-
SCAM WARNING! See how this scam works in Classifieds.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Science and Souls (for geeks and spiritual explorers)
- Thread starter Bob Loblaw
- Start date
howie105
Well-Known Member
Would the universe exist if there were no conscious life to be aware of it?
Yes, but it would not matter.
 Sort of the same thing you get with extinct religions and their gods.
Sort of the same thing you get with extinct religions and their gods.GrilledGoat
New Places

WASHINGTON, DC/Cascina, Italy
For the first time, scientists have observed ripples in the fabric of spacetime called gravitational waves, arriving at the earth from a cataclysmic event in the distant universe. This confirms a major prediction of Albert Einstein’s 1915 general theory of relativity and opens an unprecedented new window onto the cosmos.
Gravitational waves carry information about their dramatic origins and about the nature of gravity that cannot otherwise be obtained. Physicists have concluded that the detected gravitational waves were produced during the final fraction of a second of the merger of two black holes to produce a single, more massive spinning black hole. This collision of two black holes had been predicted but never observed.
The gravitational waves were detected on September 14, 2015 at 5:51 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (09:51 UTC) by both of the twin Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) detectors, located in Livingston, Louisiana, and Hanford, Washington, USA. The LIGO Observatories are funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), and were conceived, built, and are operated by Caltech and MIT. The discovery, accepted for publication in the journal Physical Review Letters, was made by the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (which includes the GEO Collaboration and the Australian Consortium for Interferometric Gravitational Astronomy) and the Virgo Collaboration using data from the two LIGO detectors.
Based on the observed signals, LIGO scientists estimate that the black holes for this event were about 29 and 36 times the mass of the sun, and the event took place 1.3 billion years ago. About 3 times the mass of the sun was converted into gravitational waves in a fraction of a second—with a peak power output about 50 times that of the whole visible universe. By looking at the time of arrival of the signals—the detector in Livingston recorded the event 7 milliseconds before the detector in Hanford—scientists can say that the source was located in the Southern Hemisphere.
According to general relativity, a pair of black holes orbiting around each other lose energy through the emission of gravitational waves, causing them to gradually approach each other over billions of years, and then much more quickly in the final minutes. During the final fraction of a second, the two black holes collide into each other at nearly one-half the speed of light and form a single more massive black hole, converting a portion of the combined black holes’ mass to energy, according to Einstein’s formula E=mc2. This energy is emitted as a final strong burst of gravitational waves. It is these gravitational waves that LIGO has observed.
The existence of gravitational waves was first demonstrated in the 1970s and 80s by Joseph Taylor, Jr., and colleagues. Taylor and Russell Hulse discovered in 1974 a binary system composed of a pulsar in orbit around a neutron star. Taylor and Joel M. Weisberg in 1982 found that the orbit of the pulsar was slowly shrinking over time because of the release of energy in the form of gravitational waves. For discovering the pulsar and showing that it would make possible this particular gravitational wave measurement, Hulse and Taylor were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1993.
The new LIGO discovery is the first observation of gravitational waves themselves, made by measuring the tiny disturbances the waves make to space and time as they pass through the earth.
“Our observation of gravitational waves accomplishes an ambitious goal set out over 5 decades ago to directly detect this elusive phenomenon and better understand the universe, and, fittingly, fulfills Einstein’s legacy on the 100th anniversary of his general theory of relativity,” says Caltech’s David H. Reitze, executive director of the LIGO Laboratory.
The discovery was made possible by the enhanced capabilities of Advanced LIGO, a major upgrade that increases the sensitivity of the instruments compared to the first generation LIGO detectors, enabling a large increase in the volume of the universe probed—and the discovery of gravitational waves during its first observation run. The US National Science Foundation leads in financial support for Advanced LIGO. Funding organizations in Germany (Max Planck Society), the U.K. (Science and Technology Facilities Council, STFC) and Australia (Australian Research Council) also have made significant commitments to the project. Several of the key technologies that made Advanced LIGO so much more sensitive have been developed and tested by the German UK GEO collaboration. Significant computer resources have been contributed by the AEI Hannover Atlas Cluster, the LIGO Laboratory, Syracuse University, and the University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee. Several universities designed, built, and tested key components for Advanced LIGO: The Australian National University, the University of Adelaide, the University of Florida, Stanford University, Columbia University of the City of New York, and Louisiana State University.
“In 1992, when LIGO’s initial funding was approved, it represented the biggest investment the NSF had ever made,” says France Córdova, NSF director. “It was a big risk. But the National Science Foundation is the agency that takes these kinds of risks. We support fundamental science and engineering at a point in the road to discovery where that path is anything but clear. We fund trailblazers. It’s why the U.S. continues to be a global leader in advancing knowledge.”
LIGO research is carried out by the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC), a group of more than 1000 scientists from universities around the United States and in 14 other countries. More than 90 universities and research institutes in the LSC develop detector technology and analyze data; approximately 250 students are strong contributing members of the collaboration. The LSC detector network includes the LIGO interferometers and the GEO600 detector. The GEO team includes scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute, AEI), Leibniz Universität Hannover, along with partners at the University of Glasgow, Cardiff University, the University of Birmingham, other universities in the United Kingdom, and the University of the Balearic Islands in Spain.
“This detection is the beginning of a new era: The field of gravitational wave astronomy is now a reality,” says Gabriela González, LSC spokesperson and professor of physics and astronomy at Louisiana State University.
read more at https://www.ligo.caltech.edu/news/ligo20160211
grokit
well-worn member

