-
SCAM WARNING! See how this scam works in Classifieds.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
I just saw the moon
- Thread starter TheMadDabber
- Start date
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
And that was pretty much designed on drafting boards and slide rules...amazing. Hate the fact that he was a Nazi.
bulllee
Agent Provocateur
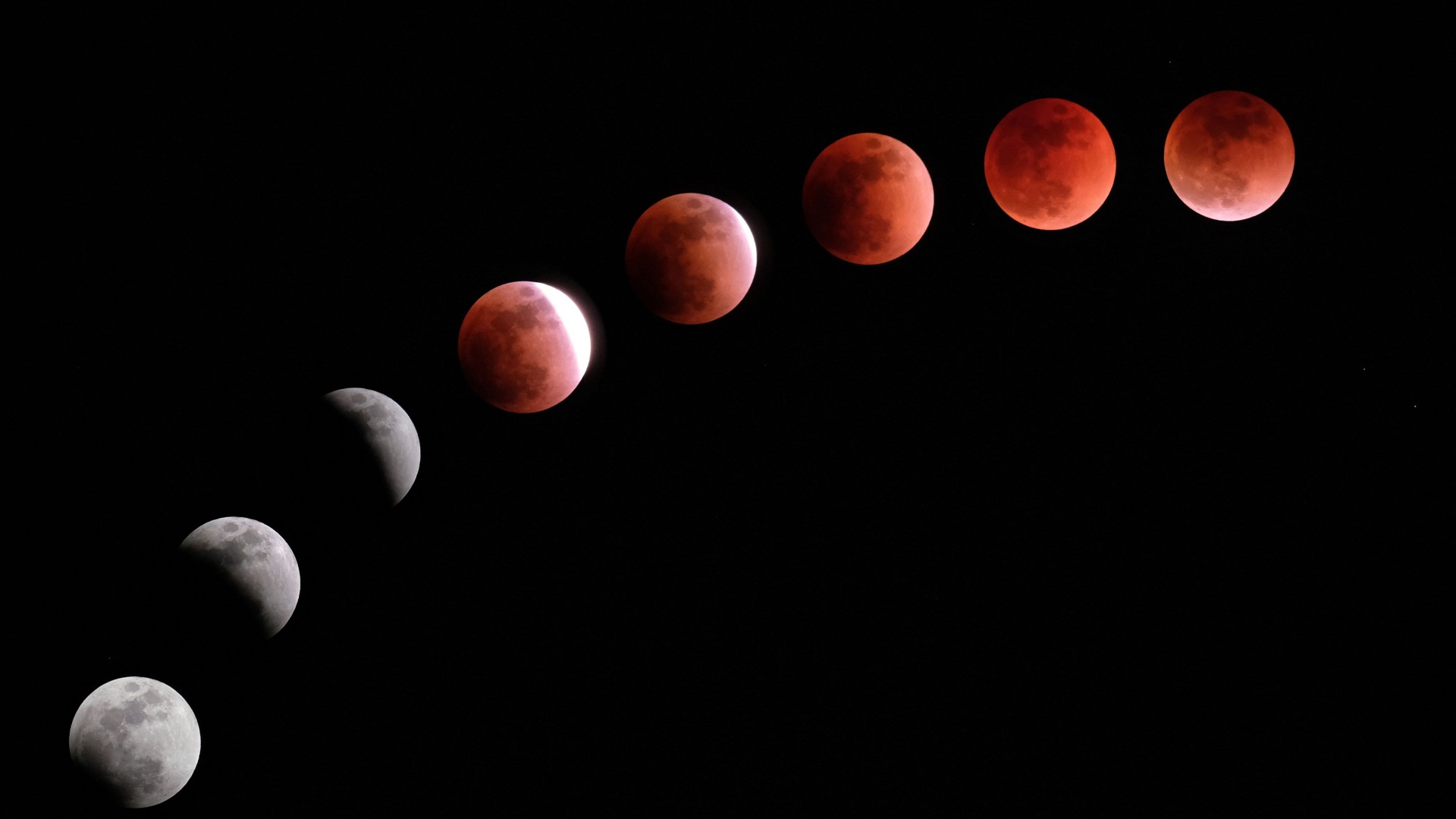

'Blood Worm Moon' US weather forecast: Best places to see tonight's total lunar eclipse
Most of the U.S. should be able to see the total lunar eclipse tonight, but clouds will be problematic for many.
Earth eclipsing the sun.

Picture taken from the moon by blue ghost lander.
Credit & copyright : firefly aerospace

Picture taken from the moon by blue ghost lander.
Credit & copyright : firefly aerospace
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
On March 14 the Moon was Full. In an appropriate celebration of Pi day, that put the Moon 3.14 radians (180 degrees) in ecliptic longitude from the Sun in planet Earth's sky. As a bonus for fans of Pi and the night sky, on that date the Moon also passed directly through Earth's umbral shadow in a total lunar eclipse. In clear skies, the colors of an eclipsed Moon can be vivid. Reflecting the deeply reddened sunlight scattered into Earth's shadow, the darkened lunar disk was recorded in this time series composite image from Cerro Tololo Observatory, Chile. The lunar triptych captures the start, middle, and end of the total eclipse phase that lasted about an hour. A faint bluish tint seen just along the brighter lunar limb at the shadow's edge is due to sunlight filtered through Earth's stratospheric ozone layer.

