-
SCAM WARNING! See how this scam works in Classifieds.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
The Weird Big Cloud Question
- Thread starter nms
- Start date
Summer
Long Island, NY
The exhalation contains spent & unspent cannabinoids(?) & CO2. The unspent is what your body didn't absorb. How much vapor is exhaled is based on the type of hit you like to take. The bigger hit, the more leftovers. But IMO, I don't see it as wasted cannabis if that's the type of hit you enjoy. Secondary to the high is the ritual of how you enjoy getting high. If you like blasting your lungs & going for a lot of vapor, your not wasting. The weed, the hit & the vape are the entire experience. It will take a few hits more, but you can get high with very little vapor exhalation. And, yes, if you want smaller hits, some vapes are better suited than others & vice versa. Sadly, my vapor output is on the light side as my lungs cough up a storm with a vaporous hit. Occasionally, depending on the weed, I can handle medium hits, & those I really like.
Last edited:
nms
Well-Known Member
spent & unspent cannabis & CO2
So CO2 will always be included as has no color. When you normally breathe you see no CO2 because it's a colorless gas. What do you think makes up spent cannabis?
I know most of the vapour is cannabinoids at least on a good vaporizer so I assume that's what gives colour to the 'vapour'(alongside whatever micro particles come along). I don't understand how cannabinoids can interact with the lungs in such a way that they become something else, what do you mean with this spent/unspent thing?
So CO2 will always be included as has no color. When you normally breathe you see no CO2 because it's a colorless gas. What do you think makes up spent cannabis?
I know most of the vapour is cannabinoids at least on a good vaporizer so I assume that's what gives colour to the 'vapour'(alongside whatever micro particles come along). I don't understand how cannabinoids can interact with the lungs in such a way that they become something else, what do you mean with this spent/unspent thing?
Summer
Long Island, NY
By spent & unspent, I mean that the lungs can only absorb so much cannabinoids per hit. What doesn't get absorbed/used is exhaled. There's FC threads where members discuss their opinions on how long to hold inhalation & how to breathe while holding the hit to get the most absorption/benefit.
Adding to my above post, some vapors like the economics of less vapor because they do think big hits as a $ waste. Different strokes ...
Adding to my above post, some vapors like the economics of less vapor because they do think big hits as a $ waste. Different strokes ...
Theoretically big exhaled clouds are wasteful, however many people feel they get stronger effects from those type of hits. I made a thread about this: https://fuckcombustion.com/threads/what-style-of-vaporizing-do-you-find-most-effective.48942/
Siebter
Less soul, more mind
I know from nicotine research that the lung is actually capable of absorbing substances (in this case: nicotine) very quickly. Even a regular draw from a cigarette will absorb 90 - 95% of the nicotine present in smoke (due to the large surface area of the lung tissue which is equivalent to a soccer field or something). That's why I'm not so sure that what we exhale is actually mainly „wasted“ substances. There might be huge differences in the absorbtion of certain substances, though.
Are there any conclusive scientific articles on the subject? I assume not particularly for cannabinoids but something we can correlate with related to other drugs delivered by inhalation.
Not really, as vapor absorption is pretty complex and has a lot of variables. Even the pharmaceutical companies have trouble dialing in inhalatory medications due to particle size and vapor deposition. But the old Volcano tests (Evaluation Of A Vaporizing Device) from the Netherlands found that on average ~35% of vaporized THC is lost on exhale.
Summer
Long Island, NY
... but something we can correlate with related to other drugs delivered by inhalation.
I don't think you can correlate as inhalation drugs are premeasrued or metered. In this scenario, the patients lung capacity would be a factor in absorption, e.g. age, body size, lung health. We never measure our vapor inhalation, we just seek duplication of the last great hit. We'd need to create a standard & have proper equipment.
nms
Well-Known Member
Correlating assumes getting to know the involved variables to take relative conclusions. The fact you do not know the exact dosage you take, doesn't exactly mean that you cannot relate how absorption happens and what are the variables that cause the most impact on that process. In that perspective, there would be no pharmaceutical industry, because no body is the same. No, generally while no body is the same, the specifics of each can be quantified or are too small to be of relevance to the effectiveness of a given medicine. Don't misunderstand me, any anecdotal evidence is welcome, but I also would like if someone who has had the same question found some relatable scientific articles on the subject(even if their application on this specific subject is questionable as it will probably be, as so are subjective experiences).
