-
SCAM WARNING! See how this scam works in Classifieds.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
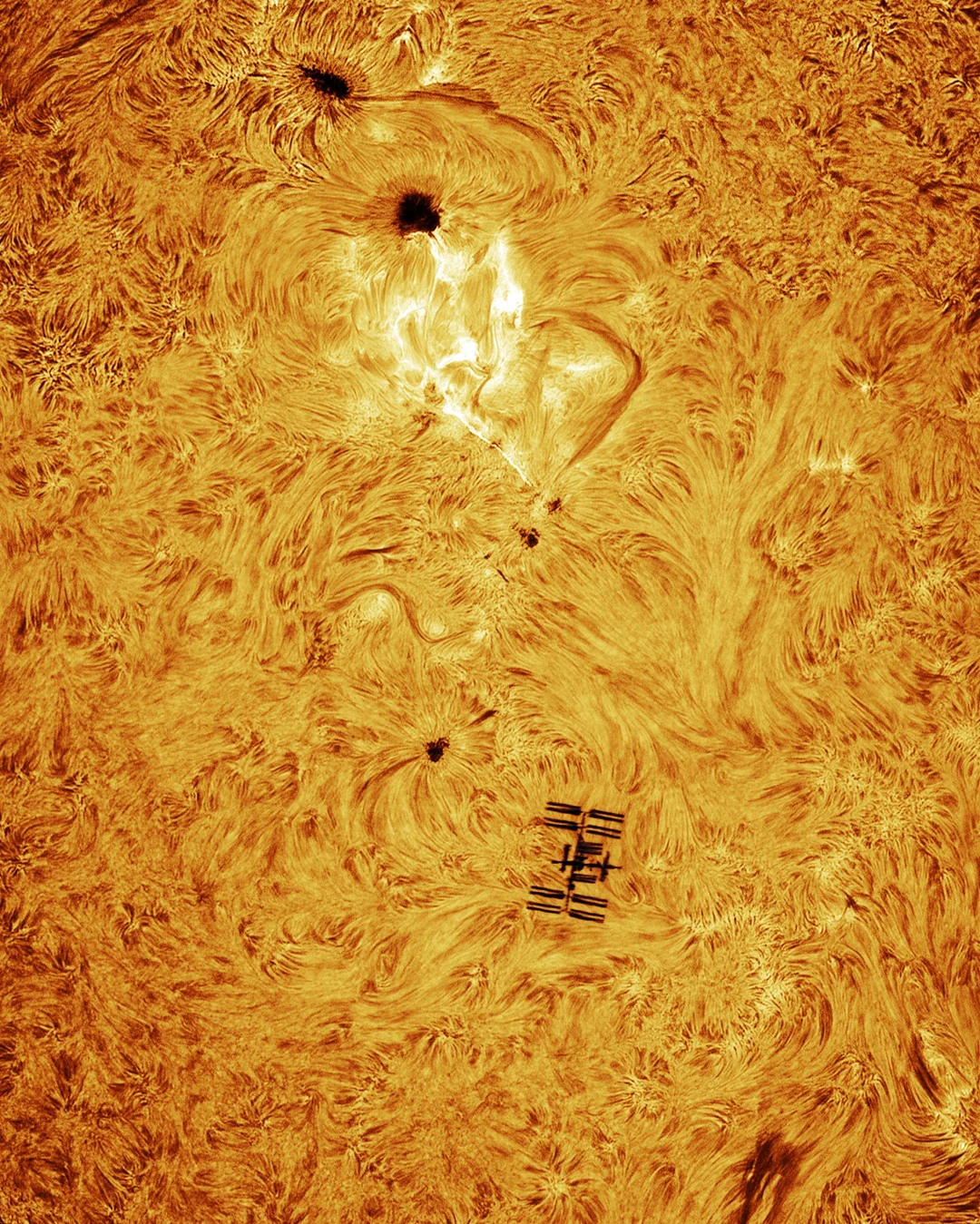
I just saw the moon
- Thread starter TheMadDabber
- Start date
bulllee
Agent Provocateur
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
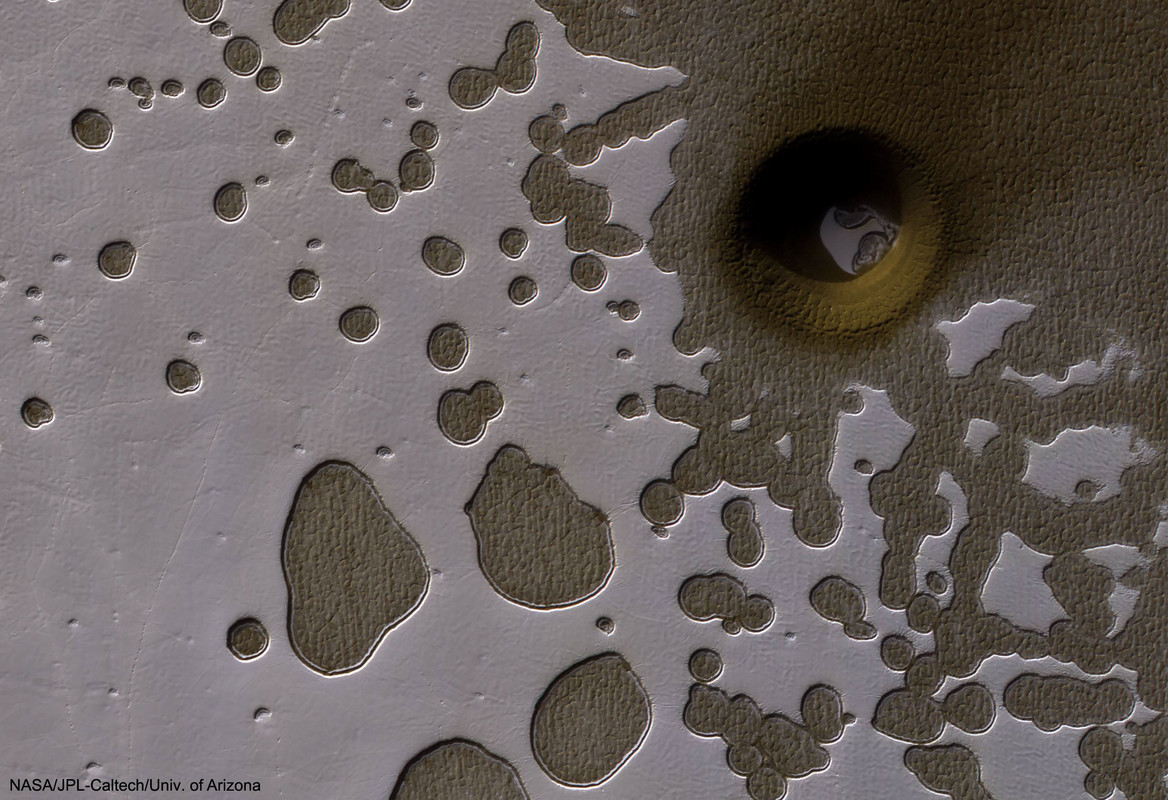
Numerous holes are pictured in this Swiss cheese-like landscape, with all-but-one of them showing a dusty, dark, Martian terrain beneath evaporating, light, carbon dioxide ice. The most unusual hole is on the upper right, spans about 100 meters, and seems to punch through to a lower level. Why this hole exists and why it is surrounded by a circular crater remains a topic of speculation, although a leading hypothesis is that it was created by a meteor impact. Holes such as this are of particular interest because they might be portals to lower levels that extend into expansive underground caves. If so, these naturally occurring tunnels are relatively protected from the harsh surface of Mars, making them relatively good candidates to contain Martian life. These pits are therefore also prime targets for possible future spacecraft, robots, and even human interplanetary explorers.