Why are there so many cyclones around the north pole of Jupiter? The topic is still being researched. NASA's robotic Juno mission orbiting Jupiter took data in 2018 that was used to construct this stunning view of the curious cyclones at Jupiter's north pole. Measuring the thermal emission from Jovian cloud tops, the infrared observations are not restricted to the hemisphere illuminated by sunlight. They reveal eight cyclonic features that surround a cyclone about 4,000 kilometers in diameter, just offset from the giant planet's geographic north pole. Similar data show a cyclone at the Jovian south pole with five circumpolar cyclones. The south pole cyclones are slightly larger than their northern cousins. Oddly, data from the once Saturn-orbiting Cassini mission has shown that Saturn's north and south poles each have only a single cyclonic storm system.

Point your telescope toward the high flying constellation Pegasus and you can find this cosmic expanse of Milky Way stars and distant galaxies. NGC 7814 is centered in the sharp field of view that would almost be covered by a full moon. NGC 7814 is sometimes Stars are usually born in clusters, and the brightest and most massive of these stars typically glow blue. Less-bright, non-blue stars like our Sun surely also exist in this M41 star cluster but are harder to see. A few bright orange-appearing red giant stars are visible. The red-light filaments are emitted by diffuse hydrogen gas, a color that was specifically filtered and enhanced in this image. In a hundred million years or so, the bright blue stars will have exploded in supernovas and disappeared, while the slightly different trajectories of the fainter stars will cause this picturesque open cluster to disperse. Similarly, billions of years ago, our own Sun was likely born into a star cluster like M41, but it has long since drifted apart from its sister stars. The featured image was captured over four hours with Chilescope T2 in Chile.

On the right, dressed in blue, is the Pleiades. Also known as the Seven Sisters and M45, the Pleiades is one of the brightest and most easily visible open clusters on the sky. The Pleiades contains over 3,000 stars, is about 400 light years away, and only 13 light years across. Surrounding the stars is a spectacular blue reflection nebula made of fine dust. A common legend is that one of the brighter stars faded since the cluster was named. On the left, shining in red, is the California Nebula. Named for its shape, the California Nebula is much dimmer and hence harder to see than the Pleiades. Also known as NGC 1499, this mass of red glowing hydrogen gas is about 1,500 light years away. Although about 25 full moons could fit between them, the featured wide angle, deep field image composite has captured them both. A careful inspection of the deep image will also reveal the star forming region IC 348 and the molecular cloud LBN 777 (the Baby Eagle Nebula).

The California Nebula. also known as NGC 1499, the classic emission nebula is around 100 light-years long. The most prominent glow is the red light characteristic of hydrogen atoms recombining with long lost electrons, stripped away (ionized) by energetic starlight. The star most likely providing the energetic starlight that ionizes much of the nebular gas is the bright, hot, bluish Xi Persei just to the right of the nebula. A regular target for astrophotographers, the California Nebula can be spotted with a wide-field telescope under a dark sky toward the constellation of Perseus, not far from the Pleiades.


Why are there so many cyclones around the north pole of Jupiter? The topic is still being researched. NASA's robotic Juno mission orbiting Jupiter took data in 2018 that was used to construct this stunning view of the curious cyclones at Jupiter's north pole. Measuring the thermal emission from Jovian cloud tops, the infrared observations are not restricted to the hemisphere illuminated by sunlight. They reveal eight cyclonic features that surround a cyclone about 4,000 kilometers in diameter, just offset from the giant planet's geographic north pole. Similar data show a cyclone at the Jovian south pole with five circumpolar cyclones. The south pole cyclones are slightly larger than their northern cousins. Oddly, data from the once Saturn-orbiting Cassini mission has shown that Saturn's north and south poles each have only a single cyclonic storm system.

Point your telescope toward the high flying constellation Pegasus and you can find this cosmic expanse of Milky Way stars and distant galaxies. NGC 7814 is centered in the sharp field of view that would almost be covered by a full moon. NGC 7814 is sometimes Stars are usually born in clusters, and the brightest and most massive of these stars typically glow blue. Less-bright, non-blue stars like our Sun surely also exist in this M41 star cluster but are harder to see. A few bright orange-appearing red giant stars are visible. The red-light filaments are emitted by diffuse hydrogen gas, a color that was specifically filtered and enhanced in this image. In a hundred million years or so, the bright blue stars will have exploded in supernovas and disappeared, while the slightly different trajectories of the fainter stars will cause this picturesque open cluster to disperse. Similarly, billions of years ago, our own Sun was likely born into a star cluster like M41, but it has long since drifted apart from its sister stars. The featured image was captured over four hours with Chilescope T2 in Chile.

On the right, dressed in blue, is the Pleiades. Also known as the Seven Sisters and M45, the Pleiades is one of the brightest and most easily visible open clusters on the sky. The Pleiades contains over 3,000 stars, is about 400 light years away, and only 13 light years across. Surrounding the stars is a spectacular blue reflection nebula made of fine dust. A common legend is that one of the brighter stars faded since the cluster was named. On the left, shining in red, is the California Nebula. Named for its shape, the California Nebula is much dimmer and hence harder to see than the Pleiades. Also known as NGC 1499, this mass of red glowing hydrogen gas is about 1,500 light years away. Although about 25 full moons could fit between them, the featured wide angle, deep field image composite has captured them both. A careful inspection of the deep image will also reveal the star forming region IC 348 and the molecular cloud LBN 777 (the Baby Eagle Nebula).