FRBs: Mystery repeating radio signals discovered emanating from unknown cosmic source

Fast Radio Bursts: Repeating FRBs discovered for first time (istock)
Repeating radio signals coming from a mystery source far beyond the Milky Way have been discovered by scientists. While one-off fast radio bursts (FRBs) have been detected in the past, this is the first time multiple signals have been detected coming from the same place in space.
FRBs are radio signals from deep space that last for just a few milliseconds. Since their discovery over a decade ago, scientists have been searching for more to try to understand their origin. At present, there are several theories as to what they could be, with most involving some cataclysmic event like a supernova or a neutron star collapsing into a black hole.
All of the events seen so far appear to have been one-offs, with subsequent observations failing to find follow-up bursts coming from the same position as the original. However, an international team of researchers has now discovered an additional 10 bursts coming from the same direction as FRB 121102, using the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico.
Publishing their findings in the journal Nature, the researchers report the subsequent bursts have the same dispersion measures and sky positions as the original FRB. This, they say, means the source must have survived whatever event caused the FRB to be produced in the first place – i.e. it cannot have been a cataclysmic one-off event. They also found the bursts differed in brightness from other FRBs, suggesting a different source.
Paul Scholz, from McGill University, was the first person to notice the repeating burst: "I knew immediately that the discovery would be extremely important in the study of FRBs."
In the study, researchers suggest the repeating bursts are coming from a very young neutron star. "Although there may be multiple physical origins for the population of fast radio bursts, these repeat bursts with high dispersion measure and variable spectra specifically seen from the direction of FRB 121102 support an origin in a young, highly magnetised, extragalactic neutron star," they wrote.
The team now hopes to identify the galaxy from which the repeating FRBs came from. "Once we have precisely localised the repeater's position on the sky, we will be able to compare observations from optical and X-ray telescopes and see if there is a galaxy there," said Jason Hessels, corresponding author on the study. "Finding the host galaxy of this source is critical to understanding its properties."
Their study follows another paper on FRBs published earlier this month. Also appearing in Nature, researchers announced the discovery of the location and host galaxy of another FRB first discovered in April last year.
They found FRB 150418 had emanated from an elliptical galaxy six billion light years away. Unlike FRB 121102, this burst did not repeat, leading scientists to say it was probably produced by merger event, where two stars that are orbiting each other come together. In the paper, the team also said they believe there are at least two different sources of FRBs.
http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/frbs-myste...vered-emanating-unknown-cosmic-source-1547133
https://www.reddit.com/r/science/comments/48njxg/repeating_radio_signals_coming_from_a_mystery/
t-dub
Vapor Sloth
Yeah SpaceX did it . . .  Here are links to the hosted and technical shows for the launch. The hosted show, first link, has a special moment when the booster lands on the barge. All the SpaceX employees were cheering so loud you couldn't hear what the commentators were saying! And then the chants of USA, USA, USA . . . amazing . . .
Here are links to the hosted and technical shows for the launch. The hosted show, first link, has a special moment when the booster lands on the barge. All the SpaceX employees were cheering so loud you couldn't hear what the commentators were saying! And then the chants of USA, USA, USA . . . amazing . . . 
---
 Here are links to the hosted and technical shows for the launch. The hosted show, first link, has a special moment when the booster lands on the barge. All the SpaceX employees were cheering so loud you couldn't hear what the commentators were saying! And then the chants of USA, USA, USA . . . amazing . . .
Here are links to the hosted and technical shows for the launch. The hosted show, first link, has a special moment when the booster lands on the barge. All the SpaceX employees were cheering so loud you couldn't hear what the commentators were saying! And then the chants of USA, USA, USA . . . amazing . . . 
t-dub
Vapor Sloth
Here is a supercut of SpaceX's development of a reusable first stage. Some of you will recognize some of the videos of the Grasshopper which I posted here a while back. I thought it was cool that we had another Grasshopper on FC for a while . . . 
It took less than 4 years for SpaceX to do this.