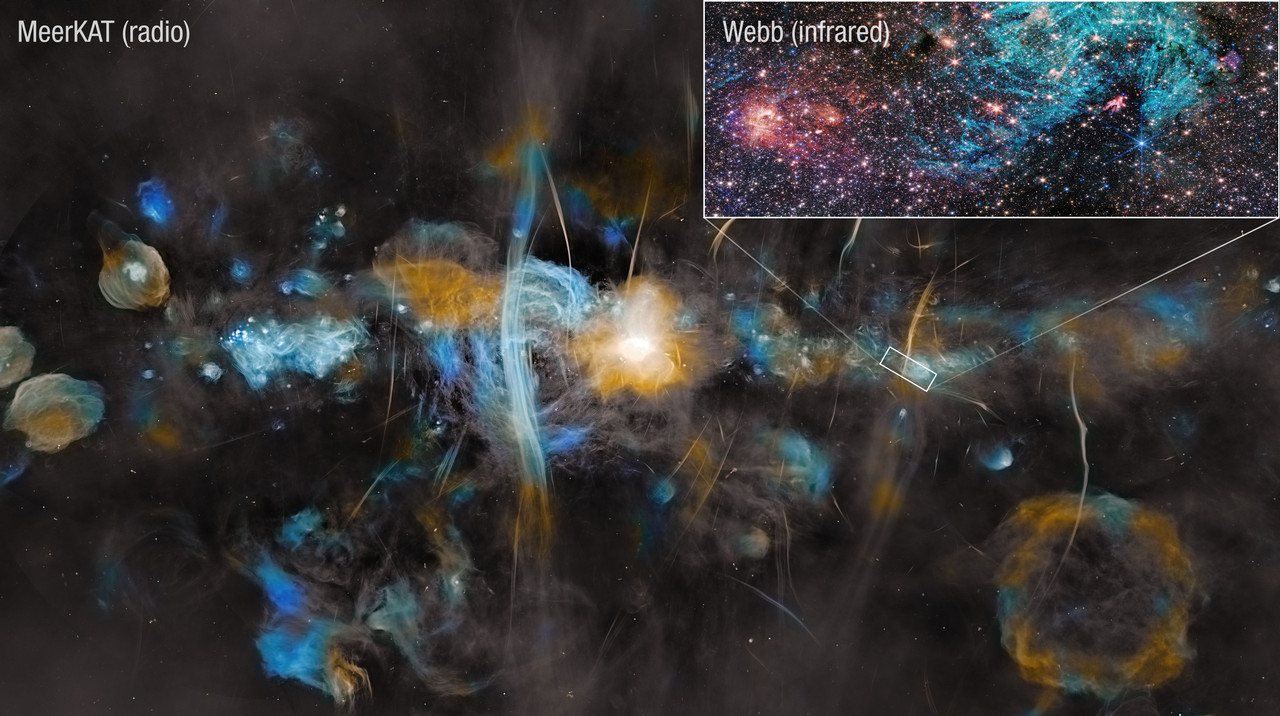
What's happening at the center of our galaxy? It's hard to tell with optical telescopes since visible light is blocked by intervening interstellar dust. In other bands of light, though, such as radio, the galactic center can be imaged and shows itself to be quite an interesting and active place. The featured picture shows an image of our Milky Way's center by the MeerKAT array of 64 radio dishes in South Africa. Spanning four times the angular size of the Moon (2 degrees), the image is impressively vast, deep, and detailed. Many known sources are shown in clear detail, including many with a prefix of Sgr, since the galactic center is in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. In our galaxy's center lies Sgr A, found here in the image center, which houses the Milky Way's central supermassive black hole. Other sources in the image are not as well understood, including the Arc, just to the left of Sgr A, and numerous filamentary threads. The inset image shows a small patch recently imaged in infrared light with the James Webb Space Telescope to investigate the effects of magnetic fields on star formation.