The California Nebula. also known as NGC 1499, the classic emission nebula is around 100 light-years long. The most prominent glow is the red light characteristic of hydrogen atoms recombining with long lost electrons, stripped away (ionized) by energetic starlight. The star most likely providing the energetic starlight that ionizes much of the nebular gas is the bright, hot, bluish Xi Persei just to the right of the nebula. A regular target for astrophotographers, the California Nebula can be spotted with a wide-field telescope under a dark sky toward the constellation of Perseus, not far from the Pleiades.


Photo gallery: Blood moon lunar eclipse from around the world
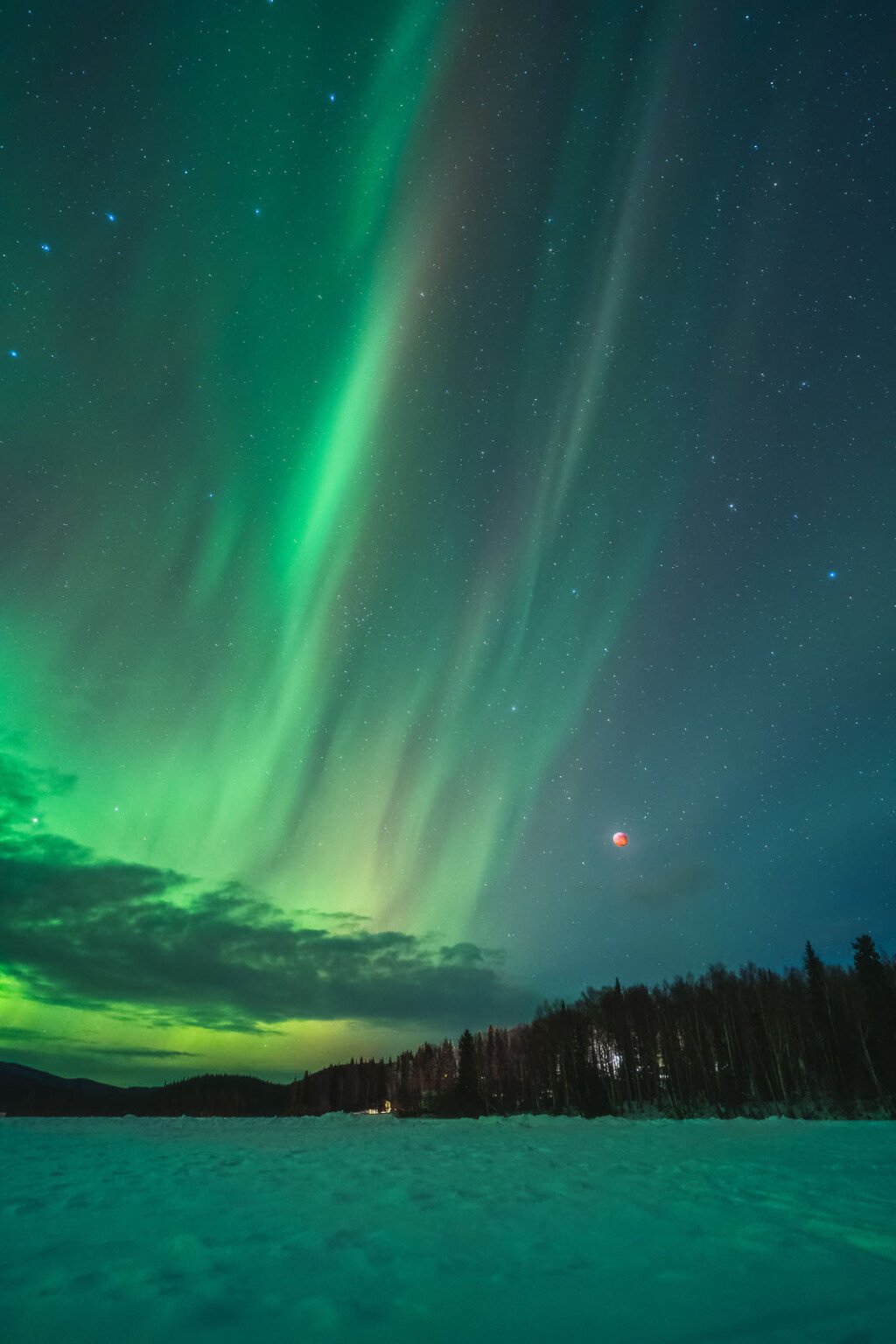
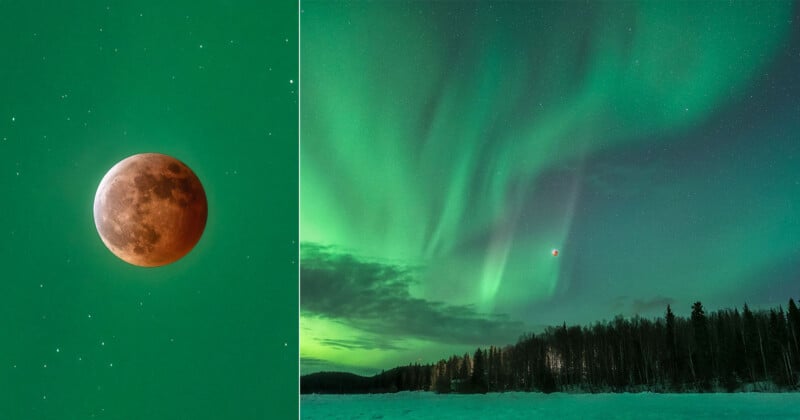
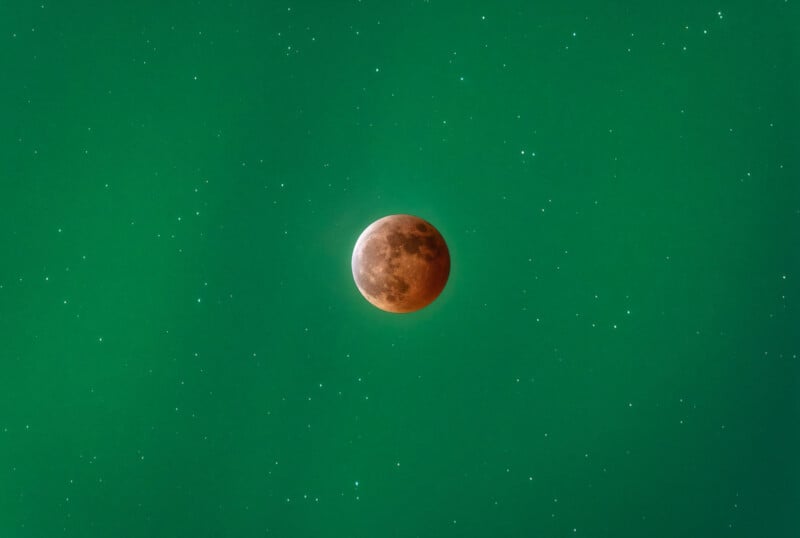
Dan Zafra went to Alaska and photographed the lunar eclipse with northern lights... this is absolutely stunning.



