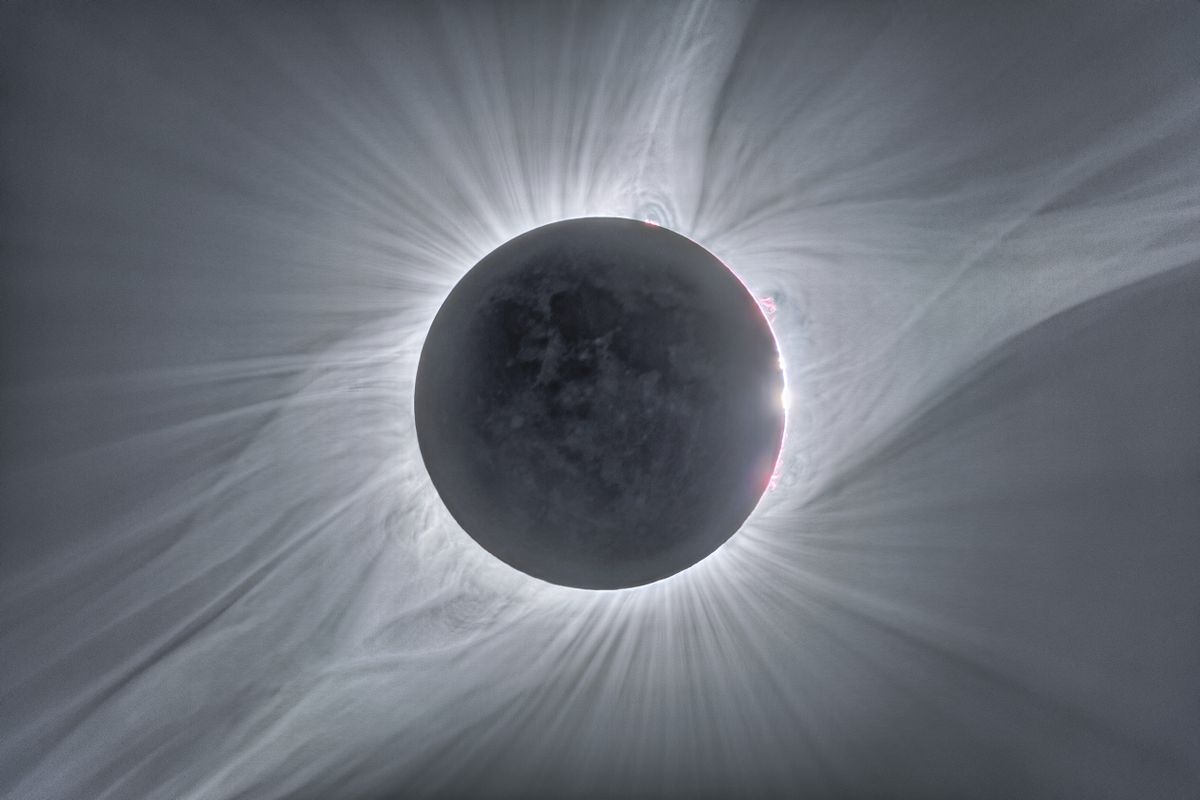
The Horsehead Nebula is one of the most famous nebulae on the sky. It is visible as the dark indentation to the orange emission nebula at the far right of the featured picture. The horse-head feature is dark because it is really an opaque dust cloud that lies in front of the bright emission nebula. Like clouds in Earth's atmosphere, this cosmic cloud has assumed a recognizable shape by chance. After many thousands of years, the internal motions of the cloud will surely alter its appearance. The emission nebula's orange color is caused by electrons recombining with protons to form hydrogen atoms. Toward the lower left of the image is the Flame Nebula, an orange-tinged nebula that also contains intricate filaments of dark dust. Two prominent reflection nebulas are visible: round IC 432 on the far left, and blue NGC 2023 just to the lower left of the Horsehead nebula. Each glows primarily by reflecting the light of their central star.

Light-years across, this suggestive shape known as the Seahorse Nebula appears in silhouette against a rich, luminous background of stars. Seen toward the royal northern constellation of Cepheus, the dusty, obscuring clouds are part of a Milky Way molecular cloud some 1,200 light-years distant. It is also listed as Barnard 150 (B150), one of 182 dark markings of the sky cataloged in the early 20th century by astronomer E. E. Barnard. Packs of low mass stars are forming within, but their collapsing cores are only visible at long infrared wavelengths. Still, the colorful stars of Cepheus add to this pretty, galactic skyscape.

Sorry it's not a larger image...To some it looks like a cat's eye. To others, perhaps like a giant cosmic conch shell. It is actually one of brightest and most highly detailed planetary nebula known, composed of gas expelled in the brief yet glorious phase near the end of life of a Sun-like star. This nebula's dying central star may have produced the outer circular concentric shells by shrugging off outer layers in a series of regular convulsions. The formation of the beautiful, complex-yet-symmetric inner structures, however, is not well understood. The featured image is a composite of a digitally sharpened Hubble Space Telescope image with X-ray light captured by the orbiting Chandra Observatory. The exquisite floating space statue spans over half a light-year across. Of course, gazing into this Cat's Eye, humanity may well be seeing the fate of our sun, destined to enter its own planetary nebula phase of evolution ... in about 5 billion years.