What happens when a star runs out of nuclear fuel? For stars like our Sun, the center condenses into a white dwarf while the outer atmosphere is expelled into space to appear as a planetary nebula. The expelled outer atmosphere of planetary nebula NGC 1514 appears to be a jumble of bubbles -- when seen in visible light. But the view from the James Webb Space Telescope in infrared, as featured here, confirms a different story: in this light the nebula shows a distinct hourglass shape, which is interpreted as a cylinder seen along a diagonal. If you look closely at the center of the nebula, you can also see a bright central star that is part of a binary system. More observations might better reveal how this nebula is evolving and how the central stars are working together to produce the interesting cylinder and bubbles observed.

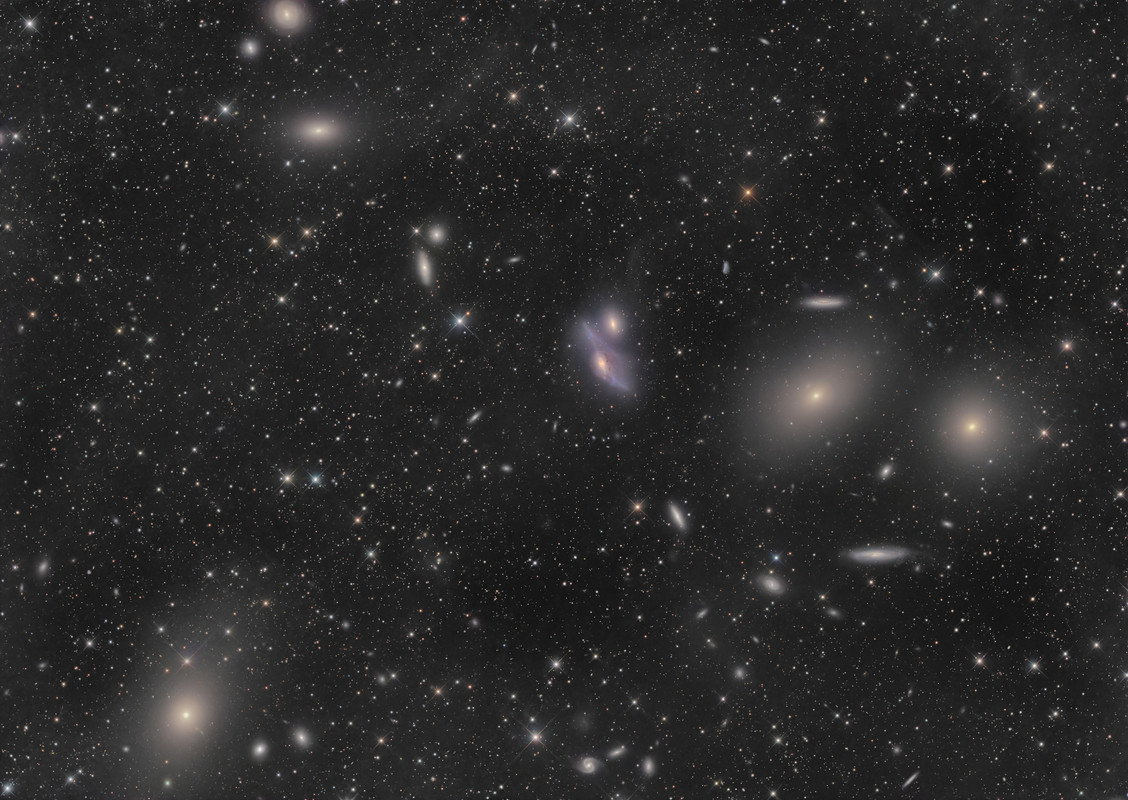
Galaxies of the Virgo Cluster are scattered across this nearly 4 degree wide telescopic field of view. About 50 million light-years distant, the Virgo Cluster is the closest large galaxy cluster to our own local galaxy group. Prominent here are Virgo's bright elliptical galaxies from the Messier catalog, M87 at bottom left, and M86 and M84 near center right. M86 and M84 are recognized as part of Markarian's Chain, the visually striking line-up of galaxies on the that runs through the upper portion of this frame. Near the middle of the chain lies an intriguing interacting pair of galaxies, NGC 4438 and NGC 4435, known to some as Markarian's Eyes. Still, giant elliptical galaxy M87 dominates the Virgo cluster. It's the home of a super massive black hole, the first black hole ever imaged by planet Earth's Event Horizon Telescope.