Timelapse :
Timelapse :
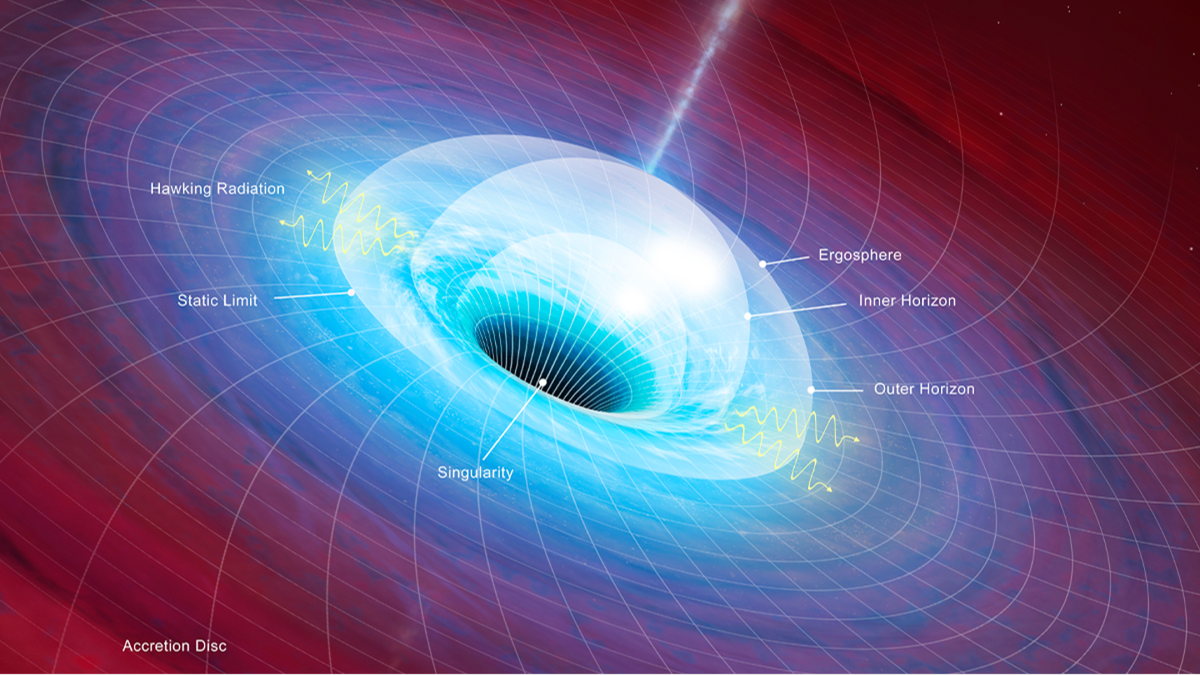
Scientist claims to have evidence 'our entire universe is trapped inside a black hole'
A Kansas University expert has outlined why he believes images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope provide evidence the universe is in a black hole.
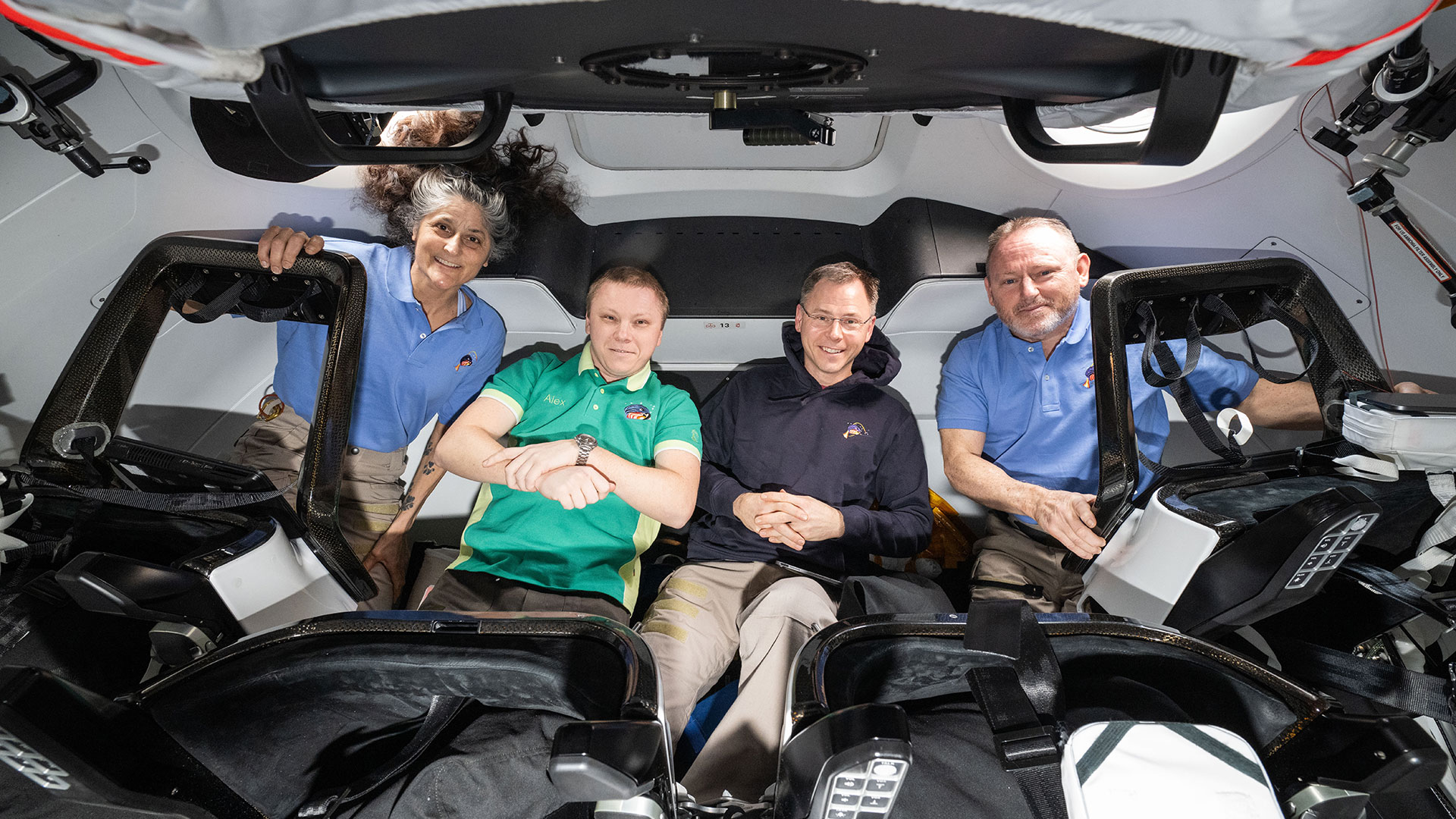