It took less than 4 years for SpaceX to do this.
t-dub
Vapor Sloth
A NOAA mapping robot working two miles beneath the ocean surface has taken video of a species of jellyfish previously unknown and its, in my opinion, stunningly beautiful.
NOAA said:The newly discovered jellyfish has two sets of tentacles, short and long. When the the long tentacles are even and extended outward, and the bell is motionless, this could mean it’s readying to ambush its prey, scientists speculate. Inside the bell, red radial canals connect what scientists say looks like the bright yellow gonads.
GetLeft
Well-Known Member
Here is a supercut of SpaceX's development of a reusable first stage.
Thanks!!
A NOAA mapping robot working two miles beneath the ocean surface has taken video of a species of jellyfish previously unknown and its, in my opinion, stunningly beautiful.
x 2
t-dub
Vapor Sloth
Well SpaceX did it again and landed the first stage of the Falcon 9 on the drone ship . . . 
This landing was hot and fast!
JCSAT 14 needed to go to a much higher orbit, requiring extra speed and fuel from the first stage engines. That meant the rocket would descend back through the atmosphere faster, with less fuel to slow down for the final approach to the vessel.
In other words, the rocket had to slam on the brakes to nail the landing.
Instead of the single-engine landing burn directly above the drone ship, the rocket fired up three engines to slow itself for touchdown, tripling the deceleration in the final moments of the flight. And the recovery maneuver omitted a “boostback” burn to direct the rocket toward the vessel.
Elon Musk, the company’s founder and CEO, said on Twitter: “May need to increase size of rocket storage hangar.”
The landing begins at 38:15 on the hosted webcast below.
Again the cheers from the SpaceX employees drowned out the commentators.
And then the chant of USA! . . . USA!! . . . USA!!!

And the technical webcast of the launch . . .
I did find this cool 360 video of the previous landing. You can use the arrows in the upper left to change your perspective. Just bump the up arrow a little bit to get a fantastic view of the rocket coming down then bump the down arrow to get a great view of the landing. Its like you are standing on the drone ship.

This landing was hot and fast!
JCSAT 14 needed to go to a much higher orbit, requiring extra speed and fuel from the first stage engines. That meant the rocket would descend back through the atmosphere faster, with less fuel to slow down for the final approach to the vessel.
In other words, the rocket had to slam on the brakes to nail the landing.
Instead of the single-engine landing burn directly above the drone ship, the rocket fired up three engines to slow itself for touchdown, tripling the deceleration in the final moments of the flight. And the recovery maneuver omitted a “boostback” burn to direct the rocket toward the vessel.
Elon Musk, the company’s founder and CEO, said on Twitter: “May need to increase size of rocket storage hangar.”
The landing begins at 38:15 on the hosted webcast below.
Again the cheers from the SpaceX employees drowned out the commentators.
And then the chant of USA! . . . USA!! . . . USA!!!