NGC 1333 is seen in visible light as a reflection nebula, dominated by bluish hues characteristic of starlight reflected by interstellar dust. A mere 1,000 light-years distant toward the heroic constellation Perseus, it lies at the edge of a large, star-forming molecular cloud. This telescopic close-up spans about two full moons on the sky or just over 15 light-years at the estimated distance of NGC 1333. It shows details of the dusty region along with telltale hints of contrasty red emission from Herbig-Haro objects, jets and shocked glowing gas emanating from recently formed stars. In fact, NGC 1333 contains hundreds of stars less than a million years old, most still hidden from optical telescopes by the pervasive stardust. The chaotic environment may be similar to one in which our own Sun formed over 4.5 billion years ago.

The small, northern constellation Triangulum harbors this magnificent face-on spiral galaxy, M33. Its popular names include the Pinwheel Galaxy or just the Triangulum Galaxy. M33 is over 50,000 light-years in diameter, third largest in the Local Group of galaxies after the Andromeda Galaxy (M31), and our own Milky Way. About 3 million light-years from the Milky Way, M33 is itself thought to be a satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy and astronomers in these two galaxies would likely have spectacular views of each other's grand spiral star systems. As for the view from planet Earth, this sharp image shows off M33's blue star clusters and pinkish star forming regions along the galaxy's loosely wound spiral arms. In fact, the cavernous NGC 604 is the brightest star forming region, seen here at about the 4 o'clock position from the galaxy center. Like M31, M33's population of well-measured variable stars have helped make this nearby spiral a cosmic yardstick for establishing the distance scale of the Universe.

Why doesn't the nearby galaxy create a gravitational lensing effect on the background galaxy? It does, but since both galaxies are so nearby, the angular shift is much smaller than the angular sizes of the galaxies themselves. The featured Hubble image of NGC 3314 shows two large spiral galaxies which happen to line up exactly. The foreground spiral NGC 3314a appears nearly face-on with its pinwheel shape defined by young bright star clusters. Against the glow of the background galaxy NGC 3314b, though, dark swirling lanes of interstellar dust can also be seen tracing the nearer spiral's structure. Both galaxies appear on the edge of the Hydra Cluster of Galaxies, a cluster that is about 200 million light years away. Gravitational lens distortions are much easier to see when the lensing galaxy is smaller and further away. Then, the background galaxy may even be distorted into a ring around the nearer. Fast gravitational lens flashes due to stars in the foreground galaxy momentarily magnifying the light from stars in the background galaxy might one day be visible in future observing campaigns with high-resolution telescopes.

In visible light the stars have been removed from this narrow-band image of NGC 281, a star forming region some 10,000 light-years away toward the constellation Cassiopeia. Stars were digitally added back to the resulting starless image though. But instead of using visible light image data, the stars were added with X-ray data (in purple) from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and infrared data (in red) from the Spitzer Space Telescope. The merged multiwavelength view reveals a multitude of stars in the region's embedded star cluster IC 1590. The young stars are normally hidden in visible light images by the natal cloud's gas and obscuring dust. Also known to backyard astro-imagers as the Pacman Nebula for its overall appearance in visible light, NGC 281 is about 80 light-years across.

Why, sometimes, does part of the Sun's atmosphere leap into space? The reason lies in changing magnetic fields that thread through the Sun's surface. Regions of strong surface magnetism, known as active regions, are usually marked by dark sunspots. Active regions can channel charged gas along arching or sweeping magnetic fields -- gas that sometimes falls back, sometimes escapes, and sometimes not only escapes but impacts our Earth. The featured one-hour time-lapse video -- taken with a small telescope in France -- captured an eruptive filament that appeared to leap off the Sun late last month. The filament is huge: for comparison, the size of the Earth is shown on the upper left. Just after the filament lifted off, the Sun emitted a powerful X-class flare while the surface rumbled with a tremendous solar tsunami. A result was a cloud of charged particles that rushed into our Solar System but mostly missed our Earth -- this time. However, enough solar plasma did impact our Earth's magnetosphere to create a few faint auroras.
Many think it is just a myth. Others think it is true but its cause isn't known. Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it. It's a green flash from the Sun. The truth is the green flash does exist and its cause is well understood. Just as the setting Sun disappears completely from view, a last glimmer appears startlingly green. The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low, distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds. A green flash is also visible for a rising Sun, but takes better timing to spot. A dramatic green flash was caught on video last month as the Sun set beyond the Ligurian Sea from Tuscany, Italy. The second sequence in the featured video shows the green flash in real time, while the first is sped up and the last is in slow motion. The Sun itself does not turn partly green -- the effect is caused by layers of the Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.