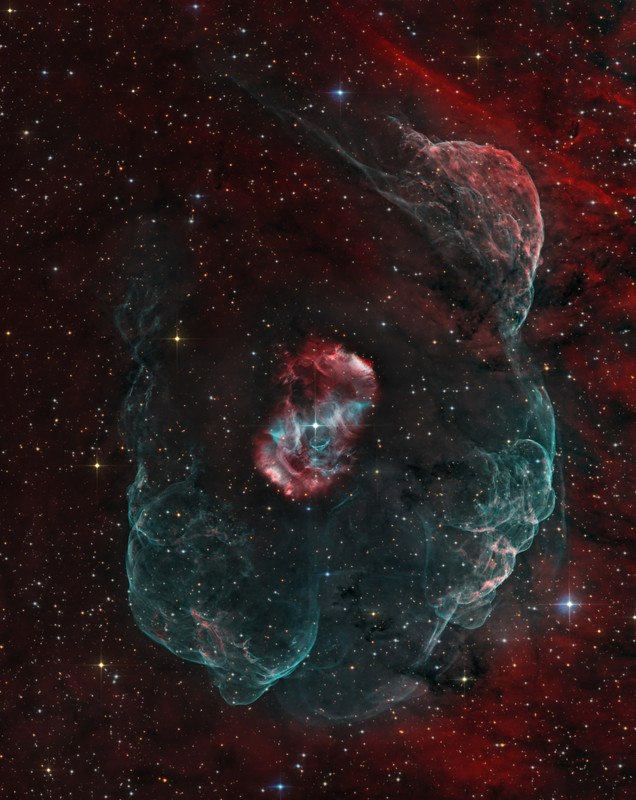
Beautiful emission nebula NGC 6164 was created by a rare, hot, luminous O-type star, some 40 times as massive as the Sun. Seen at the center of the cosmic cloud, the star is a mere 3 to 4 million years old. In another three to four million years the massive star will end its life in a supernova explosion. Spanning around 4 light-years, the nebula itself has a bipolar symmetry. That makes it similar in appearance to more common and familiar planetary nebulae - the gaseous shrouds surrounding dying sun-like stars. Also like many planetary nebulae, NGC 6164 has been found to have an extensive, faint halo, revealed in this deep image of the region. Expanding into the surrounding interstellar medium, the material in the halo is likely from an earlier active phase of the O star. This gorgeous telescopic view is a composite of extensive narrow-band image data, highlighting glowing atomic hydrogen gas in red and oxygen in greenish hues, with broad-band data for the surrounding starfield. Also known as the Dragon's Egg nebula, NGC 6164 is 4,200 light-years away in the right-angled southern constellation of Norma.

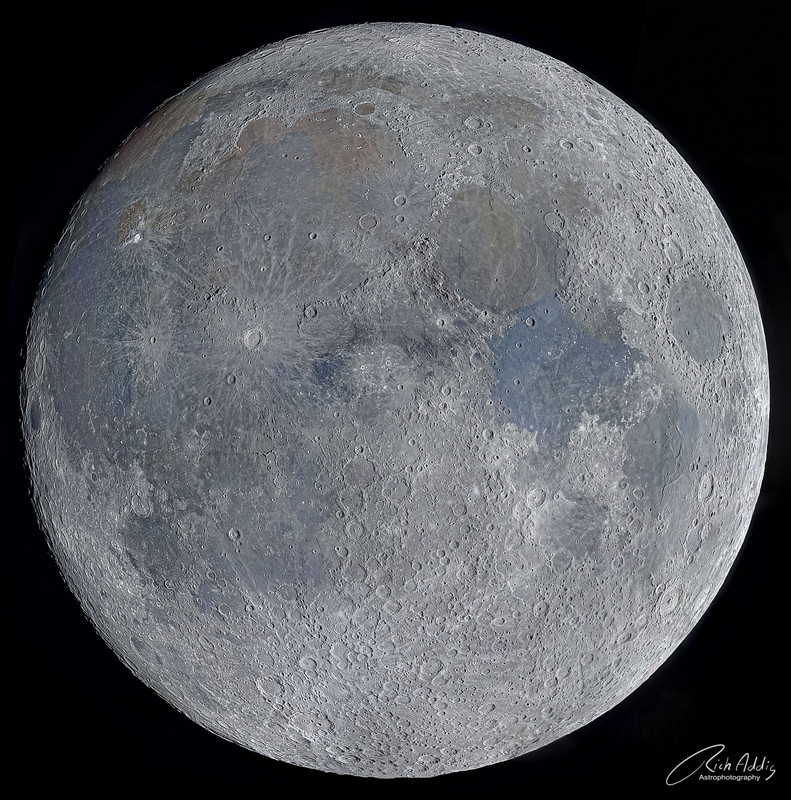
What's different about this Moon? It's the terminators. In the featured image, you can't directly see any terminator -- the line that divides the light of day from the dark of night. That's because the featured image is a digital composite of many near-terminator lunar strips over a full Moon. Terminator regions show the longest and most prominent shadows -- shadows which, by their contrast and length, allow a flat photograph to appear three-dimensional. The overlay images were taken over two weeks in early April. Many of the Moon's craters stand out because of the shadows they all cast to the right. The image shows in graphic detail that the darker regions known as maria are not just darker than the rest of the Moon -- they are also flatter.


