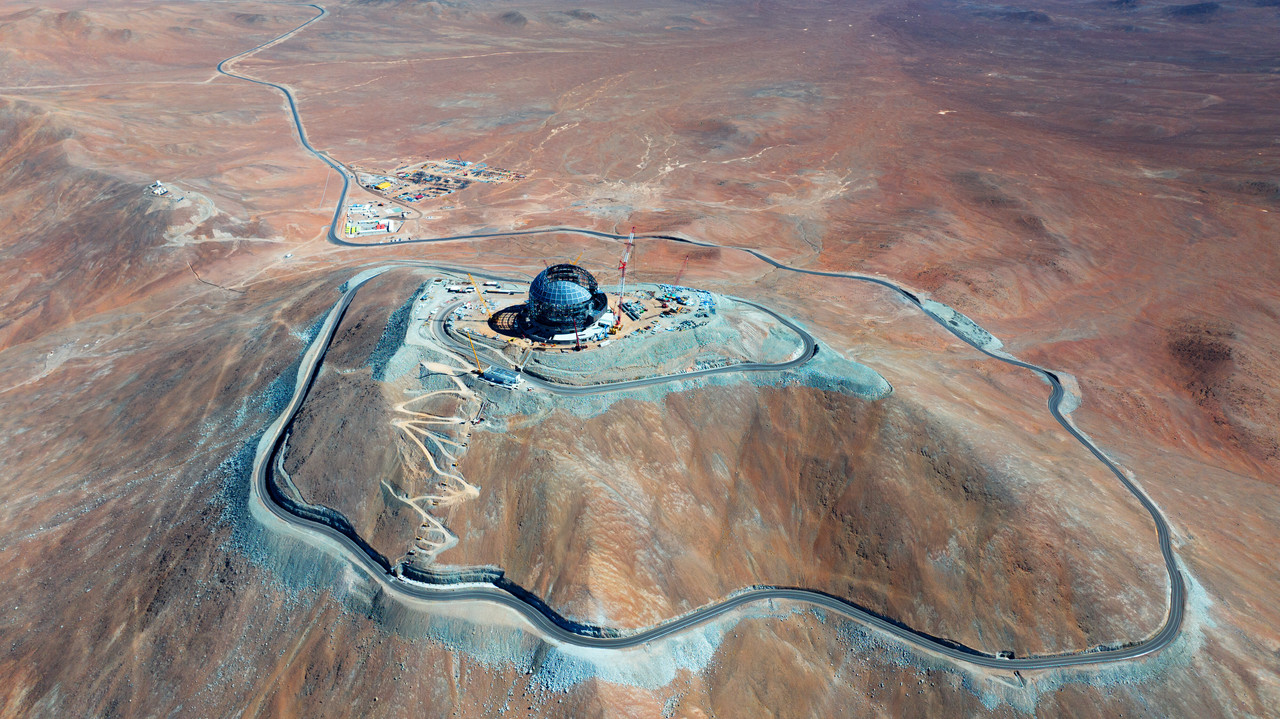
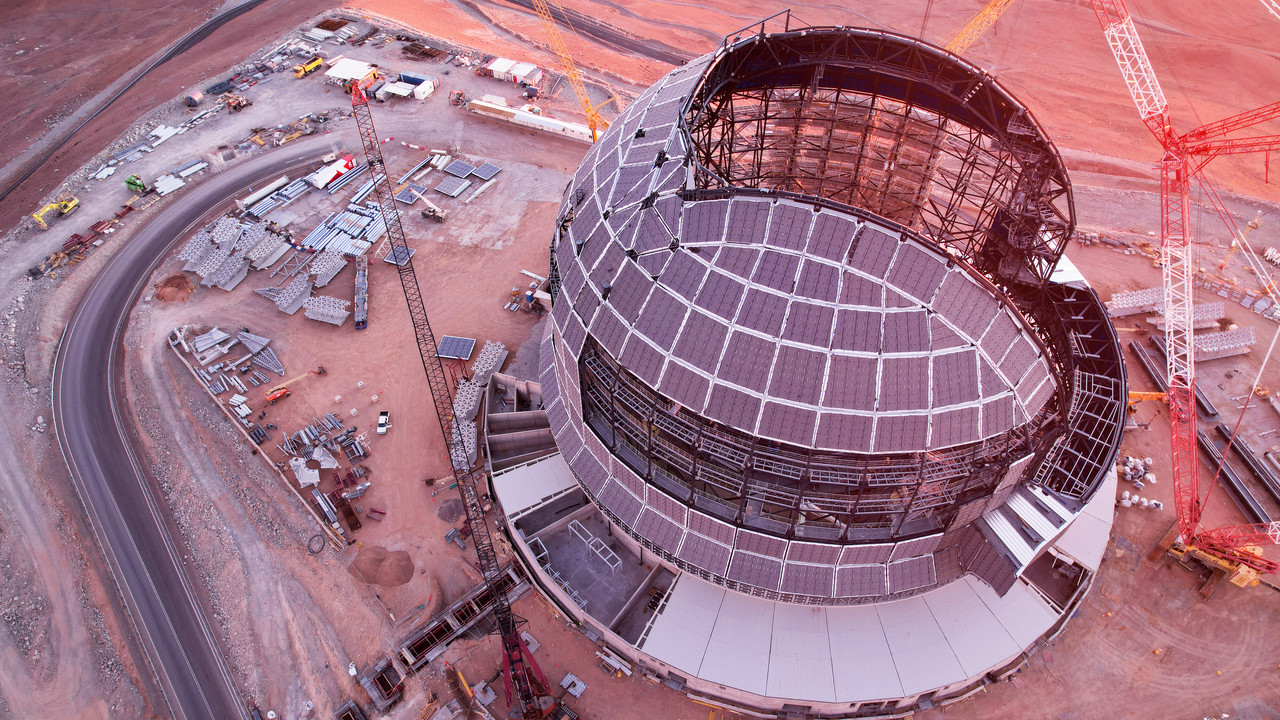
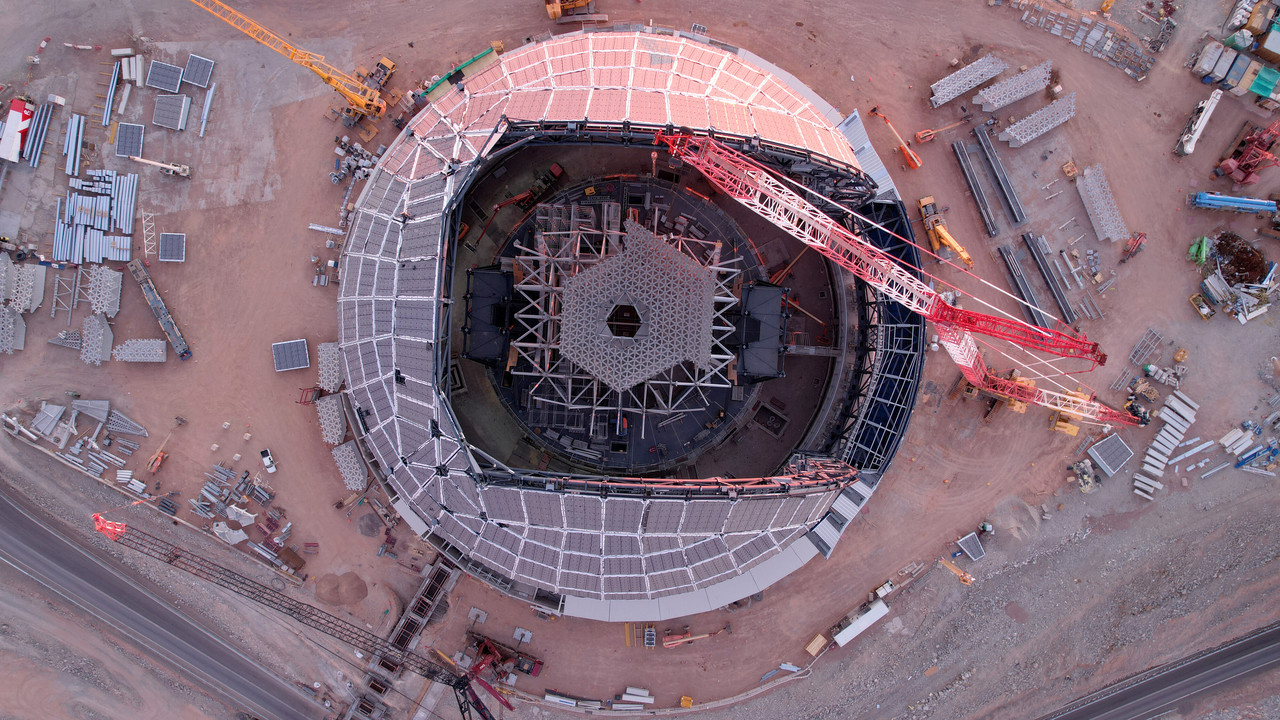
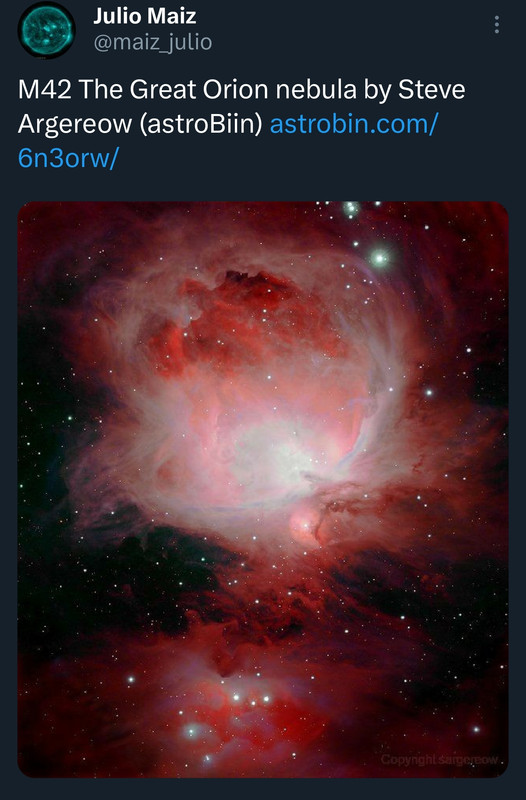
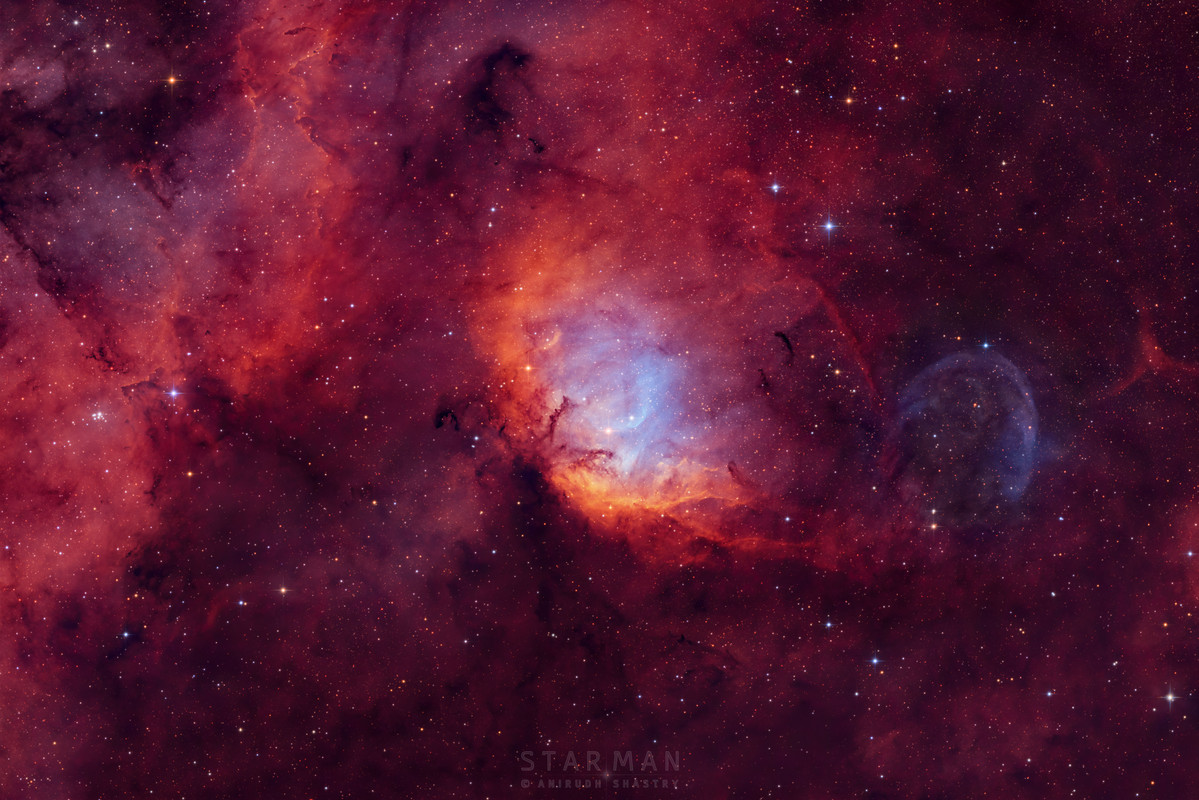
CrazyDiamond
HAL is a StarChild