And the technical webcast of the launch . . .
Last edited:
momofthegoons
vapor accessory addict
momofthegoons
vapor accessory addict
t-dub
Vapor Sloth
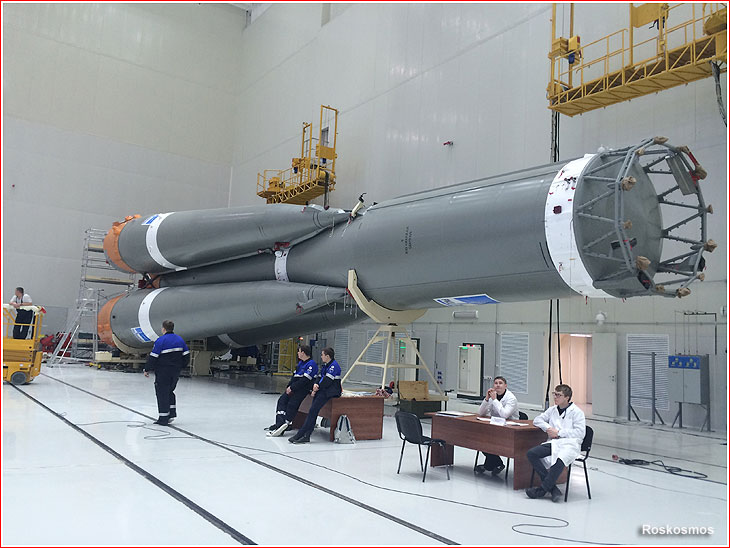
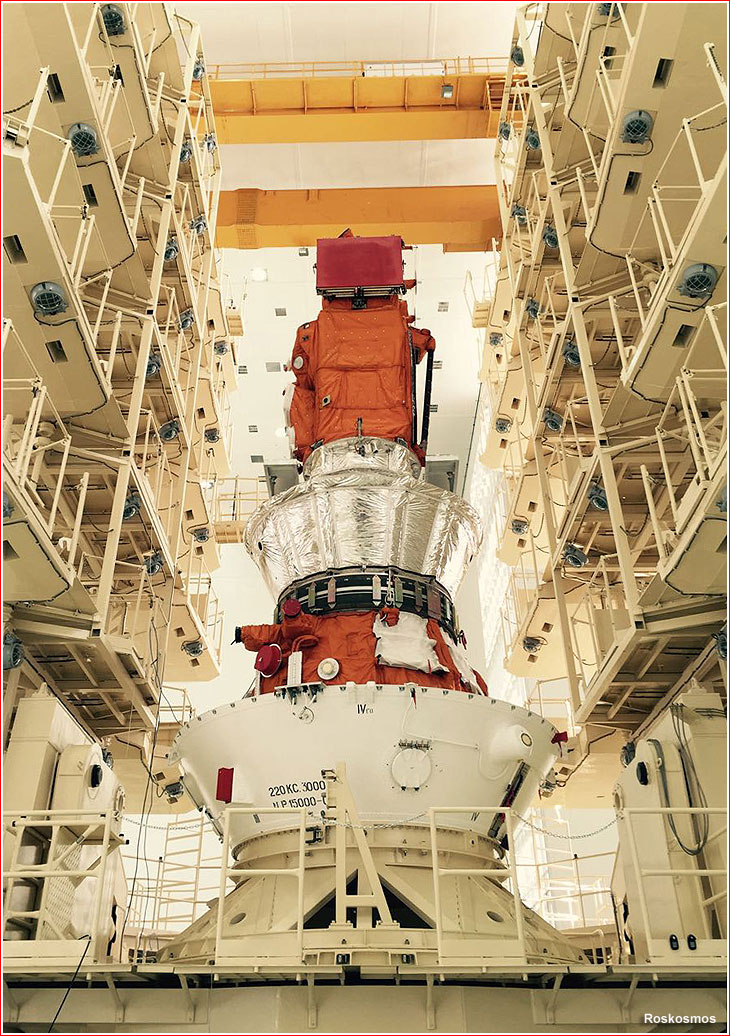
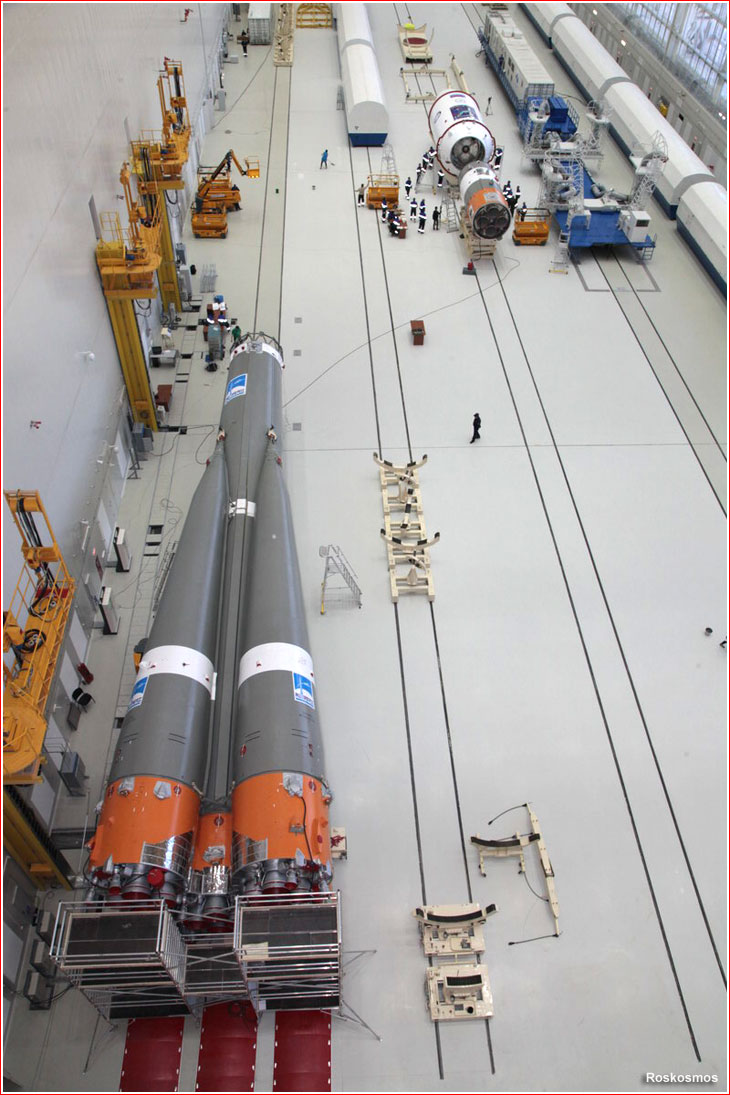
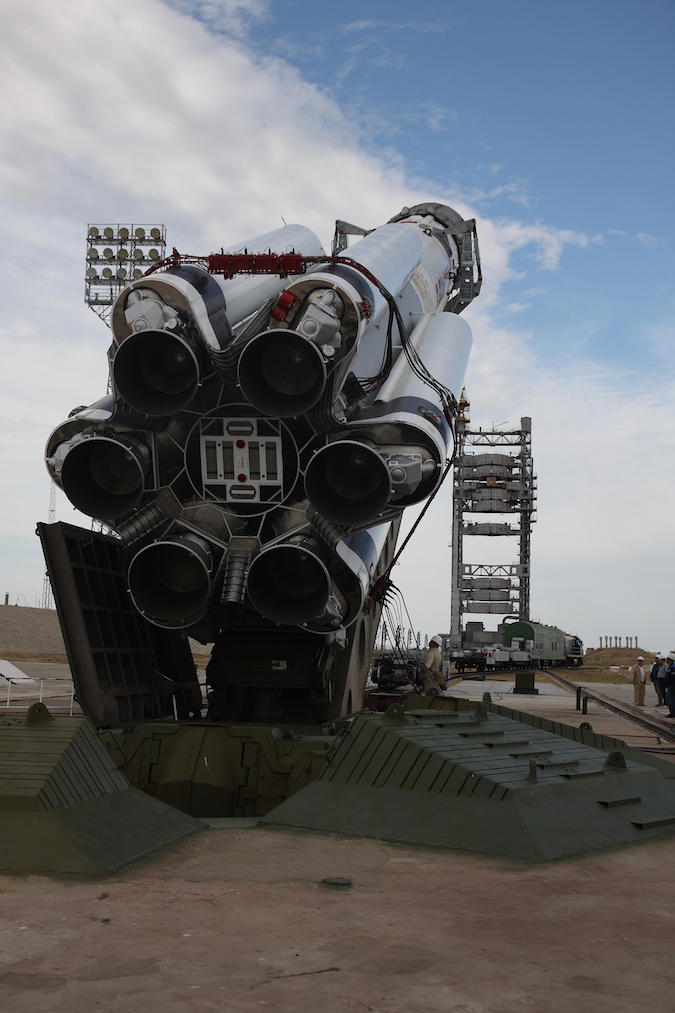
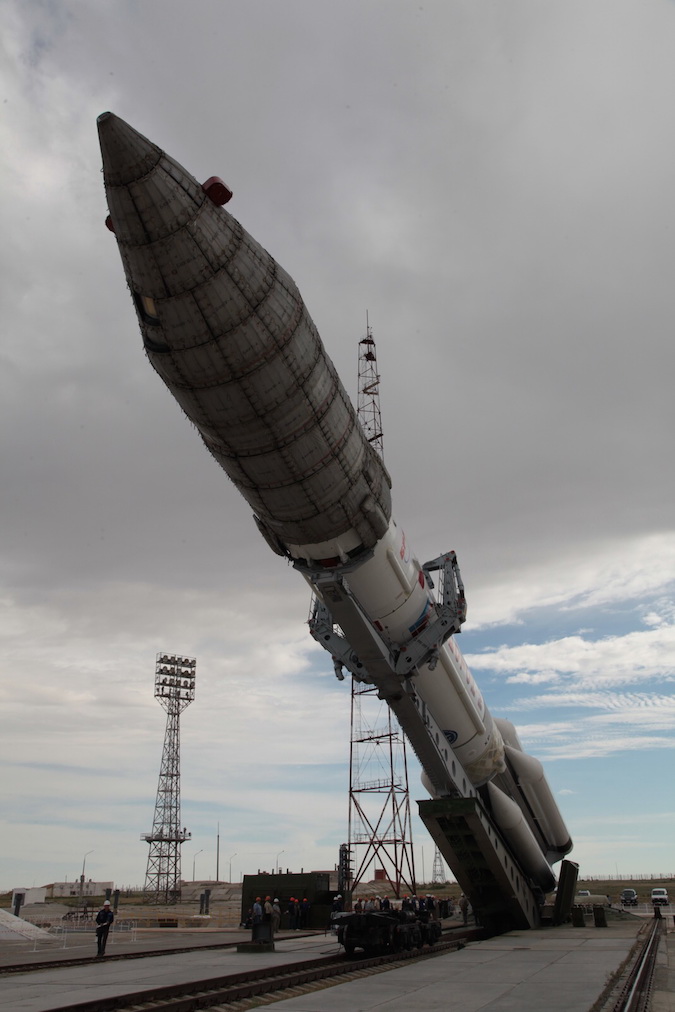
Ahhhh . . . what are those crazie Ruskies up to now eh?
I love commie steel . . .
Watch them hoist this Proton rocket into position for launch at Baikonur Cosmodrome, the busiest spaceport in the world. For an intimate view of Proton being readied for launch this video is the best I have ever seen.
This is the calm before the storm . . .
Set to go about midnight Wednesday . . . 

