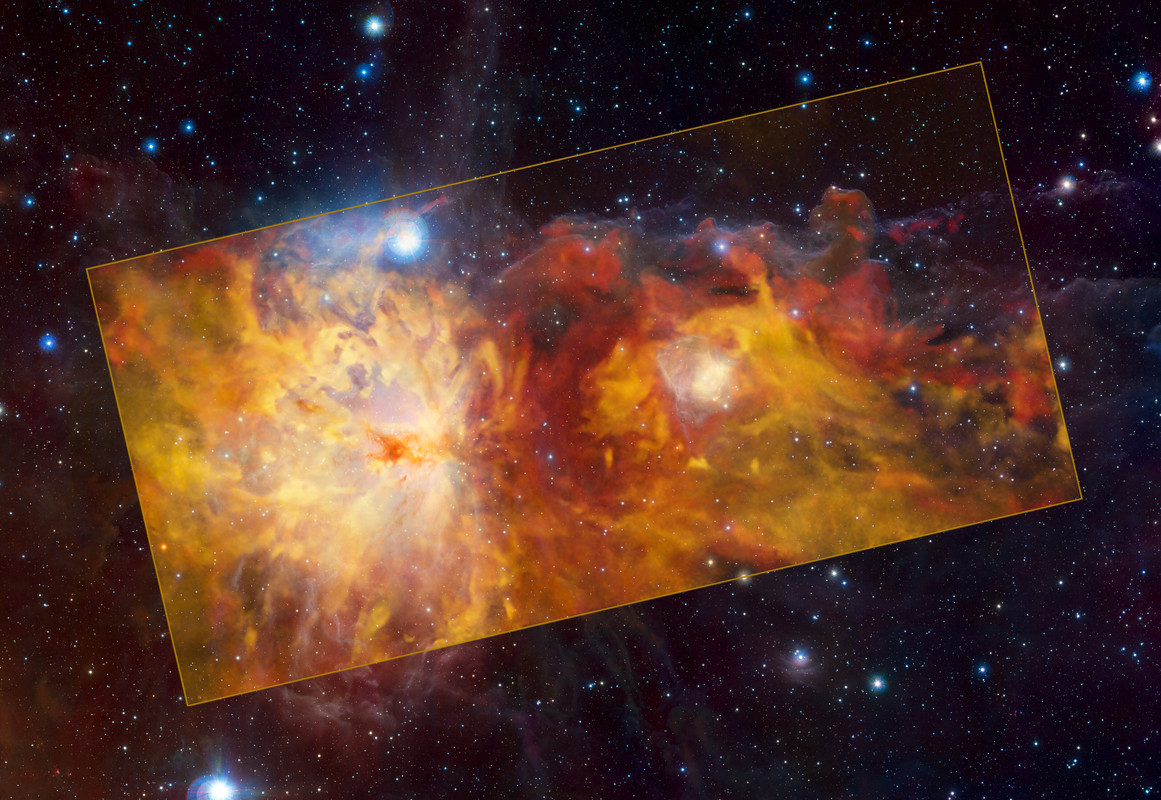
Do not let the image and the name of the depicted cosmic object fool you! What you see in this picture is not a wildfire, but the Flame Nebula and its surroundings captured in radio waves.
The Flame Nebula is the large feature on the left half of the central, yellow rectangle. The smaller feature on the right is the reflection nebula NGC 2023. To the top right of NGC 2023, the iconic Horsehead Nebula seems to emerge heroically from the “flames”. The three objects are part of the Orion cloud, a giant gas structure located between 1300 and 1600 light-years away.
The different colors indicate the velocity of the gas. The Flame Nebula and its surroundings are moving away from us, with the red clouds in the background receding faster than the yellow ones in the foreground.
The image in the rectangle is based on observations conducted with the SuperCam instrument on the ESO-operated Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) on Chile’s Chajnantor Plateau. The background image was taken in infrared light with ESO’s Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy (VISTA) at the Paranal Observatory in Chile.

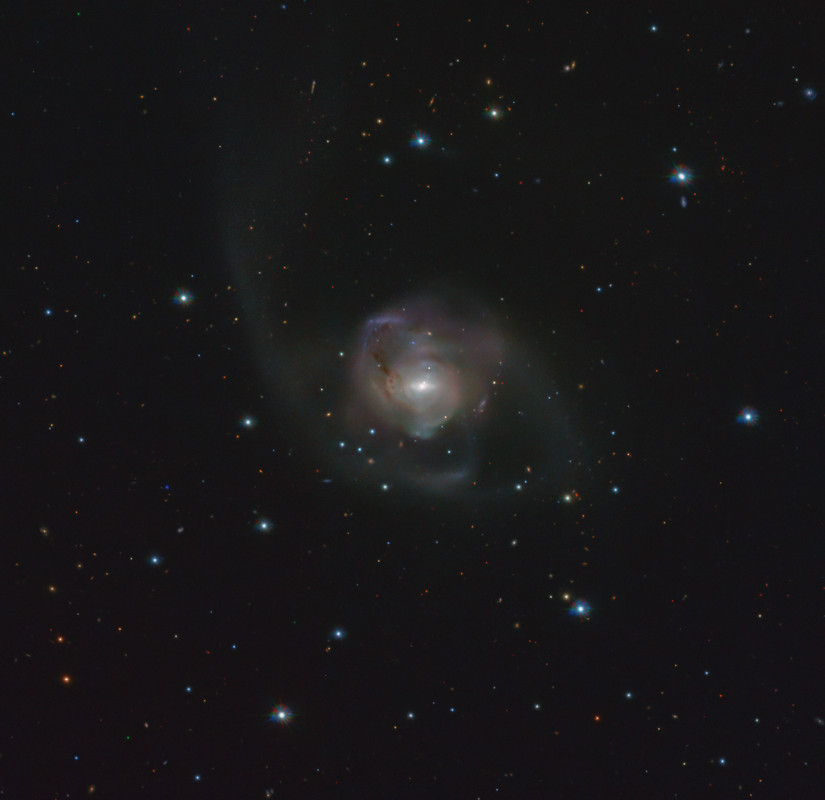
Just as people at a busy crossroad may accidentally bump into each other, so too can galaxies in the Universe! But in this case, the outcome is more dramatic than a small nudge. When two galaxies clash, they merge into each other, giving birth to a new, bigger one. One example is the NGC 7727 galaxy, shown in this image from ESO’s VLT Survey Telescope (VST) in Chile.
Located 89 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Aquarius, NGC 7727 is believed to be the result of a clash between two galaxies that occurred about one billion years ago. The consequences of this tremendous cosmic bump are still evident in the peculiar, irregular shape of NGC 7727 and the streams of stars in its outer regions.
The image was taken in visible light as part of the VST-ATLAS survey. The goal of the survey is to map a vast region of the Southern Sky — so large you could fit about 19,000 full moons in it! By studying the galaxies in this region, astronomers aim to shed new light on the nature of dark energy, the mysterious force permeating the Universe and causing its accelerating expansion.