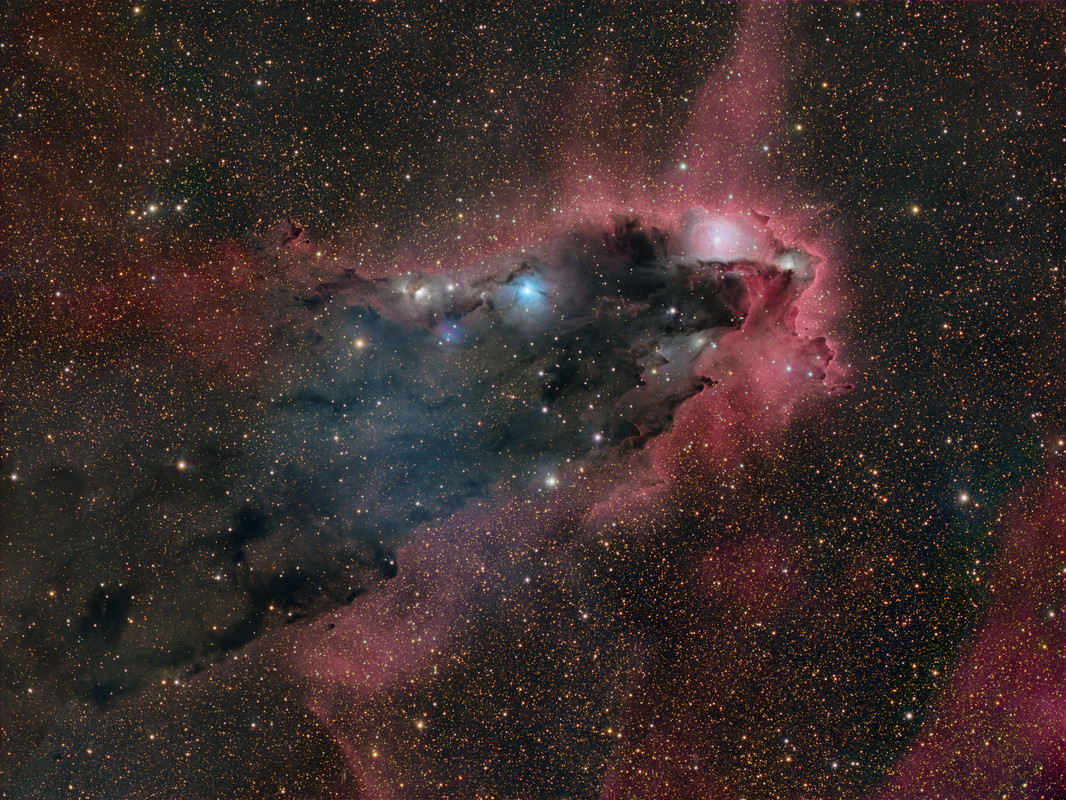
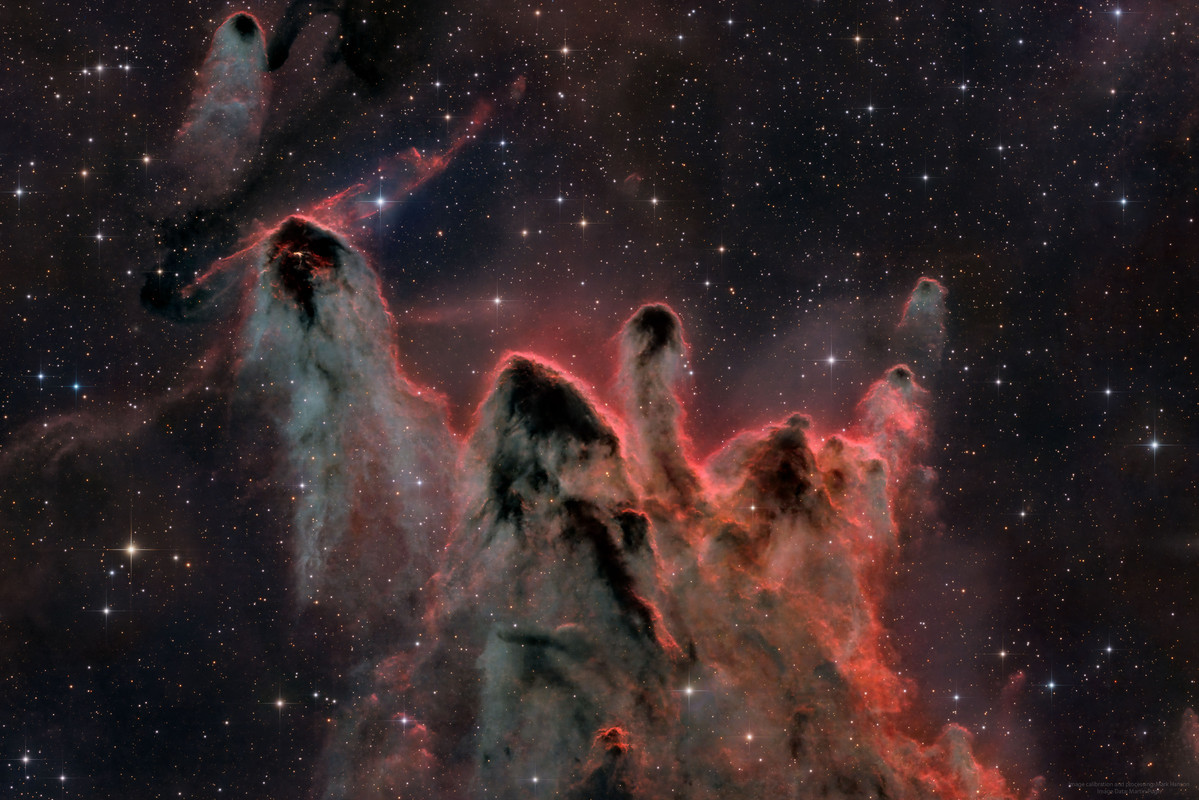
What are these unusual interstellar structures? Bright-rimmed, flowing shapes gather near the center of this rich starfield toward the borders of the nautical southern constellations Pupis and Vela. Composed of interstellar gas and dust, the grouping of light-year sized cometary globules is about 1300 light-years distant. Energetic ultraviolet light from nearby hot stars has molded the globules and ionized their bright rims. The globules also stream away from the Vela supernova remnant which may have influenced their swept-back shapes. Within them, cores of cold gas and dust are likely collapsing to form low mass stars, whose formation will ultimately cause the globules to disperse. In fact, cometary globule CG 30 (on the upper left) sports a small reddish glow near its head, a telltale sign of energetic jets from a star in the early stages of formation.