Siebter
Less soul, more mind
References?
A YouTube channel by an Austrian toxicologist named Prof. Dr. Bernd Mayer (in German, though). :-)
Edit:
In that perspective, there would be no pharmaceutical industry, because no body is the same. No, generally while no body is the same, the specifics of each can be quantified or are too small to be of relevance to the effectiveness of a given medicine.
Btw, that *is* a problem. Only recently (I think) a discussion among pharmaceutics began about the differences in dosages for men and women.
Summer
Long Island, NY
But with pharmaceuticals, you have consistency between batches. With pot, even the same strain grown in different regions has different properties. And different high-volume grower labs have differences in their hybrizied(?) flower. Do a Google search & let us know if you think there's a way to correlate. I, for one, have been working outside in the heat today (albeit,  ) & I'm heat-wasted & just want a shower & a good meal before bed.
) & I'm heat-wasted & just want a shower & a good meal before bed.
 ) & I'm heat-wasted & just want a shower & a good meal before bed.
) & I'm heat-wasted & just want a shower & a good meal before bed.
Last edited:
nms
Well-Known Member
As such quantifiable but this is really not what I'm trying to learn more about.Btw, that *is* a problem. Only recently (I think) a discussion among pharmaceutics began about the differences in dosages for men and women.
" Lipid-soluble compounds are rapidly absorbed presumably because they can integrate into the lipid bilayer surrounding the cells. This constitutes the “transcellular pathway” in which compounds pass from the apical to basolateral side by traveling through the cellular membrane. "
" there appears to be no species differences in the rates of absorption of lipophilic drugs "
" The volumes of solution injected intratracheally were approximately 2% of lung volume. At various times after drug administration, the lungs were removed and assayed for unabsorbed compound. Although the 12 drugs studied had widely different absorption rates, each was absorbed approximately 2 times more rapidly when inhaled as an aerosol than when administered by intratracheal injection, suggesting that absorption may be more rapid from the alveolar region than from the tracheobronchial region of the lung. "
" At various times after aerosol inhalation, the lungs were removed and assayed for the amount of compound that had not been absorbed. The times (min) necessary for 50% absorption were: antipyrine, 0.25; salicylic acid, 0.67 " -https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6137343/
Interesting that the salicylic acid takes .67(half this if administered via aeresol) minutes for 50% absorption on mice, I'd say it's not far fetched to say it'd be similar enough to THC, although some studies say bigger molecular weight increases absorption speed. So far nothing on the dosage variation on absorption.
Another interesting fact(wonder what these devices are):
" Traditional aerosol devices can only deliver about 10 to 20% of their loaded doses into the lungs. Thus, if a protein has an in-lung aerosol bioavailability of 50%, but the device that is used to deliver the protein has a delivery efficiency of only 10%, then the overall delivery efficiency (bioavailability from the device) will be 5%. "
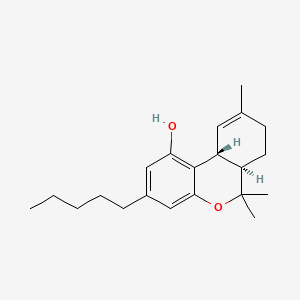
Dronabinol
Dronabinol | C21H30O2 | CID 16078 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more.
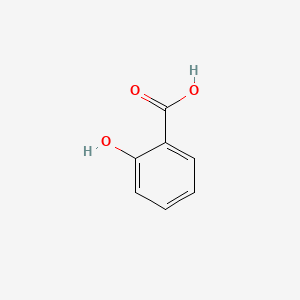
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic Acid | HOC6H4COOH or C7H6O3 | CID 338 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more.
Last edited:
I prefer bigger clouds. I might be wasting a bit but i know im 100% stoned as i can be with what herb and vape im using.