What's happening at the center of our galaxy? It's hard to tell with optical telescopes since visible light is blocked by intervening interstellar dust. In other bands of light, though, such as radio, the galactic center can be imaged and shows itself to be quite an interesting and active place. The featured picture shows an image of our Milky Way's center by the MeerKAT array of 64 radio dishes in South Africa. Spanning four times the angular size of the Moon (2 degrees), the image is impressively vast, deep, and detailed. Many known sources are shown in clear detail, including many with a prefix of Sgr, since the galactic center is in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. In our galaxy's center lies Sgr A, found here in the image center, which houses the Milky Way's central supermassive black hole. Other sources in the image are not as well understood, including the Arc, just to the left of Sgr A, and numerous filamentary threads. The inset image shows a small patch recently imaged in infrared light with the James Webb Space Telescope to investigate the effects of magnetic fields on star formation.

What happens when a star runs out of nuclear fuel? For stars like our Sun, the center condenses into a white dwarf while the outer atmosphere is expelled into space to appear as a planetary nebula. The expelled outer atmosphere of planetary nebula NGC 1514 appears to be a jumble of bubbles -- when seen in visible light. But the view from the James Webb Space Telescope in infrared, as featured here, confirms a different story: in this light the nebula shows a distinct hourglass shape, which is interpreted as a cylinder seen along a diagonal. If you look closely at the center of the nebula, you can also see a bright central star that is part of a binary system. More observations might better reveal how this nebula is evolving and how the central stars are working together to produce the interesting cylinder and bubbles observed.

Galaxies of the Virgo Cluster are scattered across this nearly 4 degree wide telescopic field of view. About 50 million light-years distant, the Virgo Cluster is the closest large galaxy cluster to our own local galaxy group. Prominent here are Virgo's bright elliptical galaxies from the Messier catalog, M87 at bottom left, and M86 and M84 near center right. M86 and M84 are recognized as part of Markarian's Chain, the visually striking line-up of galaxies on the that runs through the upper portion of this frame. Near the middle of the chain lies an intriguing interacting pair of galaxies, NGC 4438 and NGC 4435, known to some as Markarian's Eyes. Still, giant elliptical galaxy M87 dominates the Virgo cluster. It's the home of a super massive black hole, the first black hole ever imaged by planet Earth's Event Horizon Telescope.

Beautiful emission nebula NGC 6164 was created by a rare, hot, luminous O-type star, some 40 times as massive as the Sun. Seen at the center of the cosmic cloud, the star is a mere 3 to 4 million years old. In another three to four million years the massive star will end its life in a supernova explosion. Spanning around 4 light-years, the nebula itself has a bipolar symmetry. That makes it similar in appearance to more common and familiar planetary nebulae - the gaseous shrouds surrounding dying sun-like stars. Also like many planetary nebulae, NGC 6164 has been found to have an extensive, faint halo, revealed in this deep image of the region. Expanding into the surrounding interstellar medium, the material in the halo is likely from an earlier active phase of the O star. This gorgeous telescopic view is a composite of extensive narrow-band image data, highlighting glowing atomic hydrogen gas in red and oxygen in greenish hues, with broad-band data for the surrounding starfield. Also known as the Dragon's Egg nebula, NGC 6164 is 4,200 light-years away in the right-angled southern constellation of Norma.

What's different about this Moon? It's the terminators. In the featured image, you can't directly see any terminator -- the line that divides the light of day from the dark of night. That's because the featured image is a digital composite of many near-terminator lunar strips over a full Moon. Terminator regions show the longest and most prominent shadows -- shadows which, by their contrast and length, allow a flat photograph to appear three-dimensional. The overlay images were taken over two weeks in early April. Many of the Moon's craters stand out because of the shadows they all cast to the right. The image shows in graphic detail that the darker regions known as maria are not just darker than the rest of the Moon -- they are also flatter.

CANtalk
Well-Known Member
NYC_Frank
"A man with no vices is a man with no virtues"
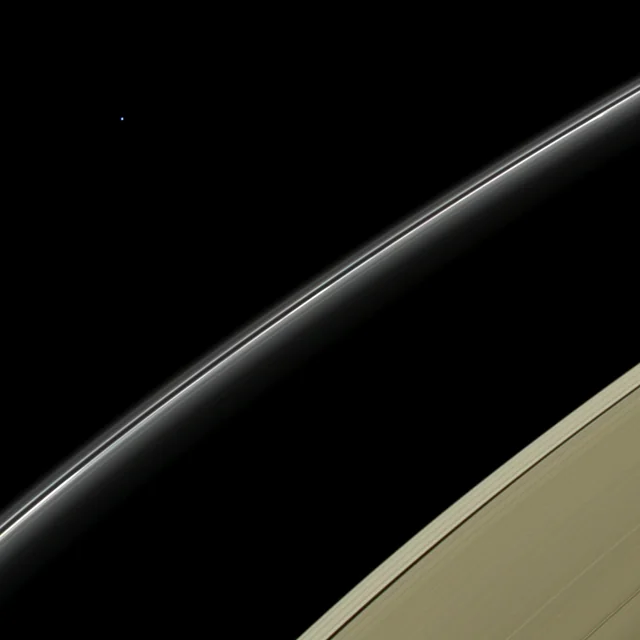
Latest prediction: reentry to occur on May 10th at 5:54 am UTC +/- 4 hours

 www.forbes.com
www.forbes.com


How To Track The Dead Soviet Lander Falling Back To Earth Soon
Kosmos 482, aka Cosmos 482 or the Venera 8 landing module, will re-enter our atmosphere in early May after spending over half a century stuck in Earth’s orbit.
 www.forbes.com
www.forbes.com