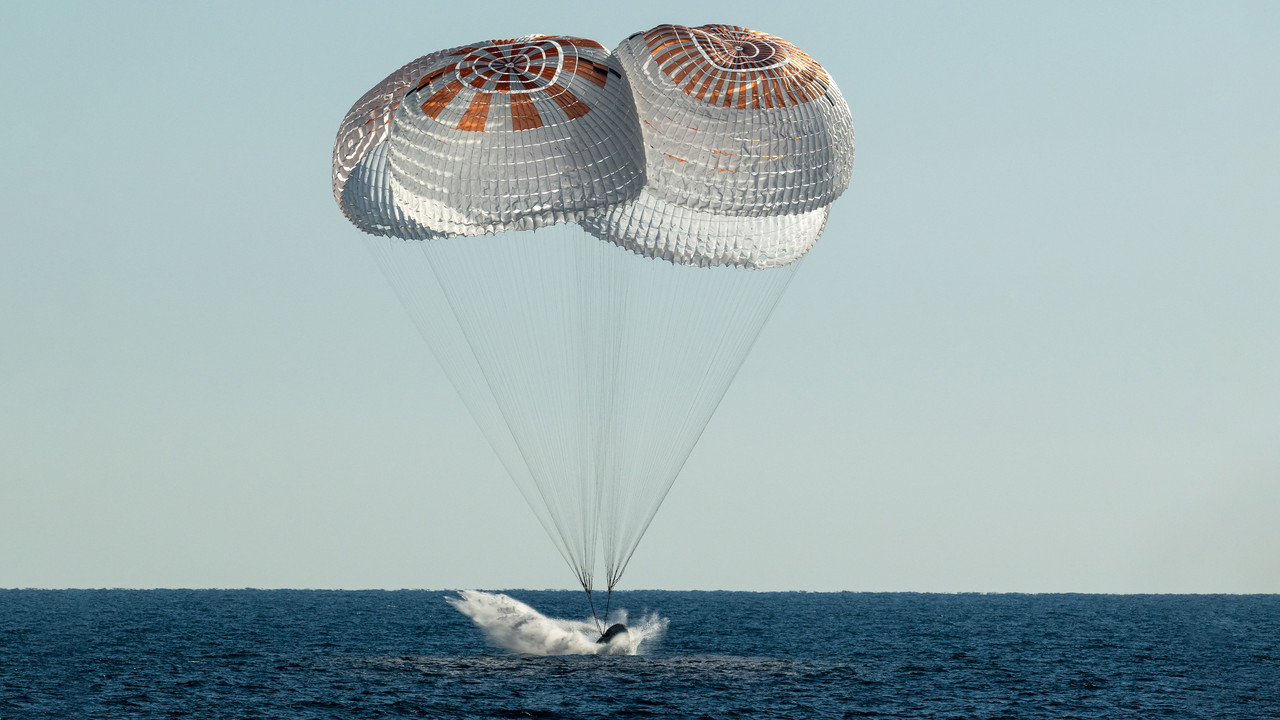
What time will NASA's Starliner astronauts land with SpaceX's Crew-9 today? How to watch live.
SpaceX's ninth operational crew return from the International Space Station is set to splash down on Tuesday, March 18, at about 5:57 p.m. EDT (2157 GMT).
Last edited:
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild

Largest-ever 3D map of the universe lets us travel back 11 billion years
DESI's first dataset maps 18.7 million celestial objects, aiding dark energy, galaxy, and universe expansion studies.
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild

A Telescope Is Taking 12 Years To Build But Could Find Extraterrestrial Life In Hours
The circumstances need to be right, but modeling suggests finding biosignatures in the atmospheres of planets orbiting nearby stars will be well within the Extremely Large Telescope’s capacity.
Parts of America will experience a partial solar eclipse this weekend
Some Americans will experience a rare celestial treat this weekend when a partial solar eclipse occurs.JWST picture of the month :
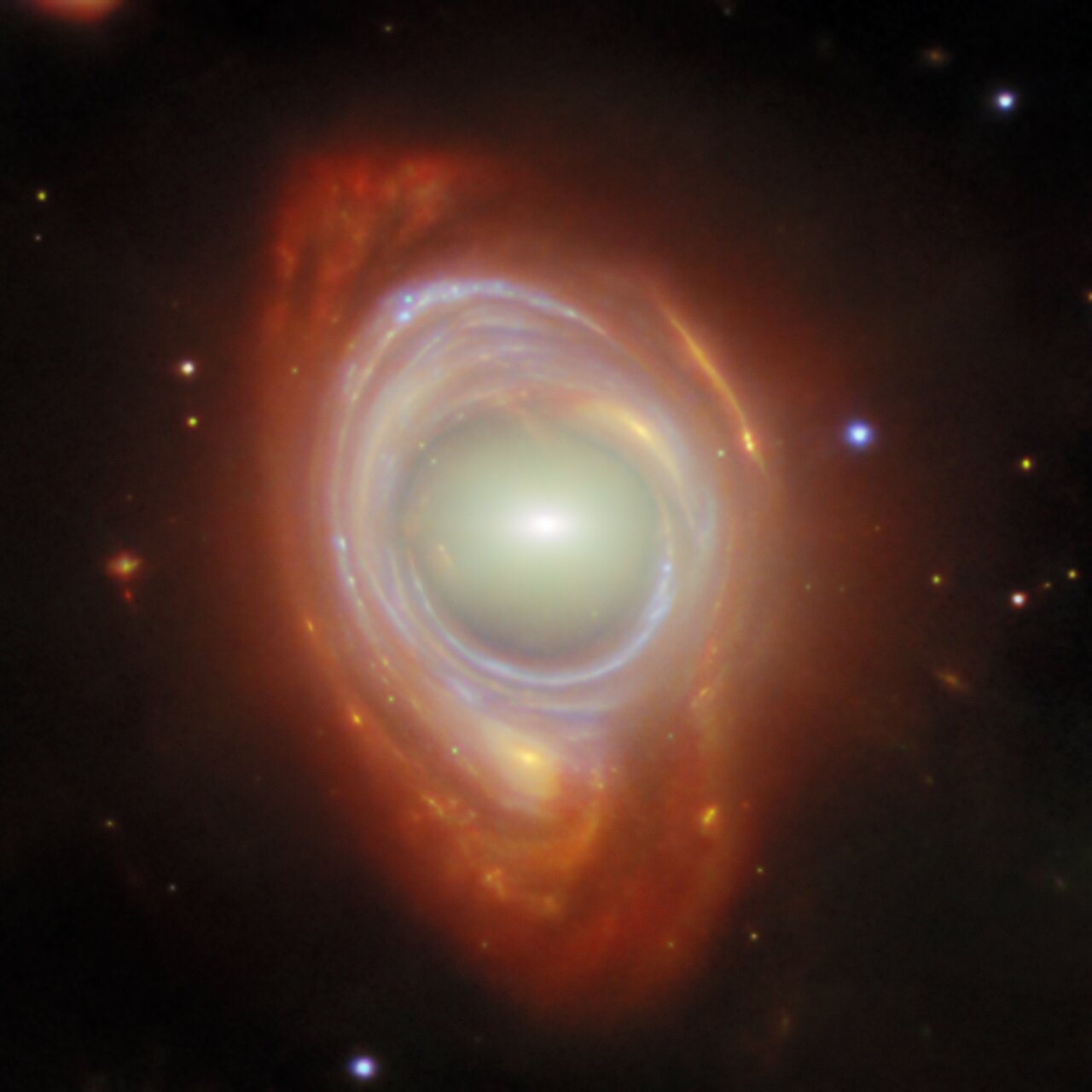