---

---

---

More here: ClickMe
I love commie steel . . .
Watch them hoist this Proton rocket into position for launch at Baikonur Cosmodrome, the busiest spaceport in the world. For an intimate view of Proton being readied for launch this video is the best I have ever seen.
This is the calm before the storm . . .


---

---

---

More here: ClickMe
Last edited:
t-dub
Vapor Sloth
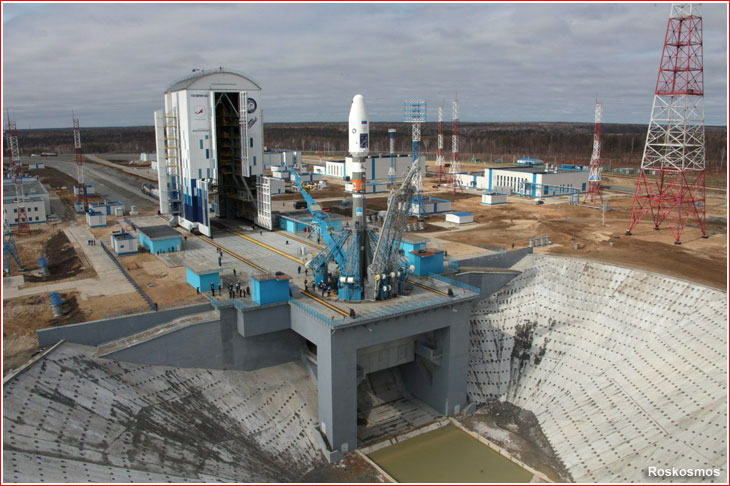
ok . . . it appears after a 24 hour delay to remedy an electrical problem, that the Russian Proton rocket, pictured ^^above^^, is being fueled with an approximate lift off time about 12:10 PDT or 3:10 a.m. EDT.
Messages from ILS . . .
"Russian officials have given approval to fuel the Proton rocket for liftoff at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 0710 GMT (3:10 a.m. EDT).
The Breeze M upper stage has already been filled with its hypergolic propellant mixture, and the three-stage Proton booster will be fueled with liquid hydrazine and nitrogen tetroxide in the next few hours."
Hmmmmm . . . these guys are serious. Live broadcast starts in one hour here:
http://spaceflightnow.com/2016/06/07/intelsat-31-mission-status-center/
Edit: the stream is live now . . .
T-minus 15 minutes. The final launch pad workers are evacuating to a safe distance away from the rocket.
Liftoff of the Proton rocket with Intelsat 31/DLA-2, a 7-ton spacecraft to broadcast high-definition television programming across Latin America for Intelsat and DirecTV.

Messages from ILS . . .
"Russian officials have given approval to fuel the Proton rocket for liftoff at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 0710 GMT (3:10 a.m. EDT).
The Breeze M upper stage has already been filled with its hypergolic propellant mixture, and the three-stage Proton booster will be fueled with liquid hydrazine and nitrogen tetroxide in the next few hours."
Hmmmmm . . . these guys are serious. Live broadcast starts in one hour here:
http://spaceflightnow.com/2016/06/07/intelsat-31-mission-status-center/
Edit: the stream is live now . . .

T-minus 15 minutes. The final launch pad workers are evacuating to a safe distance away from the rocket.
Liftoff of the Proton rocket with Intelsat 31/DLA-2, a 7-ton spacecraft to broadcast high-definition television programming across Latin America for Intelsat and DirecTV.

Last edited:
momofthegoons
vapor accessory addict
"There is a fifth dimension beyond that which is known to man. It is a dimension as vast as space and as timeless as infinity. It is the middle ground between light and shadow, between science and superstition, and it lies between the pit of man's fears and the summit of his knowledge. This is the dimension of imagination. It is an area which we call "The Twilight Zone"."

A celestial spark, or butterfly, is a relatively short-lived phenomenon that occurs at the end of the life of mid-sized stars. As a star's nuclear fuel runs out, its outer layers are puffed out, leaving only the hot core of the star behind. As the gaseous envelope heats up, the atoms in it are excited, and it lights up like a fluorescent sign.
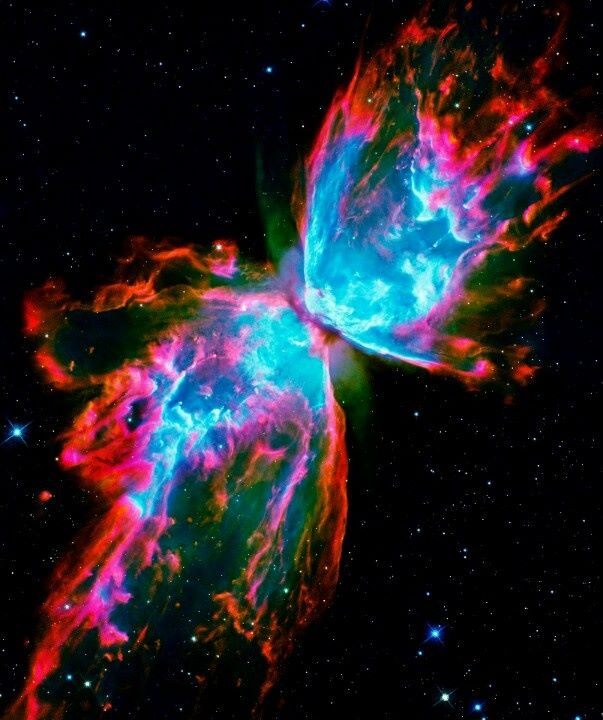