CANtalk
Well-Known Member
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
The objects in this image from JWST span an incredible range of distances, from stars within our own Milky Way, marked by diffraction spikes, to galaxies billions of light-years away.
Link to 67MB version https://cdn.esawebb.org/archives/images/large/potm2504a.jpg

Central to this image from JWST is galaxy cluster Abel S1063. It is a strong gravitational lens: the galaxy cluster is so massive that the light of distant galaxies aligned behind it is bent around it, creating the warped arcs that we see here. This image showcases an incredible forest of lensing arcs around Abell S1063, which reveal distorted background galaxies at a range of cosmic distances, along with a multitude of faint galaxies and previously unseen features. This image is what’s known as a deep field — a long exposure of a single area of the sky, collecting as much light as possible to draw out the most faint and distant galaxies that don’t appear in ordinary images. With 9 separate snapshots of different near-infrared wavelengths of light, totalling around 120 hours of observing time and aided by the magnifying effect of gravitational lensing, this is Webb’s deepest gaze on a single target to date.

This cosmic skyscape features glowing gas and dark dust clouds alongside the young stars of NGC 3572. A beautiful emission nebula and star cluster, it sails far southern skies within the nautical constellation Carina. Stars from NGC 3572 are toward top center in the telescopic frame that would measure about 100 light-years across at the cluster's estimated distance of 9,000 light-years. The visible interstellar gas and dust, shown in colors of the Hubble palette, is part of the star cluster's natal molecular cloud, itself cataloged as Gum 37. Dense streamers of material within the nebula, eroded by stellar winds and radiation, clearly trail away from the energetic young stars. They are likely sites of ongoing star formation with shapes reminiscent of the Tadpoles of IC 410 -- better known to northern skygazers. In the coming tens to hundreds of millions of years, gas and stars in the cluster will be dispersed though, by gravitational tides and by violent supernova explosions that end the short lives of the massive cluster stars.
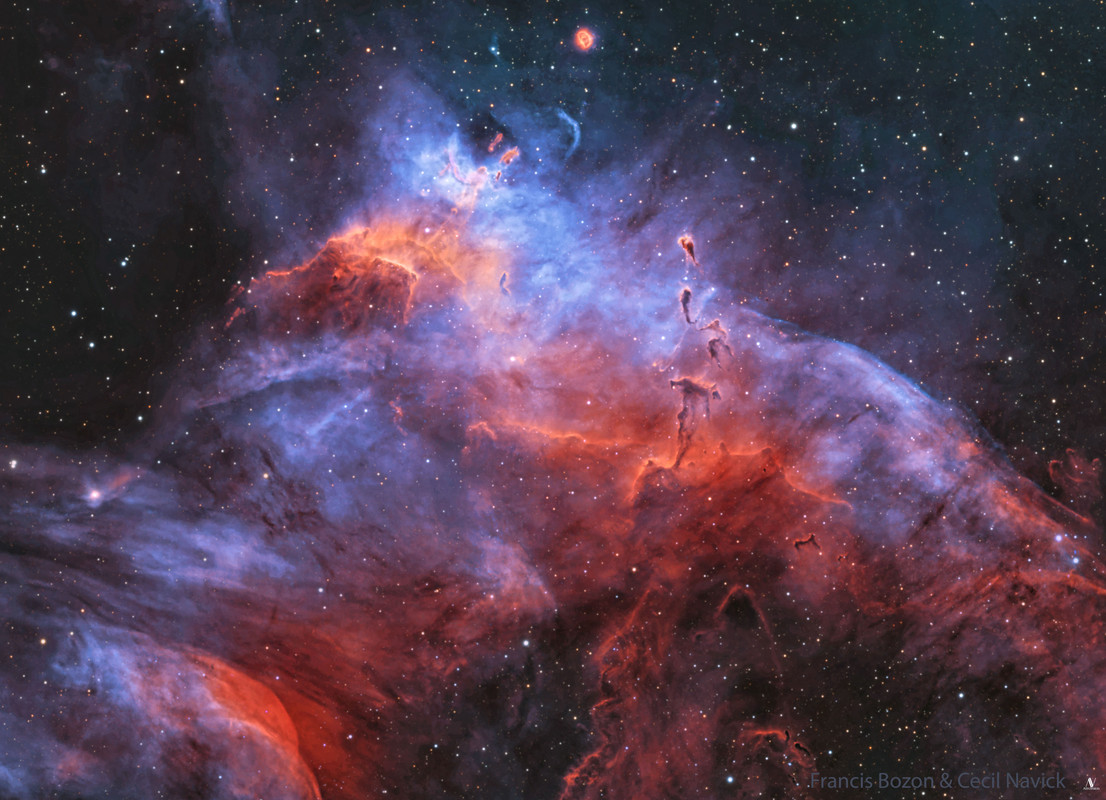