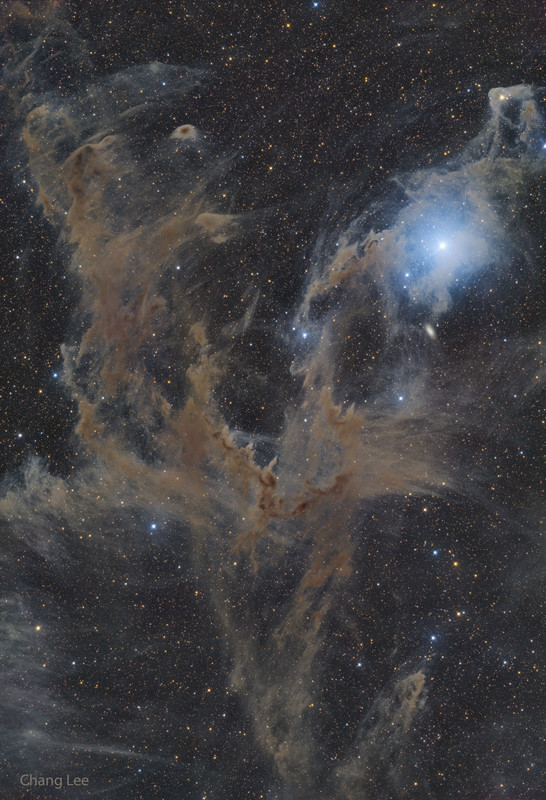
Sometimes the dark dust of interstellar space has an angular elegance. Such is the case toward the far-south constellation of Chamaeleon. Normally too faint to see, dark dust is best known for blocking visible light from stars and galaxies behind it. In this 36.6-hour exposure, however, the dust is seen mostly in light of its own, with its strong red and near-infrared colors creating a brown hue. Contrastingly blue, the bright star Beta Chamaeleontis is visible on the upper right, with the dust that surrounds it preferentially reflecting blue light from its primarily blue-white color. All of the pictured stars and dust occur in our own Milky Way Galaxy with one notable exception: the white spot just below Beta Chamaeleontis is the galaxy IC 3104 which lies far in the distance. Interstellar dust is mostly created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars and dispersed into space by stellar light, stellar winds, and stellar explosions such as supernovas.

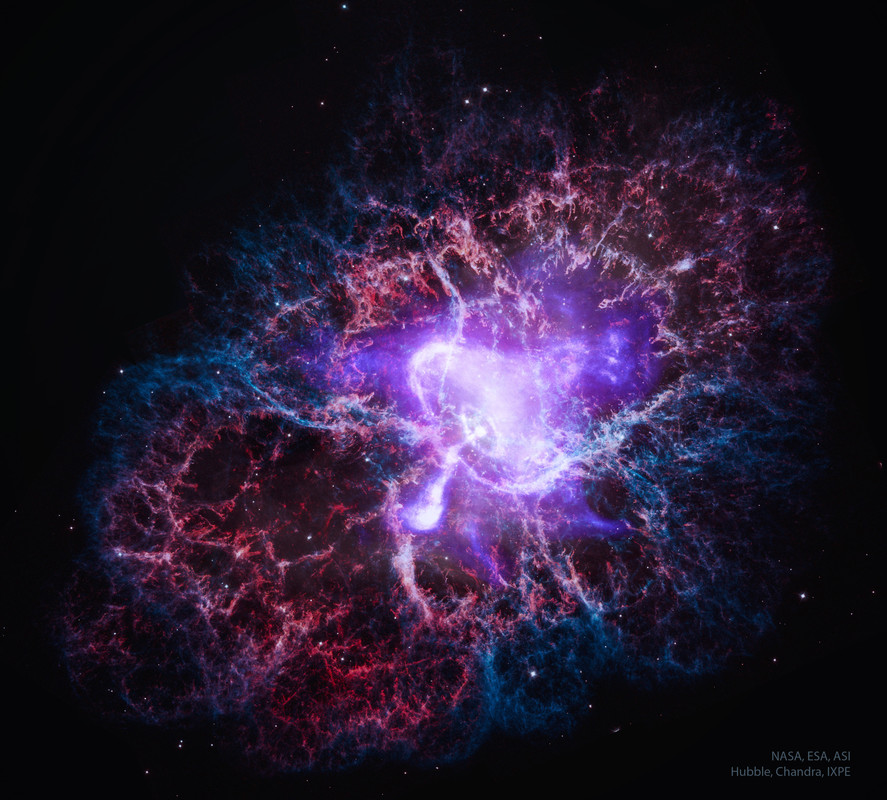
What powers the Crab Nebula? A city-sized magnetized neutron star spinning around 30 times a second. Known as the Crab Pulsar, it is the bright spot in the center of the gaseous swirl at the nebula's core. About 10 light-years across, the spectacular picture of the Crab Nebula (M1) frames a swirling central disk and complex filaments of surrounding and expanding glowing gas. The picture combines visible light from the Hubble Space Telescope in red and blue with X-ray light from the Chandra X-ray Observatory shown in white, and diffuse X-ray emission detected by Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) in diffuse purple. The central pulsar powers the Crab Nebula's emission and expansion by slightly slowing its spin rate, which drives out a wind of energetic electrons. The featured image released today, the 25th Anniversary of the launch of NASA's flagship-class X-ray Observatory: Chandra.