In the metaphysical world, these 'butterflies' are believed to be new spirits that have formed when a person passes.
My father passed away a month ago. During this time, I did a lot of meditation with certain crystals that I own; in particular a Lemurian that really 'called' to me. I noticed some colors forming in it 3 days before he died. As the days progressed, they became more formed and 'solid.' The morning he died, the crystal looked like this....
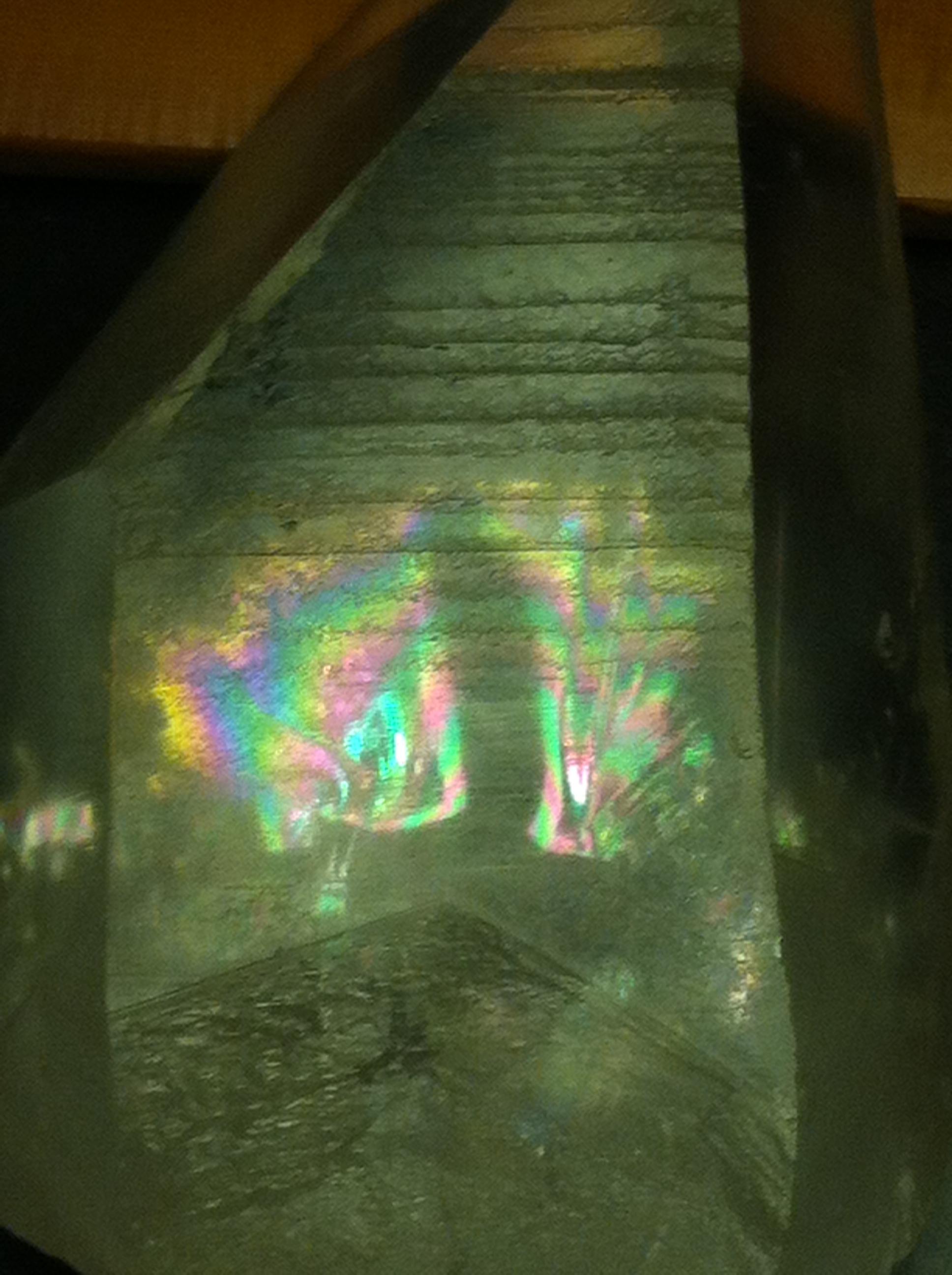

A celestial spark, or butterfly, is a relatively short-lived phenomenon that occurs at the end of the life of mid-sized stars. As a star's nuclear fuel runs out, its outer layers are puffed out, leaving only the hot core of the star behind. As the gaseous envelope heats up, the atoms in it are excited, and it lights up like a fluorescent sign.

In the metaphysical world, these 'butterflies' are believed to be new spirits that have formed when a person passes.
My father passed away a month ago. During this time, I did a lot of meditation with certain crystals that I own; in particular a Lemurian that really 'called' to me. I noticed some colors forming in it 3 days before he died. As the days progressed, they became more formed and 'solid.' The morning he died, the crystal looked like this....