Behold one of the most photogenic regions of the night sky, captured impressively. Featured, the band of our Milky Way Galaxy runs diagonally along the bottom-left corner, while the colorful Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is visible just right of center and the large red circular Zeta Ophiuchi Nebula appears near the top. In general, red emanates from nebulas glowing in the light of excited hydrogen gas, while blue marks interstellar dust preferentially reflecting the light of bright young stars. Thick dust usually appears dark brown. Many iconic objects of the night sky appear, including (can you find them?) the bright star Antares, the globular star cluster M4, and the Blue Horsehead nebula. This wide field composite, taken over 17 hours, was captured from South Africa last June.
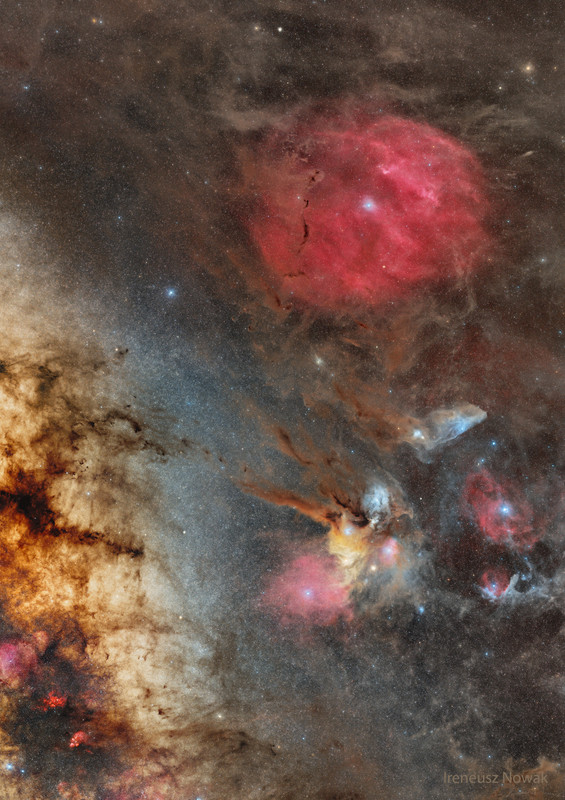

One of @NYC_Frank favorites, the Veil Nebula supernova remnant.
Wisps like this are all that remain visible of a Milky Way star that exploded about 7,000 years ago in a supernova, leaving the Veil Nebula. At the time, the expanding cloud was likely as bright as a crescent Moon, remaining visible for weeks to people living at the dawn of recorded history. Today, the resulting supernova remnant, also known as the Cygnus Loop, has faded and is now visible only through a small telescope directed toward the constellation of the Swan (Cygnus). The remaining Veil Nebula is physically huge, however, and even though it lies about 1,400 light-years distant, it covers over five times the size of the full Moon. The featured picture was taken in Kuwait in mid-2024 and features light emitted by hydrogen in red and oxygen in blue. In deep images of the complete Veil Nebula like this, even studious readers might not be able to identify the iconic filaments.

Some ELT images...it's coming along nicely.



Link to 67MB version https://cdn.esawebb.org/archives/images/large/potm2504a.jpg

Central to this image from JWST is galaxy cluster Abel S1063. It is a strong gravitational lens: the galaxy cluster is so massive that the light of distant galaxies aligned behind it is bent around it, creating the warped arcs that we see here. This image showcases an incredible forest of lensing arcs around Abell S1063, which reveal distorted background galaxies at a range of cosmic distances, along with a multitude of faint galaxies and previously unseen features. This image is what’s known as a deep field — a long exposure of a single area of the sky, collecting as much light as possible to draw out the most faint and distant galaxies that don’t appear in ordinary images. With 9 separate snapshots of different near-infrared wavelengths of light, totalling around 120 hours of observing time and aided by the magnifying effect of gravitational lensing, this is Webb’s deepest gaze on a single target to date.

This cosmic skyscape features glowing gas and dark dust clouds alongside the young stars of NGC 3572. A beautiful emission nebula and star cluster, it sails far southern skies within the nautical constellation Carina. Stars from NGC 3572 are toward top center in the telescopic frame that would measure about 100 light-years across at the cluster's estimated distance of 9,000 light-years. The visible interstellar gas and dust, shown in colors of the Hubble palette, is part of the star cluster's natal molecular cloud, itself cataloged as Gum 37. Dense streamers of material within the nebula, eroded by stellar winds and radiation, clearly trail away from the energetic young stars. They are likely sites of ongoing star formation with shapes reminiscent of the Tadpoles of IC 410 -- better known to northern skygazers. In the coming tens to hundreds of millions of years, gas and stars in the cluster will be dispersed though, by gravitational tides and by violent supernova explosions that end the short lives of the massive cluster stars.

Behold one of the most photogenic regions of the night sky, captured impressively. Featured, the band of our Milky Way Galaxy runs diagonally along the bottom-left corner, while the colorful Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is visible just right of center and the large red circular Zeta Ophiuchi Nebula appears near the top. In general, red emanates from nebulas glowing in the light of excited hydrogen gas, while blue marks interstellar dust preferentially reflecting the light of bright young stars. Thick dust usually appears dark brown. Many iconic objects of the night sky appear, including (can you find them?) the bright star Antares, the globular star cluster M4, and the Blue Horsehead nebula. This wide field composite, taken over 17 hours, was captured from South Africa last June.