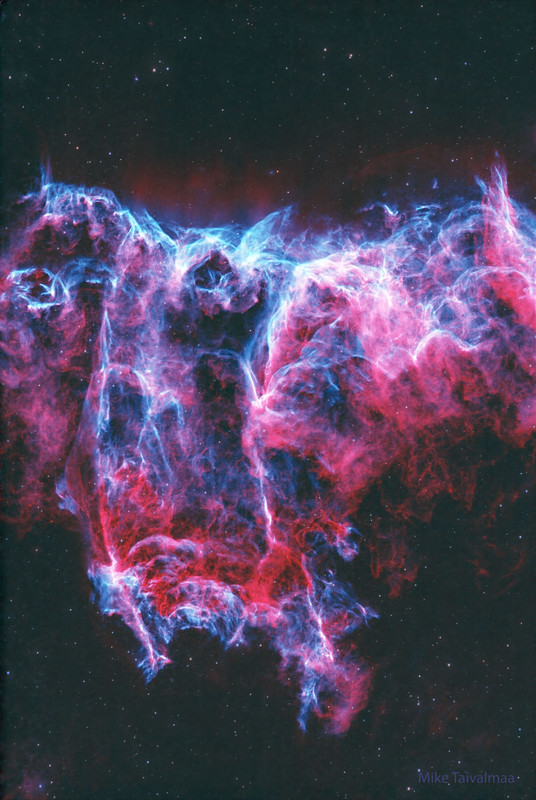
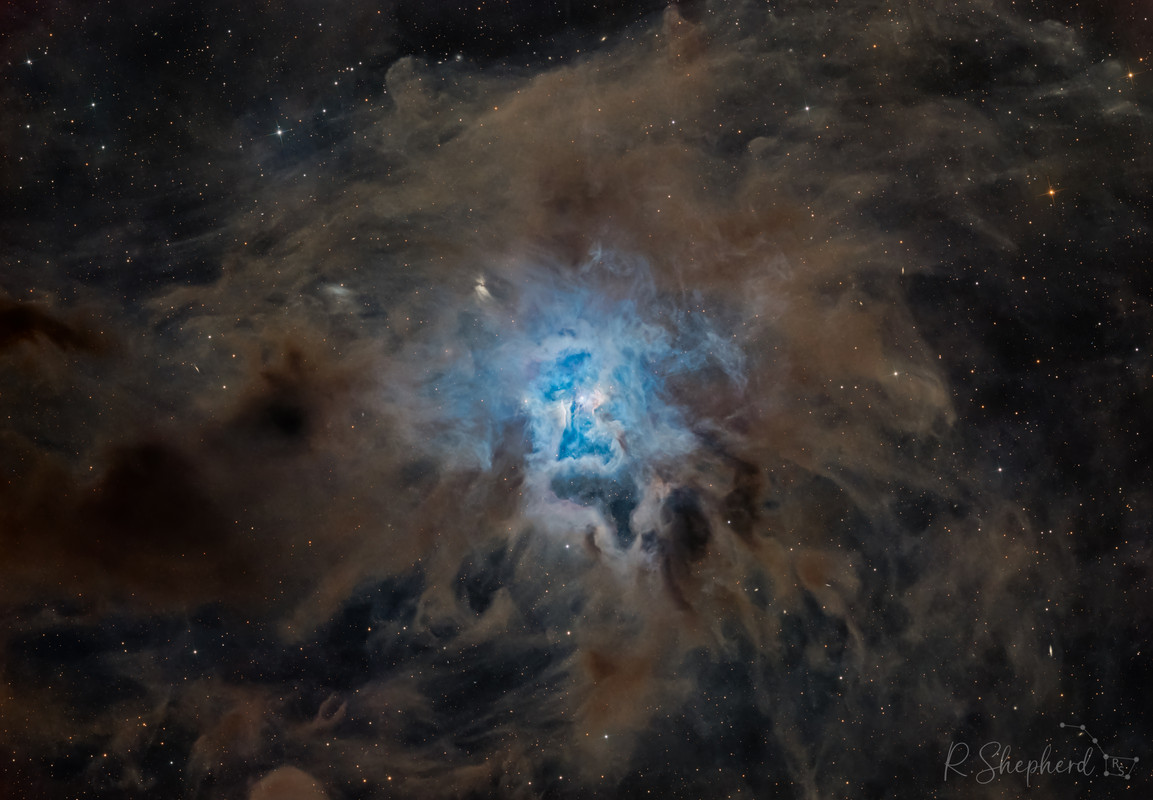
These cosmic clouds have blossomed 1,300 light-years away in the fertile starfields of the constellation Cepheus. Called the Iris Nebula, NGC 7023 is not the only nebula to evoke the imagery of flowers. Still, this deep telescopic image shows off the Iris Nebula's range of colors and symmetries embedded in surrounding fields of interstellar dust. Within the Iris itself, dusty nebular material surrounds a hot, young star. The dominant color of the brighter reflection nebula is blue, characteristic of dust grains reflecting starlight. Central filaments of the reflection nebula glow with a faint reddish photoluminescence as some dust grains effectively convert the star's invisible ultraviolet radiation to visible red light. Infrared observations indicate that this nebula contains complex carbon molecules known as PAHs. The dusty blue petals of the Iris Nebula span about six light-years.


Sometimes the dark dust of interstellar space has an angular elegance. Such is the case toward the far-south constellation of Chamaeleon. Normally too faint to see, dark dust is best known for blocking visible light from stars and galaxies behind it. In this 36.6-hour exposure, however, the dust is seen mostly in light of its own, with its strong red and near-infrared colors creating a brown hue. Contrastingly blue, the bright star Beta Chamaeleontis is visible on the upper right, with the dust that surrounds it preferentially reflecting blue light from its primarily blue-white color. All of the pictured stars and dust occur in our own Milky Way Galaxy with one notable exception: the white spot just below Beta Chamaeleontis is the galaxy IC 3104 which lies far in the distance. Interstellar dust is mostly created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars and dispersed into space by stellar light, stellar winds, and stellar explosions such as supernovas.