Einstein ring.What at first appears to be a single, strangely shaped galaxy is actually two galaxies that are separated by a large distance. The closer foreground galaxy sits at the center of the image, while the more distant background galaxy appears to be wrapped around the closer galaxy, forming a ring.

NASA's Curiosity Rover accidentally cracked open a rock on Mars and found something that shouldn't be there
The Curiosity Rover, sent up to Mars by NASA, accidentally cracked open a Martian rock by driving over it and made an interesting discovery inside
Two Dead Stars Found Just 150 Light Years Away Will Explode 10x Brighter Than the Moon
A nearby cosmic ticking time bomb has been found! Just 150 light years away, a pair of white dwarfstars are on a death spiral, destined to explode in a type 1a supernova.
CANtalk
Well-Known Member
Trump Admin to Slice NASA in Half and Cancel New Telescopes

Trump Admin to Slice NASA in Half and Cancel New Telescopes
The White House further plans to cancel upcoming plans for new telescopes to study the cosmos.


CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
Popularly called Thor's Helmet, NGC 2359 is a hat-shaped cosmic cloud with wing-like appendages. Heroically sized even for a Norse god, Thor's Helmet is about 30 light-years across. In fact, the cosmic head-covering is more like an interstellar bubble, blown by a fast wind from the bright, massive star near the bubble's center. Known as a Wolf-Rayet star, the central star is an extremely hot giant thought to be in a brief, pre-supernova stage of evolution. NGC 2359 is located about 15,000 light-years away toward the constellation of the Great Overdog. This sharp image is a mixed cocktail of data from narrowband filters, capturing not only natural looking stars but details of the nebula's filamentary structures. The star in the center of Thor's Helmet is expected to explode in a spectacular supernova sometime within the next few thousand years.
 post image
post image
LDN 1235, the Shark Nebula, is made up of a lot of dark dust. The dark dust is somewhat like cigarette smoke and created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars. After expelling gas and gravitationally recondensing, massive stars may carve intricate structures into their birth cloud using their high energy light and fast stellar winds as sculpting tools. The heat they generate evaporates the murky molecular cloud as well as causing ambient hydrogen gas to disperse and glow red. During disintegration, we humans can enjoy imagining these great clouds as common icons, like we do for water clouds on Earth. Including smaller dust nebulae such as Van den Bergh 149 & 150, the Shark nebula, sometimes cataloged as LDN 1235, spans about 15 light years and lies about 650 light years away toward the constellation of the King of Aethiopia (Cepheus).

Shimmering ejections emitted by two actively forming stars make up Lynds 483 (L483). High-resolution near-infrared light captured by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope shows incredible new detail and structure within these lobes, including asymmetrical lines that appear to run into one another. L483 is 650 light-years away in the constellation Serpens.

What's at the tip of this interstellar jet? First let's consider the jet: it is being expelled by a star system just forming and is cataloged as Herbig-Haro 49 (HH 49). The star system expelling this jet is not visible -- it is off to the lower right. The complex conical structure featured in this infrared image by the James Webb Space Telescope also includes another jet cataloged as HH 50. The fast jet particles impact the surrounding interstellar gas and form shock waves that glow prominently in infrared light -- shown here as reddish-brown ridges. This JWST image also resolved the mystery of the unusual object at HH 49's tip: it is a spiral galaxy far in the distance. The blue center is therefore not one star but many, and the surrounding circular rings are actually spiral arms.

This new image shows NGC 2283 through the eyes of Webb’s Near-InfraRed Camera (NIRCam) and Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI). Webb gazed at NGC 2283 for a combined 17 minutes to collect the data for this image, which is constructed from six snapshots taken with different near- and mid-infrared filters. These filters reveal the emission from NGC 2283’s sparkling stellar population, as well as the light from clouds of hydrogen gas that have been heated by young stars. Sooty molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, of great interest to astronomers, emit light that’s mapped by two of the filters used here. The large, bright stars with prominent diffraction spikes on display in this image are inhabitants of our own galaxy, which lie between us and NGC 2283.

 post image
post imageLDN 1235, the Shark Nebula, is made up of a lot of dark dust. The dark dust is somewhat like cigarette smoke and created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars. After expelling gas and gravitationally recondensing, massive stars may carve intricate structures into their birth cloud using their high energy light and fast stellar winds as sculpting tools. The heat they generate evaporates the murky molecular cloud as well as causing ambient hydrogen gas to disperse and glow red. During disintegration, we humans can enjoy imagining these great clouds as common icons, like we do for water clouds on Earth. Including smaller dust nebulae such as Van den Bergh 149 & 150, the Shark nebula, sometimes cataloged as LDN 1235, spans about 15 light years and lies about 650 light years away toward the constellation of the King of Aethiopia (Cepheus).