This wide-field view of the sky around the bright star Alpha Centauri was created from photographic images forming part of the Digitized Sky Survey 2. The star appears so big just because of the scattering of light by the telescope's optics as well as in the photographic emulsion. Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to the Solar System.

What will become of Jupiter's Great Red Spot? Gas giant Jupiter is the solar system's largest world with about 320 times the mass of planet Earth. Jupiter is home to one of the largest and longest lasting storm systems known, the Great Red Spot (GRS), visible to the left. The GRS is so large it could swallow Earth, although it has been shrinking. Comparison with historical notes indicate that the storm spans only about one third of the exposed surface area it had 150 years ago. NASA's Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program has been monitoring the storm more recently using the Hubble Space Telescope. The featured Hubble OPAL image shows Jupiter as it appeared in 2016, processed in a way that makes red hues appear quite vibrant. Modern GRS data indicate that the storm continues to constrict its surface area, but is also becoming slightly taller, vertically. No one knows the future of the GRS, including the possibility that if the shrinking trend continues, the GRS might one day even do what smaller spots on Jupiter have done -- disappear completely.

You may have seen Orion's belt before -- but not like this. The three bright stars across this image are, from left to right, Mintaka, Alnilam, and Alnitak: the iconic belt stars of Orion. The rest of the stars in the frame have been digitally removed to highlight the surrounding clouds of glowing gas and dark dust. Some of these clouds have intriguing shapes, including the Horsehead and Flame Nebulas, both near Alnitak on the lower right. This deep image, taken last month from the Marathon Skypark and Observatory in Marathon, Texas, USA, spans about 5 degrees, required about 20 hours of exposure, and was processed to reveal the gas and dust that we would really see if we were much closer. The famous Orion Nebula is off to the upper right of this colorful field. The entire region lies only about 1,500 light-years distant and so is one of the closest and best studied star formation nurseries known

Do not let the image and the name of the depicted cosmic object fool you! What you see in this picture is not a wildfire, but the Flame Nebula and its surroundings captured in radio waves.
The Flame Nebula is the large feature on the left half of the central, yellow rectangle. The smaller feature on the right is the reflection nebula NGC 2023. To the top right of NGC 2023, the iconic Horsehead Nebula seems to emerge heroically from the “flames”. The three objects are part of the Orion cloud, a giant gas structure located between 1300 and 1600 light-years away.
The different colors indicate the velocity of the gas. The Flame Nebula and its surroundings are moving away from us, with the red clouds in the background receding faster than the yellow ones in the foreground.
The image in the rectangle is based on observations conducted with the SuperCam instrument on the ESO-operated Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) on Chile’s Chajnantor Plateau. The background image was taken in infrared light with ESO’s Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy (VISTA) at the Paranal Observatory in Chile.

Just as people at a busy crossroad may accidentally bump into each other, so too can galaxies in the Universe! But in this case, the outcome is more dramatic than a small nudge. When two galaxies clash, they merge into each other, giving birth to a new, bigger one. One example is the NGC 7727 galaxy, shown in this image from ESO’s VLT Survey Telescope (VST) in Chile.
Located 89 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Aquarius, NGC 7727 is believed to be the result of a clash between two galaxies that occurred about one billion years ago. The consequences of this tremendous cosmic bump are still evident in the peculiar, irregular shape of NGC 7727 and the streams of stars in its outer regions.
The image was taken in visible light as part of the VST-ATLAS survey. The goal of the survey is to map a vast region of the Southern Sky — so large you could fit about 19,000 full moons in it! By studying the galaxies in this region, astronomers aim to shed new light on the nature of dark energy, the mysterious force permeating the Universe and causing its accelerating expansion.

This wide-field view of the sky around the bright star Alpha Centauri was created from photographic images forming part of the Digitized Sky Survey 2. The star appears so big just because of the scattering of light by the telescope's optics as well as in the photographic emulsion. Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to the Solar System.

cybrguy
Putin is a War Criminal

Bad weather delays SpaceX Dragon's departure from space station to Saturday
Dragon was scheduled to come home on Friday (Jan. 21), but Mother Nature had other ideas.

Historic Mars weather delay pushes Ingenuity helicopter's next flight to Sunday
Dusty skies are to blame.