I prefer bigger clouds. I might be wasting a bit but i know im 100% stoned as i can be with what herb and vape im using.
There's always room for more... er, stoned

Tranquility
Well-Known Member
When you're reading a blog like this, sometimes it's helpful to dig a little on your own. For instance, I was able to cut and paste the sentence:References?
"(Evaluation Of A Vaporizing Device) from the Netherlands found that on average ~35% of vaporized THC is lost on exhale. " into duckduckgo and got the same references others posted. I'm glad others were so accommodating here, but if you're really curious about something, you have to go down the rabbit hole on your own.
nms
Well-Known Member
From someone that's used to reading research papers, and given that reading that specific one brought me down to reading 29 others, which have made me loose quite a few hours afterwards on the same kind of behavior, I think it's acceptable to ask for a reference to the person who makes the claim. Thankfully the others were accommodating, something I don't see as an extra step like you, because this is how knowledge is actually obtained, shared and improved upon, with a slight contribution by everyone who participates. This is not a blog, because a blog exists for marketing purposes, this is a forum whose only goal seems to be sharing knowledge on different subjects. As such, and because referencing one's claims is the basis of any scientific knowledge(notice above I also accepted any anecdotal evidence as 'valuable'), it is nothing but a must do, that I would oblige to, and I hope that anyone else would do so as well. It seems to me that you have little faith in your fellow members.
MinnBobber
Well-Known Member
Our lungs are not perfect absorption machines. The best study I found was on oxygen absorption rates, noting that that is the main purpose of our lungs, absorbing oxygen into the blood stream.
Lungs absorbed about 1/3 of the available oxygen coming into them. From memory, Air came into the lungs with about 21% oxygen and left with about 14% oxygen.
I do wonder what cannabinoid absorption rate in the lungs truly is.
Lungs absorbed about 1/3 of the available oxygen coming into them. From memory, Air came into the lungs with about 21% oxygen and left with about 14% oxygen.
I do wonder what cannabinoid absorption rate in the lungs truly is.
nms
Well-Known Member
@MinnBobber Some of the studies shared here do have some interesting facts regarding that question. Also oxygen wouldn't be the best thing to compare to, as it's absorbed quite differently from THC, which would use the venue described in the post above for lipid soluble molecules(which the article also says as a curiosity that the rate of which remains pretty consistent over different species).
Last edited:
PPN
Volute of Vapor
Hi, just giving my 2 cents... I liked a lot to exhale clouds, big clouds but my lungs suffered of that since I was coughing a lot right after, not painfull but annoying (my wife throws me worry eyes while I was coughing like hell after a big hit). So I'm now taking smaller hits or lowering the temperature. My best "high&stone" I get is while vaping an half gram (or more, who know I never weight it in fact, just an estimation) in my HA 2.2 at 170-175°C... vapor output isn't impressive but effects are so much powerfull it's pretty difficult to handle for me, not only it break my brain but gave me deep body reliefs... so deep I need time to recover. When used at higer T° (not so hot cause here the HA can heat up at 400°F at max) the vapor output is more satisfying, there is a more direct effect but, finally, it doesn't hit me as hard as a longer, colder session... but even if I'm now aware of that I continue to take huge dense vapor hits using my GH, TM and MV mainly!
PPN
Volute of Vapor
Hi... I had to read... and re-read a few times your question before to understand it... maybe cause I'm still asleep (it's soon in the morning here)...@PPN Could you elaborate on what measure would you create to quantify the power of that hit keeping comparison(or differentiation) with the higher temperature hit in mind?
All in all it's pretty difficult to measure but I'm thinking the high t° are simplifyoing the cannabinoids relief we get whereas the low temp (not so low in fact I use 170-180°C) hits offer more various and complex reliefs, the"hit" is smoother but the bowl push me higher and stoner imo. I saw a video explaining how terpènes brings the cannabinoids into our body and why they are essentials for a full relief, maybe this is the reason why I feel that... high temps tend to push all/most terps in one hit, after there is only cannabinoids.... which can't reach your body as efficiently without their carrier, the terps... it may appear I'm extrapolating a bit too much but that's my 2 cents.... thank you for your interest!