What powers the Crab Nebula? A city-sized magnetized neutron star spinning around 30 times a second. Known as the Crab Pulsar, it is the bright spot in the center of the gaseous swirl at the nebula's core. About 10 light-years across, the spectacular picture of the Crab Nebula (M1) frames a swirling central disk and complex filaments of surrounding and expanding glowing gas. The picture combines visible light from the Hubble Space Telescope in red and blue with X-ray light from the Chandra X-ray Observatory shown in white, and diffuse X-ray emission detected by Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) in diffuse purple. The central pulsar powers the Crab Nebula's emission and expansion by slightly slowing its spin rate, which drives out a wind of energetic electrons. The featured image released today, the 25th Anniversary of the launch of NASA's flagship-class X-ray Observatory: Chandra.

These cosmic clouds have blossomed 1,300 light-years away in the fertile starfields of the constellation Cepheus. Called the Iris Nebula, NGC 7023 is not the only nebula to evoke the imagery of flowers. Still, this deep telescopic image shows off the Iris Nebula's range of colors and symmetries embedded in surrounding fields of interstellar dust. Within the Iris itself, dusty nebular material surrounds a hot, young star. The dominant color of the brighter reflection nebula is blue, characteristic of dust grains reflecting starlight. Central filaments of the reflection nebula glow with a faint reddish photoluminescence as some dust grains effectively convert the star's invisible ultraviolet radiation to visible red light. Infrared observations indicate that this nebula contains complex carbon molecules known as PAHs. The dusty blue petals of the Iris Nebula span about six light-years.





/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/bf/17/bf1740cb-d313-41a8-8a30-bb24dac99e40/dscovrepicmoontransitfull.gif)