SSVUN~YAH
You Must Unlearn, What You Have Learned...
That gave me goose bumps Motg! Though not near as emotionally charged as your story, I have a signed Hank Aaron and Willie Mays NL Hr Leaders plaque and the night Barry Bonds past Willie Mays, who is also his godfather IIRC, Mays picture mysteriously fell out of the plaque. I noticed the four bolts or pins fastening the plaque weren't touched when I placed the picture back. It has never moved a cm out of place since and never moved a cm before, and nobody was over that evening to take it out. Really strange but true coincidence."There is a fifth dimension beyond that which is known to man. It is a dimension as vast as space and as timeless as infinity. It is the middle ground between light and shadow, between science and superstition, and it lies between the pit of man's fears and the summit of his knowledge. This is the dimension of imagination. It is an area which we call "The Twilight Zone"."
A celestial spark, or butterfly, is a relatively short-lived phenomenon that occurs at the end of the life of mid-sized stars. As a star's nuclear fuel runs out, its outer layers are puffed out, leaving only the hot core of the star behind. As the gaseous envelope heats up, the atoms in it are excited, and it lights up like a fluorescent sign.

In the metaphysical world, these 'butterflies' are believed to be new spirits that have formed when a person passes.
My father passed away a month ago. During this time, I did a lot of meditation with certain crystals that I own; in particular a Lemurian that really 'called' to me. I noticed some colors forming in it 3 days before he died. As the days progressed, they became more formed and 'solid.' The morning he died, the crystal looked like this....

BD9
Well-Known Member
I've lurked this thread several times while not logged on and have felt that I'm not intelligent enough to share anything. After reading @momofthegoons and @SSVUN~YAH's posts I wanted to share something.
I'm agnostic, leaning more toward Atheist, but I have always been interested in spiritual things. Not ghosts and angels, though I have seen and heard some weird things, but more like Buddhist beliefs and principles. If that made sense.
My brother in law died in a boating accident 6 years ago. Two weeks before he died I started having violent nightmares. I mean extremely violent to the point started not sleeping. The night he died I was able to sleep but woke up at 3am with an odd feeling. We got the call he was missing at 4am. We got my wife on flight later that day to be with her family. They found his body the next day, which was also mother's day. But my nightmares had stopped that night I woke up at 3am.
My uncle died three years ago. A week before he died I started having disturbing dreams. Not really nightmares, but bad enough I would wake up violently. The night before he died, i had one the best nights of sleep and most pleasant dreams I can remember ever having.
My uncle died of heart failure. My brother in law died from drowning. I wonder if the difference in dreams is that my brother in law suffered and my uncle's suffering stopped.
I have had other 'precursor' (?) dreams as well. I don't know, I'm just odd I guess.
I'm agnostic, leaning more toward Atheist, but I have always been interested in spiritual things. Not ghosts and angels, though I have seen and heard some weird things, but more like Buddhist beliefs and principles. If that made sense.

My brother in law died in a boating accident 6 years ago. Two weeks before he died I started having violent nightmares. I mean extremely violent to the point started not sleeping. The night he died I was able to sleep but woke up at 3am with an odd feeling. We got the call he was missing at 4am. We got my wife on flight later that day to be with her family. They found his body the next day, which was also mother's day. But my nightmares had stopped that night I woke up at 3am.
My uncle died three years ago. A week before he died I started having disturbing dreams. Not really nightmares, but bad enough I would wake up violently. The night before he died, i had one the best nights of sleep and most pleasant dreams I can remember ever having.
My uncle died of heart failure. My brother in law died from drowning. I wonder if the difference in dreams is that my brother in law suffered and my uncle's suffering stopped.
I have had other 'precursor' (?) dreams as well. I don't know, I'm just odd I guess.
Run your finger along the ridges of the crystal. When meditating and thinking of him. He left you a message there before catching his flight."There is a fifth dimension beyond that which is known to man. It is a dimension as vast as space and as timeless as infinity. It is the middle ground between light and shadow, between science and superstition, and it lies between the pit of man's fears and the summit of his knowledge. This is the dimension of imagination. It is an area which we call "The Twilight Zone"."
A celestial spark, or butterfly, is a relatively short-lived phenomenon that occurs at the end of the life of mid-sized stars. As a star's nuclear fuel runs out, its outer layers are puffed out, leaving only the hot core of the star behind. As the gaseous envelope heats up, the atoms in it are excited, and it lights up like a fluorescent sign.

In the metaphysical world, these 'butterflies' are believed to be new spirits that have formed when a person passes.
My father passed away a month ago. During this time, I did a lot of meditation with certain crystals that I own; in particular a Lemurian that really 'called' to me. I noticed some colors forming in it 3 days before he died. As the days progressed, they became more formed and 'solid.' The morning he died, the crystal looked like this....

packed my bags last night pre flight
Zero hour nine a.m.
And I'm gonna be high, as a kite by then
I miss the earth so much, I miss my wife
It's lonely out in space
On such a timeless flight...



 Kind of a buzzkill but interesting nonetheless.
Kind of a buzzkill but interesting nonetheless.