One of @NYC_Frank favorites, the Veil Nebula supernova remnant.
Wisps like this are all that remain visible of a Milky Way star that exploded about 7,000 years ago in a supernova, leaving the Veil Nebula. At the time, the expanding cloud was likely as bright as a crescent Moon, remaining visible for weeks to people living at the dawn of recorded history. Today, the resulting supernova remnant, also known as the Cygnus Loop, has faded and is now visible only through a small telescope directed toward the constellation of the Swan (Cygnus). The remaining Veil Nebula is physically huge, however, and even though it lies about 1,400 light-years distant, it covers over five times the size of the full Moon. The featured picture was taken in Kuwait in mid-2024 and features light emitted by hydrogen in red and oxygen in blue. In deep images of the complete Veil Nebula like this, even studious readers might not be able to identify the iconic filaments.

Some ELT images...it's coming along nicely.



CANtalk
Well-Known Member
CANtalk
Well-Known Member
Scientists find universe's missing matter while watching fast radio bursts shine through 'cosmic fog'

Scientists find universe's missing matter while watching fast radio bursts shine through 'cosmic fog'
"Fast radio bursts shine through the fog of the intergalactic medium, and by precisely measuring how the light slows down, we can weigh that fog, even when it's too faint to see."
https://www.reddit.com/r/spaceporn/comments/1lfgtiw


CANtalk
Well-Known Member


Anyway,
First images of universe taken by largest digital camera ever shows colorful nebulas, stars and galaxies

First images of universe taken by largest digital camera ever shows colorful nebulas, stars and galaxies
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, located on a mountaintop in Chile, unveiled vibrant images Monday of colorful nebulas, stars and galaxies.
Explorer | Skyviewer
Explorer | Skyviewer


Bazinga
Well-Known Member
Many years ago while playing softball the Shuttle on top of an aircraft passed us directly overhead. Everyone stopped and watched the flight until it was out of sight. It was awesome to witness. I don't believe it was a NASA aircraft. Is that possible?The Space Shuttle flying past the Hollywood sign in 2012

coolbreeze
Well-Known Member
There's the Air Force's shuttle but it's a lot smaller; not sure how it's transported. Maybe it was the Enterprise?Many years ago while playing softball the Shuttle on top of an aircraft passed us directly overhead. Everyone stopped and watched the flight until it was out of sight. It was awesome to witness. I don't believe it was a NASA aircraft. Is that possible?
bulllee
Agent Provocateur
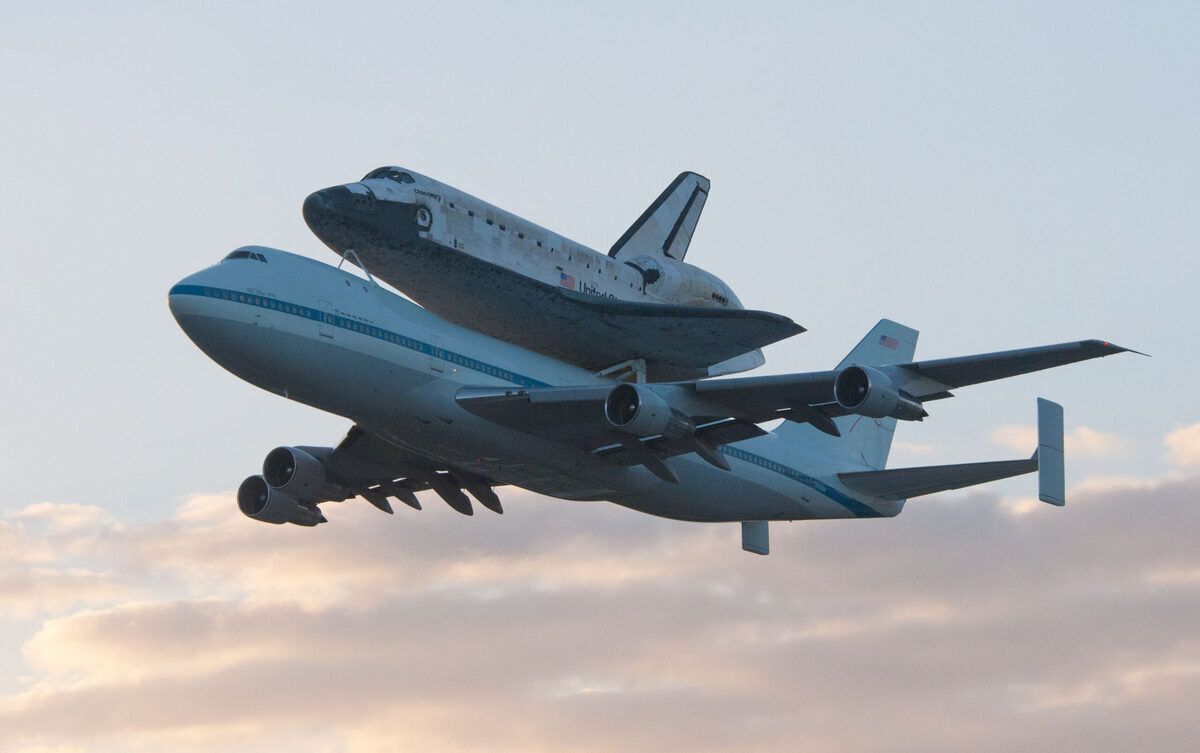

How The Boeing 747 Carried The Space Shuttle
Bazinga
Well-Known Member
Ahh. Thank you. That's what we saw.
How The Boeing 747 Carried The Space Shuttle
simpleflying.com