Shimmering ejections emitted by two actively forming stars make up Lynds 483 (L483). High-resolution near-infrared light captured by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope shows incredible new detail and structure within these lobes, including asymmetrical lines that appear to run into one another. L483 is 650 light-years away in the constellation Serpens.

What's at the tip of this interstellar jet? First let's consider the jet: it is being expelled by a star system just forming and is cataloged as Herbig-Haro 49 (HH 49). The star system expelling this jet is not visible -- it is off to the lower right. The complex conical structure featured in this infrared image by the James Webb Space Telescope also includes another jet cataloged as HH 50. The fast jet particles impact the surrounding interstellar gas and form shock waves that glow prominently in infrared light -- shown here as reddish-brown ridges. This JWST image also resolved the mystery of the unusual object at HH 49's tip: it is a spiral galaxy far in the distance. The blue center is therefore not one star but many, and the surrounding circular rings are actually spiral arms.

This new image shows NGC 2283 through the eyes of Webb’s Near-InfraRed Camera (NIRCam) and Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI). Webb gazed at NGC 2283 for a combined 17 minutes to collect the data for this image, which is constructed from six snapshots taken with different near- and mid-infrared filters. These filters reveal the emission from NGC 2283’s sparkling stellar population, as well as the light from clouds of hydrogen gas that have been heated by young stars. Sooty molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, of great interest to astronomers, emit light that’s mapped by two of the filters used here. The large, bright stars with prominent diffraction spikes on display in this image are inhabitants of our own galaxy, which lie between us and NGC 2283.

astronomers find planet in perpendicular orbit around pair of stars
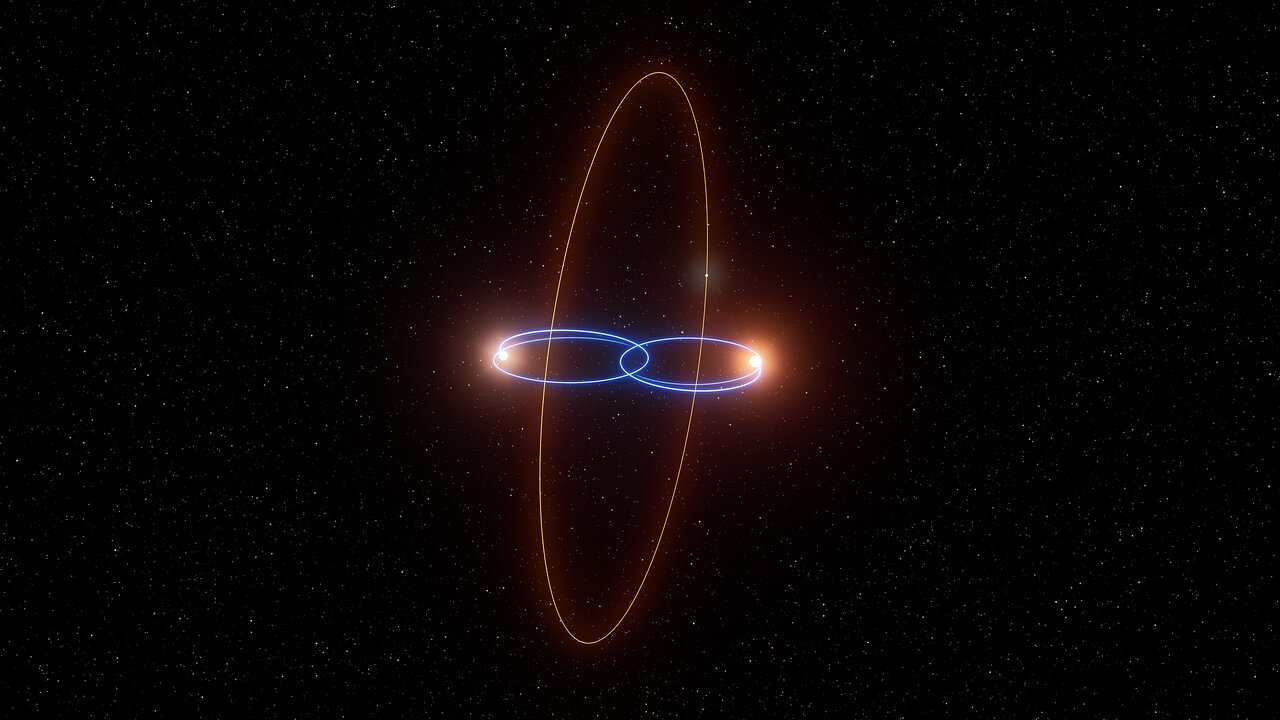
"Big surprise": astronomers find planet in perpendicular orbit around pair of stars
Astronomers have found a planet that orbits at an angle of 90 degrees around a rare pair of peculiar stars. This is the first time we have strong evidence for one of these ‘polar planets’ orbiting a stellar pair. The surprise discovery was made using the European Southern Observatory’s Very...










